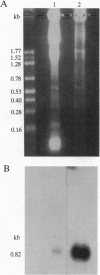
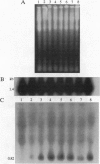
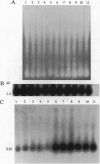
Abstract
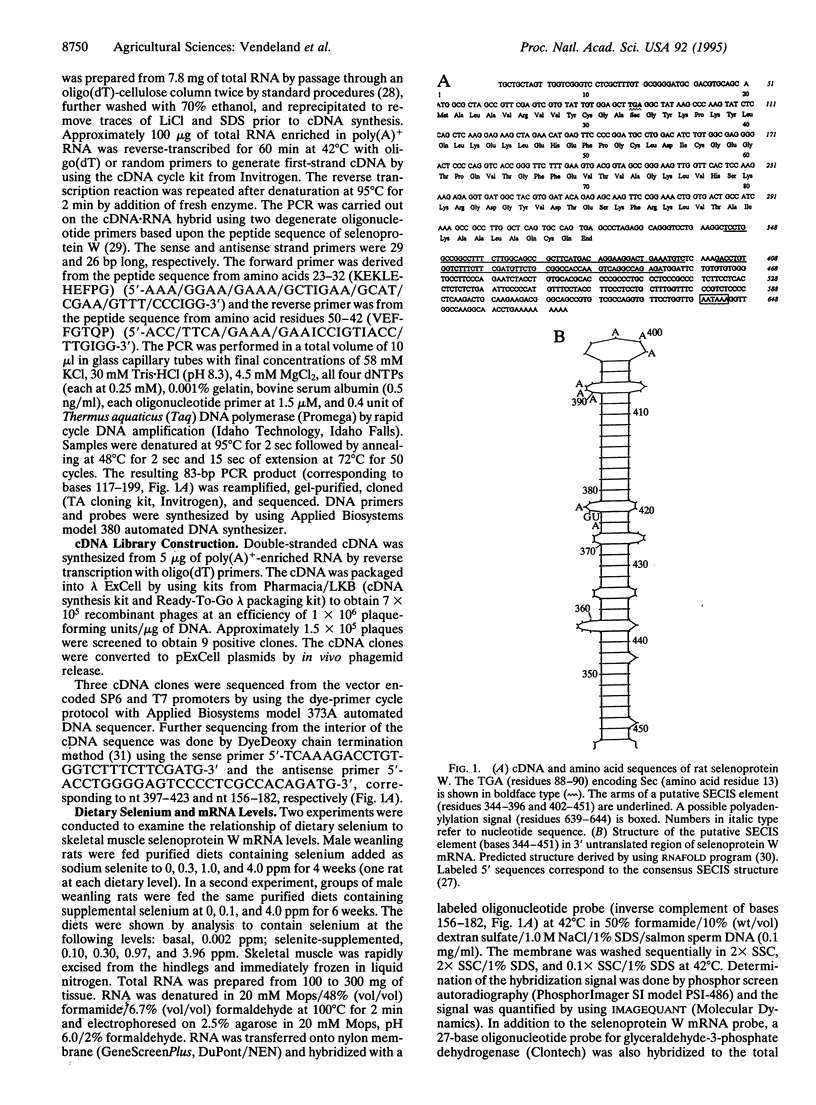
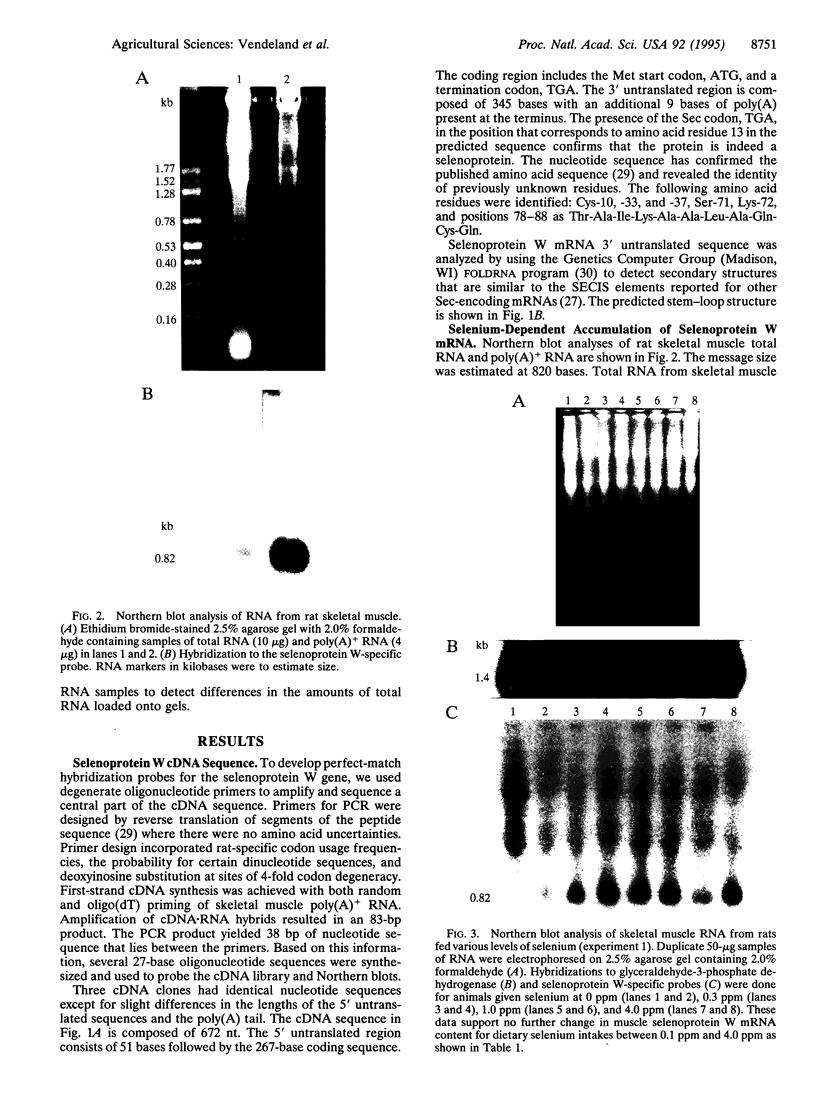
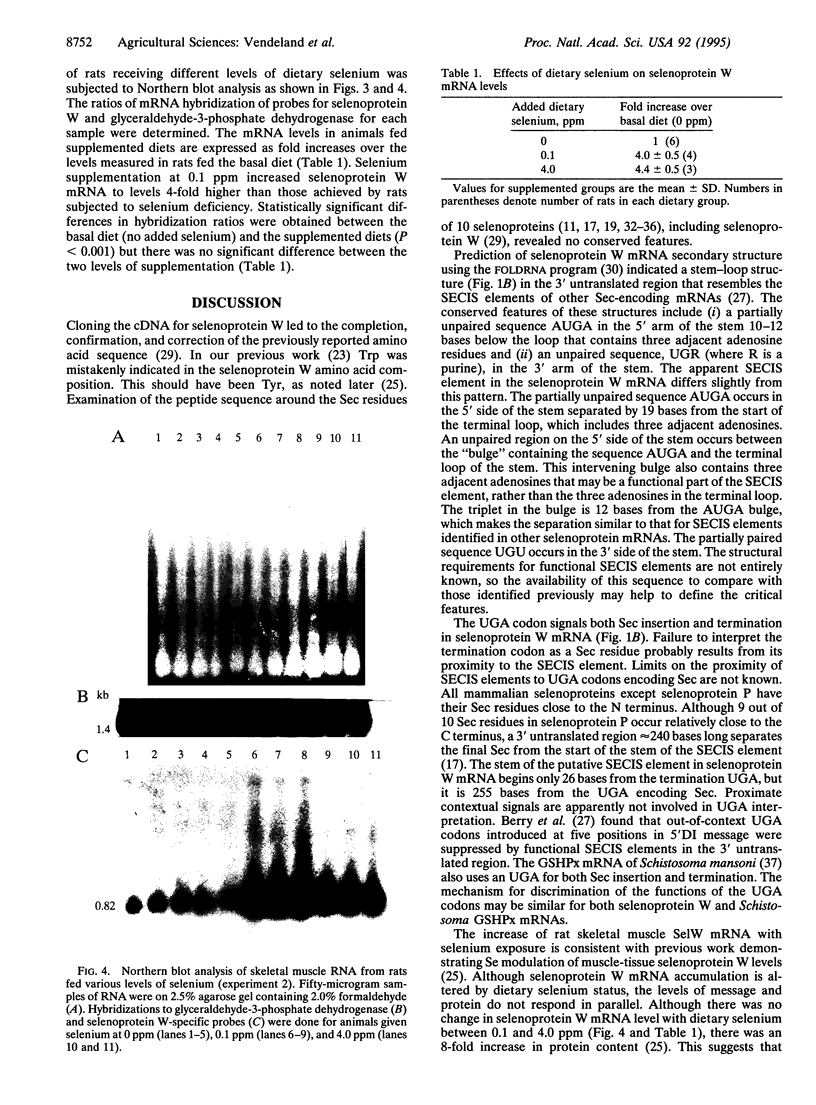
Rat skeletal muscle selenoprotein W cDNA was isolated and sequenced. The isolation strategy involved design of degenerate PCR primers from reverse translation of a partial peptide sequence. A reverse transcription-coupled PCR product from rat muscle mRNA was used to screen a muscle cDNA library prepared from selenium-supplemented rats. The cDNA sequence confirmed the known protein primary sequence, including a selenocysteine residue encoded by TGA, and identified residues needed to complete the protein sequence. RNA folding algorithms predict a stem-loop structure in the 3' untranslated region of the selenoprotein W mRNA that resembles selenocysteine insertion sequence (SE-CIS) elements identified in other selenocysteine coding cDNAs. Dietary regulation of selenoprotein W mRNA was examined in rat muscle. Dietary selenium at 0.1 ppm as selenite increased muscle mRNA 4-fold relative to a selenium-deficient diet. Higher dietary selenium produced no further increase in mRNA levels.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Behne D., Hilmert H., Scheid S., Gessner H., Elger W. Evidence for specific selenium target tissues and new biologically important selenoproteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Jul 14;966(1):12–21. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(88)90123-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behne D., Kyriakopoulos A., Meinhold H., Köhrle J. Identification of type I iodothyronine 5'-deiodinase as a selenoenzyme. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Dec 31;173(3):1143–1149. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)80905-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berry M. J., Banu L., Harney J. W., Larsen P. R. Functional characterization of the eukaryotic SECIS elements which direct selenocysteine insertion at UGA codons. EMBO J. 1993 Aug;12(8):3315–3322. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06001.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berry M. J., Banu L., Larsen P. R. Type I iodothyronine deiodinase is a selenocysteine-containing enzyme. Nature. 1991 Jan 31;349(6308):438–440. doi: 10.1038/349438a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. R., Cohen H. J., Lyons J. M., Curtis T. W., Thunberg B., Cochran W. J., Klish W. J. Proximal muscle weakness and selenium deficiency associated with long term parenteral nutrition. Am J Clin Nutr. 1986 Apr;43(4):549–554. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/43.4.549. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu F. F., Doroshow J. H., Esworthy R. S. Expression, characterization, and tissue distribution of a new cellular selenium-dependent glutathione peroxidase, GSHPx-GI. J Biol Chem. 1993 Feb 5;268(4):2571–2576. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deagen J. T., Butler J. A., Zachara B. A., Whanger P. D. Determination of the distribution of selenium between glutathione peroxidase, selenoprotein P, and albumin in plasma. Anal Biochem. 1993 Jan;208(1):176–181. doi: 10.1006/abio.1993.1025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flohe L., Günzler W. A., Schock H. H. Glutathione peroxidase: a selenoenzyme. FEBS Lett. 1973 May 15;32(1):132–134. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80755-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganther H. E., Kraus R. J. Oxidation states of glutathione peroxidase. Methods Enzymol. 1984;107:593–602. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(84)07043-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Günzler W. A., Steffens G. J., Grossmann A., Kim S. M., Otting F., Wendel A., Flohé L. The amino-acid sequence of bovine glutathione peroxidase. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1984 Feb;365(2):195–212. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1984.365.1.195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halliwell B. Oxidants and human disease: some new concepts. FASEB J. 1987 Nov;1(5):358–364. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkes W. C., Wilhelmsen E. C., Tappel A. L. Abundance and tissue distribution of selenocysteine-containing proteins in the rat. J Inorg Biochem. 1985 Feb;23(2):77–92. doi: 10.1016/0162-0134(85)83011-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill K. E., Lloyd R. S., Yang J. G., Read R., Burk R. F. The cDNA for rat selenoprotein P contains 10 TGA codons in the open reading frame. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jun 5;266(16):10050–10053. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho Y. S., Howard A. J., Crapo J. D. Nucleotide sequence of a rat glutathione peroxidase cDNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jun 10;16(11):5207–5207. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.11.5207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ji L. L., Stratman F. W., Lardy H. A. Antioxidant enzyme systems in rat liver and skeletal muscle. Influences of selenium deficiency, chronic training, and acute exercise. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1988 May 15;263(1):150–160. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(88)90623-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karimpour I., Cutler M., Shih D., Smith J., Kleene K. C. Sequence of the gene encoding the mitochondrial capsule selenoprotein of mouse sperm: identification of three in-phase TGA selenocysteine codons. DNA Cell Biol. 1992 Nov;11(9):693–699. doi: 10.1089/dna.1992.11.693. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Read R., Bellew T., Yang J. G., Hill K. E., Palmer I. S., Burk R. F. Selenium and amino acid composition of selenoprotein P, the major selenoprotein in rat serum. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 15;265(29):17899–17905. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotruck J. T., Pope A. L., Ganther H. E., Swanson A. B., Hafeman D. G., Hoekstra W. G. Selenium: biochemical role as a component of glutathione peroxidase. Science. 1973 Feb 9;179(4073):588–590. doi: 10.1126/science.179.4073.588. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHUBERT J. R., MUTH O. H., OLDFIELD J. E., REMMERT L. F. Experimental results with selenium in white muscle disease of lambs and calves. Fed Proc. 1961 Jul;20:689–694. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saedi M. S., Smith C. G., Frampton J., Chambers I., Harrison P. R., Sunde R. A. Effect of selenium status on mRNA levels for glutathione peroxidase in rat liver. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Jun 16;153(2):855–861. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)81174-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuckelt R., Brigelius-Flohé R., Maiorino M., Roveri A., Reumkens J., Strassburger W., Ursini F., Wolf B., Flohé L. Phospholipid hydroperoxide glutathione peroxidase is a selenoenzyme distinct from the classical glutathione peroxidase as evident from cDNA and amino acid sequencing. Free Radic Res Commun. 1991;14(5-6):343–361. doi: 10.3109/10715769109093424. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sunde R. A., Dyer J. A., Moran T. V., Evenson J. K., Sugimoto M. Phospholipid hydroperoxide glutathione peroxidase: full-length pig blastocyst cDNA sequence and regulation by selenium status. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993 Jun 30;193(3):905–911. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1993.1711. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi K., Akasaka M., Yamamoto Y., Kobayashi C., Mizoguchi J., Koyama J. Primary structure of human plasma glutathione peroxidase deduced from cDNA sequences. J Biochem. 1990 Aug;108(2):145–148. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a123172. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi K., Avissar N., Whitin J., Cohen H. Purification and characterization of human plasma glutathione peroxidase: a selenoglycoprotein distinct from the known cellular enzyme. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1987 Aug 1;256(2):677–686. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(87)90624-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ursini F., Maiorino M., Gregolin C. The selenoenzyme phospholipid hydroperoxide glutathione peroxidase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Mar 29;839(1):62–70. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(85)90182-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vendeland S. C., Beilstein M. A., Chen C. L., Jensen O. N., Barofsky E., Whanger P. D. Purification and properties of selenoprotein W from rat muscle. J Biol Chem. 1993 Aug 15;268(23):17103–17107. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams D. L., Pierce R. J., Cookson E., Capron A. Molecular cloning and sequencing of glutathione peroxidase from Schistosoma mansoni. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1992 May;52(1):127–130. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(92)90042-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang J. G., Hill K. E., Burk R. F. Dietary selenium intake controls rat plasma selenoprotein P concentration. J Nutr. 1989 Jul;119(7):1010–1012. doi: 10.1093/jn/119.7.1010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeh J. Y., Beilstein M. A., Andrews J. S., Whanger P. D. Tissue distribution and influence of selenium status on levels of selenoprotein W. FASEB J. 1995 Mar;9(5):392–396. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.9.5.7896009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimura S., Watanabe K., Suemizu H., Onozawa T., Mizoguchi J., Tsuda K., Hatta H., Moriuchi T. Tissue specific expression of the plasma glutathione peroxidase gene in rat kidney. J Biochem. 1991 Jun;109(6):918–923. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a123480. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuker M., Stiegler P. Optimal computer folding of large RNA sequences using thermodynamics and auxiliary information. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jan 10;9(1):133–148. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.1.133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Rij A. M., McKenzie J. M., Thomson C. D., Robinson M. F. Selenium supplementation in total parenteral nutrition. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 1981 Mar-Apr;5(2):120–124. doi: 10.1177/0148607181005002120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]