Abstract
Background
The periodontitis is one of the most prevalent diseases with alveolar resorption in adult people and is the main cause of the tooth loss. To investigate the possibility for protecting the loss of alveolar bone in periodontal diseases, a RNAi-based therapeutic strategy is applied for silencing RANK signaling using thermosensitive chitosan hydrogel as siRNA reservoir and vector.
Results
The thermosensitive chitosan hydrogel was formed from solution (PH = 7.2, at 4°C) at 37°C within 8 minutes. The degradation rates of hydrogel were ~50% and 5% (W remaining/W beginning) in the presence and absence of lysozyme, respectively, over a period of 20 days. The concurrent cumulative in vitro release of Cy3-labeled siRNA from the hydrogel was 50% and 17% over 14 days, with or without lysozyme digestion, respectively. High cell viability (>88%) was maintained for cells treated with hydrogel loaded with RANK specific siRNA and RANK knockdown was prolonged for up to 9 days when cells were incubated with siRNA/hydrogel complex. In vivo release of siRNA was investigated in a subcutaneous delivery setup in mice. The fluorescent signal from siRNA within hydrogel was remained for up to 14 days compared to less than one day for siRNA alone.
Conclusions
Chitosan hydrogel can potentially serve as a suitable reservoir and vector for local sustained delivery of siRNA in potential therapy.
Background
Most of periodontal diseases are highly destructive and characterized by loss of the periodontal ligament and alveolar bone, eventually causing tooth loss. It is possible to minimalize the disease progression to some extent via routine dental hygiene improvements but no traditional therapy can efficiently recover the reattachment of periodontal ligament tissues and induce the bone regeneration.
The alveolar bone damage is usually caused by abnormal activity of osteoclast. The receptor activator of NF-κB (RANK) and its ligand RANKL are key molecules for differentiation and activation of osteoclasts [1]. When RANKL binds to RANK, it triggers downstream signaling that results in transformation of precursor cells to mature osteoclast. It would therefore be desirable to inhibit the pathway of osteoclast maturation via targeting RANK for prevention of alveolar bone loss.
RNA-interference (RNAi) is a post-transcriptional gene silencing process that is mediated either by synthetic small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) or endogenous microRNAs. RNAi has been established as an efficient tool for investigation of gene function due to its high specificity of gene silencing including genes associated with many diseases [2]. Therapeutic RNAi applications have been well developed over the recent years and significant progress have been made in therapies for cancer [3], neurodegenerative diseases [4], infectious [5] and inflammatory lesions [6-8]. However, the main concern for siRNA therapeutics is the development of a safe delivery system for the siRNA that can protect siRNA from degradation and deliver it into specific cells without side effects. Among non-viral delivery systems, traditional lipid-based transfection system has been developed for decades and widely applied due to its well-controlled pharmacokinetic behavior and high transfection efficiency; however, the drawbacks are cytotoxicity and limited durability, which limit the application in vivo [9]. Chitosan is a natural cationic polymer that can bind negative charged siRNAs via an electrostatic interaction to form complexes spontaneously in slightly acidic aqueous milieu. It has been comprehensively investigated for drug, plasmid [10] and siRNA delivery [11,12], and considered a suitable transfection vehicle due to its low toxicity, low immunogenicity, low cost, and good biocompatibility [13]. We have also successfully applied chitosan/siRNA derived therapies for arthritis and radiation-induced fibrosis in animal disease models [7,8]. Hydrogel containing siRNA has also been demonstrated effective in cancer therapy [14] and chitosan-based hydrogel has been used as a reservoir for drug loading to enable sustained release of variously therapeutic agents at controlled positions [15,16]. In particular, a chitosan-glycerol phosphate thermosensitive hydrogel, with improved biocompatibility [17,18] and rapid solution-gel state shifting [19], has been employed to deliver ellagic acid [20], collagen composite [21] or ferulic acid [22] for the treatment of various diseases including cancer [23]. In our study the chitosan hydrogel is loaded with RANK siRNA with aim to develop potential RNAi- based therapeutic strategy for periodontitis.
Results
siRNA Validation
Three siRNAs, designed to target mouse RANK, were transfected in murine macrophage cell line, RAW264.7. Two of these siRNAs showed a strong knockdown of RANK mRNA expression (Additional file 1: Figure S1). siRNA2 was selected for further experiments and referred as siR-RANK.
Hydrogel mediated prolonged gene silencing
The bioactivity of hydrogel loaded with siR-RANK was investigated in RAW264.7 cells. The efficiency of RANK gene silencing was evaluated at day 3, 6 and 9 post-transfection. Transfection with siRNA formulated using the commercial reagent TransIT-TKO was included as positive control for transfection efficiency. Compared to the >70% knockdown effect 48 h post transfection by TKO (Additional file 1: Figure S1), the RANK mRNA expression was partly recovered after 72 h (3 days) (Figure 1) (>40%), and completely returned to untreated level 6 and 9 days post transfection (Figure 1). In contrast, cells treated with hydrogel loaded with siR-RANK demonstrated a significant prolonged RANK mRNA knockdown effect gradually increasing from 30%, 50% to 60% at 3 d, 6 d and 9 d post transfection, respectively (Figure 1), with statistical significance of p < 0.05 (evaluated by one-way ANOVA).
Figure 1.
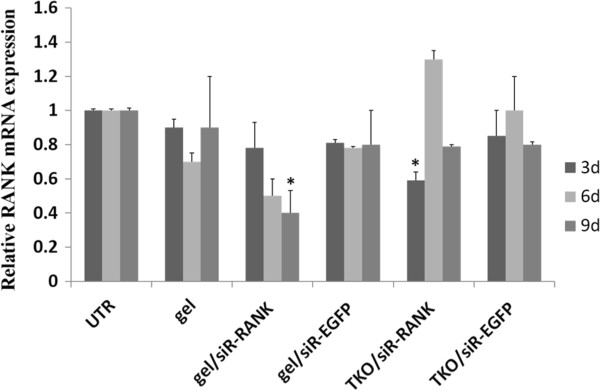
Prolonged gene silencing by siRNA/hydrogel complex. Cells were treated by hydrogel loaded with siR-RANK for 3, 6, and 9 days. Cells transfected via TransIT TKO/siR-RANK was included as positive control, and other controls included untransfected cells (UTR), empty hydrogel (Gel), or hydrogel formulated with siR-EGFP and TKO/siR-EGFP. The knockdown efficiency was evaluated by Real Time RT-PCR. RANK mRNA expression was normalized with β-actin and the relative RANK mRNA expression was calculated with UTR set to 1 and the data was presented as mean ± SD (n = 3). *p < 0.05 compared to untransfected cells.
Cell viability assay
To evaluate the cytotoxicity of the hydrogel alone or hydrogel/siRNA complex, MTT assay was performed for cell treated with hydrogel and chitosan/siRNA hydrogel for 3 days (Figure 2). Compared to the non-treated control, viability of cells incubated with chitosan hydrogel alone or formulated with siRNAs was ~90%, indicating good biocompatibility and relatively low cytotoxicity of the hydrogel with and without siRNA.
Figure 2.
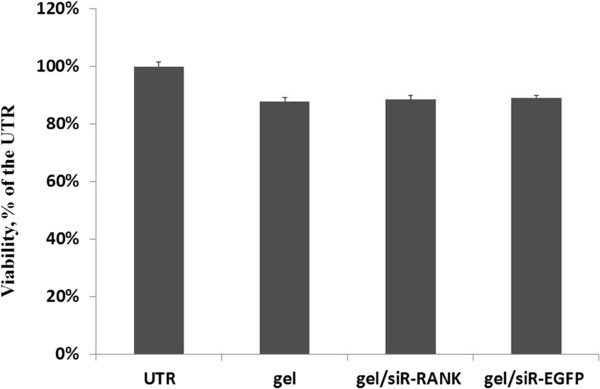
Viability for cells incubated with chitosan hydrogel alone or coupled with siRNA. Cell viability was assessed by MTT assay at 72 h post-transfection. The relative absorbance (at 570 nm) was measured and normalized to the level of non-treated control. Data was presented as mean ± SD (n = 3).
siRNA release test in vitro
In order to determine the release profile of siRNA from chitosan hydrogel, Cy3-labeled siRNA was formulated with the hydrogel and subsequently incubated at 37°C in PBS. As a reference, a fluorescence intensity-concentration standard curve was determined with multiple dilution of Cy3-labeled siRNA in PBS and PBS alone. Fluorescence intensity was measured for samples collected from various time points and background signal from PBS alone was subtracted. The accumulative release profiles were calculated based on the concentrations obtained (Figure 3). A biphasic release profile was observed: A low initial burst for the first 2–3 days followed by a sustained slow release with a total of 17% released siRNA at day 14. The siRNA was released much faster when the hydrogel was treated with lysozyme, accumulating to a total of 50% release at day 14 (Figure 3).
Figure 3.
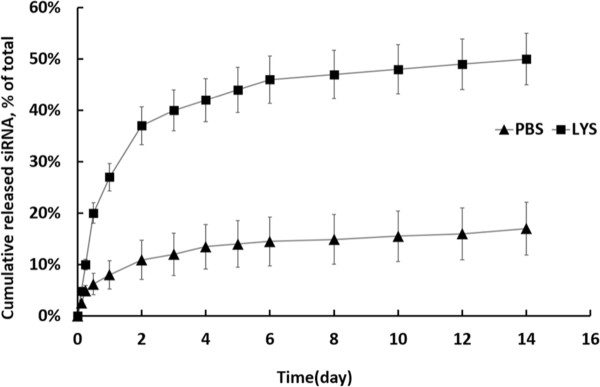
Cumulative release profile of siRNA from chitosan hydrogel/siRNA. The formulated hydrogel was degraded either in PBS alone (marked as PBS) or PBS contained lysozyme (marked as LYS). Fluorescence intensity was measured for samples collected from various time points and background level from blank well was subtracted. The accumulative release profiles were calculated based on concentrations obtained. Data was presented as mean ± SD (n = 3).
To investigate whether siRNA is released as free siRNA or siRNA complexed with chitosan, a filter assay was performed. As expected, free siRNA, with a molecular weight of 13.3 kD, passes nearly completely through a membrane with MWCO of 100 kDa (Additional file 2: Figure S2). In contrast, less than 10% siRNA was recovered in the filter assay when formulated with chitosan indicating that the siRNA remains bound positively charged chitosan after release from the hydrogel.
Hydrogel degradation in vitro
To understand the degradation behavior of the hydrogel material, FE-SEM imaging was used to visualize the gel structure at different time points after gel-formation. Surface images showed that the non-treated hydrogel formed a complicated sponge-like structure with abundant cross-linking and the average diameter of pores of approximately 50 m (Figure 4A-E). The lysozyme treatment changed the apparent structure dramatically (Figures 4F-J and 5K-O), especially in the presence of 0.5g/L of lysozyme at day 10. Here the frame structure was loosened during the incubation and the cross-linking was destroyed, resulting in enlarged cavities (Figure 4K vs. 4A and F). No significant difference was observed between 0.1g/L and 0.5 g/L after extended incubation (>20 days) (Figure 4G-J and 5I-O). To quantify the hydrogel degradation, the residual chitosan hydrogel was weighed at different time points. The lysozyme clearly enhanced the degradation rate and the mass loss showed a positive correlation with the concentration of lysozyme (Figure 5). It is reasonable to speculate that the initial burst of chitosan/siRNA hydrogel in PBS may derive from surface associated siRNA by simple diffusion, while the prolonged release might involve interiorly located siRNA depending on the hydrogel degradation for release.
Figure 4.
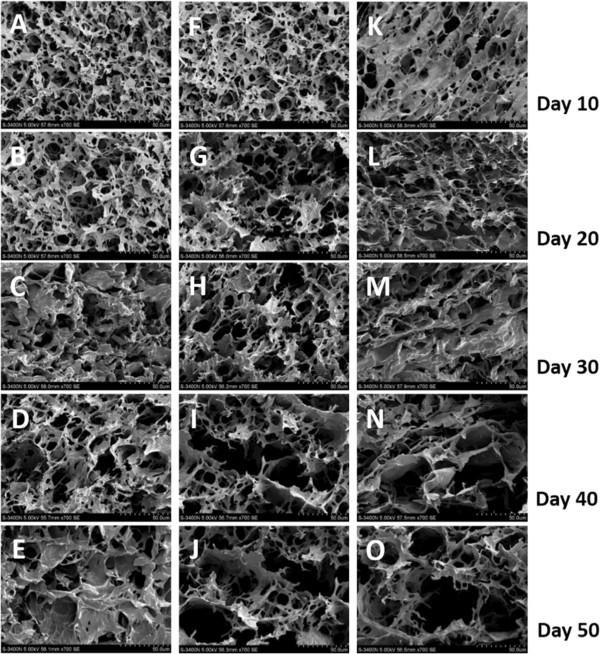
FE-SEM images of hydrogel. Hydrogel incubated in the absence (A-E) or presence of, 0.1 g/L and 0.5 g/L lysozyme (F-J and K-O, respectively; scale bar = 50 μm).
Figure 5.
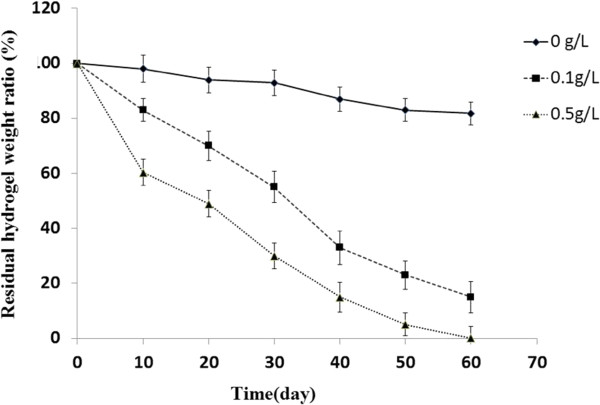
Mass loss of hydrogel treated by lysozyme. Hydrogel was incubated in the absence or presence of lysozyme at various concentrations (0.1 g/L and 0.5 g/L), and the residual weight of dried hydrogel was measured at different intervals. Data were presented as mean ± SD (n = 3).
siRNA release test in vivo
In vivo release of siRNA was investigated by optical in vivo imaging after subcutaneous injection of Cy5-siRNA loaded hydrogel in mice. Injection of siRNA alone in PBS was included as control. The fluorescent signal from siRNA within hydrogel remained for up to 7 days compared to less than one day for siRNA alone (Figure 6A). A quantitative release profile was provided by measuring the fluorescent signal using Living Image 4.2 Software (Figure 6B). A more sustained siRNA signal was demonstrated for mice injected with siRNA loaded in hydrogel than from mice injected with siRNA alone (~70% vs >95% decrease in signal intensity 24 h post-injection, respectively; Figure 6B).
Figure 6.
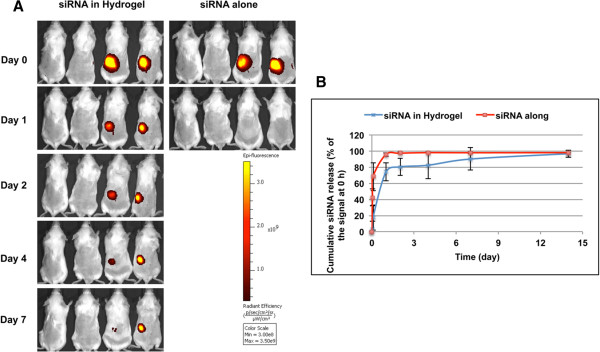
Release profile of Cy5 labeled siRNA complexed within hydrogel in mice. Mice were injected s.c. with chitosan hydrogel/Cy5-siRNA, Cy5-siRNA alone and PBS buffer (n = 4). Fluorescent optical imaging was performed at the indicated time points after injection. (A), Images from 2 mice 0, 1, 2, 4 and 7 days after injection with chitosan hydrogen/Cy5-siRNA and images from 2 mice 0 and 1 day after injection with Cy5-siRNA alone. Two mice injected with buffer (Two mice on the left in each panel) were included as control for both scanning. (B), After quantifying the signal intensity of images, siRNA release was calculated as reduction of fluorescent signal: (RE (0 h) – RE (Designed Time Point)) /RE (0 h) * 100%. Average value from each time point (0, 1, 2 h, and 1, 2, 4, 7, 14 d) was presented (mean ± SD, n = 4).
Discussion
We have demonstrated that siRNA, loaded into chitosan hydrogel, is released in a sustained fashion both in vitro and in vivo. Using this system, RANK specific siRNA exhibited a prolonged specific silencing effect for up to 9 days in vitro without apparent cytotoxicity.
RNAi has recently proven a promising approach for the development of new treatment protocols for human diseases. However, the lack of suitably non-viral systemic delivery vehicles has limited its application in clinic where effective and prolonged silencing effects are needed. Compared to systemic delivery, local delivery systems can provide a relatively high drug concentration in the lesion areas and reduce side effects. For instance, local delivery of siRNA using biodegradable polymer enabled a scaffold to support and repair bone defects [24]. However, the predetermined shape restricts the application for many kinds of lesions encountered in clinic. To address this, injectable hydrogel is widely applied for tissue engineering, also for drug delivery including siRNA delivery [25-27], due to its ability to undergo sol–gel phase transition.
We have successfully applied chitosan/siRNA therapies in several animal disease models with arthritis and radiation-induced fibrosis [7,8]. Among chitosan-based hydrogels, the one cross-linked with β-glycerophosphate has been most extensively employed and already proven effective in several kinds of drug delivery [20-22,25]. In addition, the chitosan-based gels have been used for tissue regeneration in periodontal disease [28]. We have developed an injectable thermosensitive chitosan hydrogel system for siRNA delivery and observed prolonged knockdown efficacy for up to 9 days. The effect is more pronounced than in a previous collagen gel study where substantial knockdown of GFP was observed for only up to 6 days in GFP expressing HEK293 cells [26].
The in vitro siRNA release profile suggests that electrostatic interactions between the nucleotides and positively charged polymer slow down the release. In addition, diffusion through the biopolymer pores facilitated by biopolymer degradation may also control the release. This resembles the observation in a previous report for siRNA release from calcium cross-linked alginate with chitosan [26]. In that study siRNA could only be released from the hydrogel when gradually degraded by an enzyme [26]. In another study, gelatin hydrogel, incorporated with cationized gelatin (CG)-siRNA complexes, was enzymatically degraded by the treatment with collagenase to enable the release of siRNA [25]. Similarly, we observed clear degradation in the presence of lysozyme, indicating that this enzyme is able to degrade the chitosan gel in vitro [29-31].
Compared to in vitro, siRNA was released more quickly in vivo, implying the existence of lysozyme or other degradation pathways in vivo [32]. The chitosan hydrogel/siRNA system has previously been applied in tumor therapy in mice [27]. They observed labelled siRNA uptake in tumour cells up to 270 μm away from the hydrogel edge 24 h post intra-tumoral injection, however, the half-life of siRNA in vivo was not addressed. The hydrogel was administrated twice weekly at a dose of 150 μg/kg body weight and resulted in significant antitumor effect [27]. Similarly, the biodegradable hydrogel, poly-D, L-lactic acid-p-dioxanonepolyethylene glycol block co-polymer (PLA-DX-PEG) has been used as a carrier for Noggin specific siRNA in vivo, resulting in efficient silencing of the target mRNA expression and successfully induces the ectopic bone formation [24].
The RANK-RANKL system has been proven to play a vital role in the differentiation and activation of osteoclasts in periodontitis and silencing the RANK expression in osteoclast precursors may provide a new approach to prevent and convert the alveolar absorption in periodontitis. In this study, we demonstrate chitosan hydrogel could prolong gene silencing effect of siRNA up to 9 days in vitro. Theoretically, this extended release profile may be provide sufficient siRNA to prevent activation of osteoclasts and maintain the therapeutic effects on periodontitis for an extended period of time. In combination with the excellent biocompatibility we observed, our system may potentially serve as a suitable vector for continuous local delivery of RANK siRNA in periodontitis therapy.
Conclusions
In this study we have developed a chitosan-glycerol phosphate thermosensitive hydrogel enabling to functionally deliver RANK siRNA into cells. The hydrogel exhibited prolonged siRNA release profiles both in vitro and in vivo, accompanied with sustained gene silencing effect in cell. The next step will be to investigate its efficacy in animal periodontitis model and explore its potential to regenerate periodontal tissues.
Methods
siRNA target RANK screening
Three siRNA duplexes targeting RANK (siRNA1, siRNA2, and siRNA3) were ordered from GenePharma (Shanghai, China). The negative control siRNA (siNC) was provided by Genepharm, and siRNA-EGFP duplex was purchased from Ribotask (Odense, Denmark). All the sequences were listed in Table 1.
Table 1.
Sequence of siRNAs
| Target | Sense sequence (5′-3′) | Antisense sequence (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| RANK1 |
GAGCAGAACUGACUCUAUGUU |
CAUAGAGUCAGUUCUGCUCUU |
| RANK2 |
GCGCAGACUUCACUCCAUAUU |
UAUGGAGUGAAGUCUGCGCUU |
| RANK3 |
GCGCUGACAGCUAAUUUGUTT |
ACAAAUUAGCUGUCAGCGCTT |
| EGFP |
GACGUAAACGGCCACAAGUTC |
ACUUGUGGCCGUUUACGUCGC |
| Negative control | UUCUCCGAACGUGUCACGUTT | ACGUGACACGUUCGGAGAATT |
Mouse macrophage cell line, RAW264.7 (ATCC® TIB-71™), used as osteoclast precursor, was maintained in RPMI media (Gibco®) supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (Sigma), 1% penicillin-streptomycin (Gibco®) at 37°C in 5% CO2 and 100% humidity. Cells were seeded onto 24-well plate twenty-four hours before transfection. siRNA was transfected using the commercial reagent TransIT-TKO (Mirus Bio Corporation) at final siRNA concentration 50 nM. Cells were harvested at 48 hr post-transfection.
mRNA expression level was assessed by Quantitative Real-Time RT-PCR (qRT-PCR) following routine procedures of total RNA purification using TRIzol reagent (Invitrogen, Copenhagen) and reverse transcription using SuperScript® II Reverse Transcriptase (RT) kit (Invitrogen, Copenhagen). The comparative CT (threshold cycle) method described in the manufacturer’s protocol (Stratagene, Copenhagen) was used to quantitate the relative RANK mRNA expression level. The β-actin mRNA was amplified as an internal control to normalise the expression level. The primer sequences for RANK gene are, forward: 5’-TAGGACGTCAGGCCAAAGGACAAA -3’, reverse: 5’-AGGGCCTACTGCCTAAGTGTGTTT -3’, with a product size of 132 bp. Primer sequences for β-actin gene are, forward: 5’-ACACAGTGCTGTCTGGTGGT-3’, Reverse: 5’-CTGGAAGGTGGACAGTGAGG-3’ with a product size of 172 bp.
Formulation of chitosan hydrogel /siRNA complex
Chitosan (150 kDa, 95% deacetylation) was provided by HEPPE MEDICAL (Germany). Indicated chitosan was dissolved in 1% acetic acid (Sigma) at the concentration of 2% w/v. Sodium glycerophosphate (Sigma) were used as crosslink reagent and added dropwise into chitosan solution while stirring (pH 7.2, 4°C). Pre-calculated siRNA (5 μg) were added into the clear and homogeneous liquid solution (200 μl). The hydrogel spontaneously became solid during the incubation at 37°C for 8 minutes, which was ready for further experiments.
siRNA transfection mediated by hydrogel
The 24-well transwell ( Thincert, In Vitro As, Fredensborg, Denmark) loaded with hydrogel was inserted over the cell culture plates where containing pre-seeded cells (RAW264.7, 2 × 104/well), as shown in Figure 7. The transfection was terminated and the RANK gene expression was measured by Quantitative Real Time RT-PCR after transfected for 3, 6, 9 days.
Figure 7.
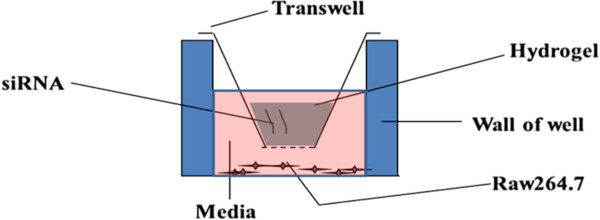
Relative position of chitosan/siRNA hydrogel in transwell during cell culture.
Cytotoxicity of hydrogel/siRNA complex
The cell viability was determined by MTT assay at day 3 of hydrogel mediated transfection as described above (n = 3). MTT reagent (5 mg/ml, Sigma, Copenhagen) was then added to each well at 1:3 dilution, after removed transwells, rinsed with PBS and exchanged the medium. After incubation of 2 ~ 4 h at 37°C, the reaction was stopped by replacing of DMSO (Sigma, Copenhagen) while the color changes became visible. The relative absorbance (at 570 nm) was measured using a Victor X5 Multilabel Plate reader (PerkinElmer).
siRNA release test in vitro
To assess siRNA release profile, the Cy3-labled siRNA (5 μg) was formulated with chitosan hydrogel as described above. The hydrogel was immersed in 500 μl phosphate buffer (PBS, Gibco®) solution (pH 7.4) with or without lysozyme (0.5 mg/ml, Sigma). At pre-determined intervals, all of the supernatant was drawn and replaced by the fresh buffer accordingly. The fluorescence intensity from the supernatant was measured by fluorescence plate reader (FLUOstar OPTIMA) and PBS solution was used as blank control.
To investigate whether siRNA in release solution as free or chitosan complexed siRNA, Cy3-labled siRNA was encapsulated in chitosan hydrogel (n = 3). After gelation, 500 μl of PBS was added and incubated 2 h at 37°C. The PBS solution was collected and 250 μl the solution was loaded on to a centrifugal device with molecular weight cut off (MWCO) of 100 kDa (Pall Corporation) and centrifuged at 3000 g for 5 min. The Cy3 fluorescent intensity of filtered solution was measured by FLUOstar OPTIMA (BMG Labtechnologies) and normalized to input solution. As a non-particulate control, free Cy3-siRNA was also loaded on a centrifuge device treated similarly.
Hydrogel degradation in vitro
To further understand the mechanism of siRNA release from the hydrogel, the hydrogel degradation was assessed. Briefly, 1ml chitosan hydrogel solution was placed into 37°C incubator to form the hydrogel. The hydrogel, treated using three concentration of lysozyme (0, 0.1, 0.5 g/L), was quickly frozen with liquid nitrogen for 5min and totally freeze-dried before precisely weighed by electronic balance. The percentage of mass loss was determined by measuring hydrogel weight at initial time point (Wi) and weight at different time points pre-designed (Wd), and calculated by ((Wi-Wd)/Wi). After gold coating, the freeze-dried sample was also observed with Field Emission Scanning Electron Microscope (FE-SEM).
siRNA release test in vivo
To evaluate siRNA release within hydrogel in vivo, BALB/c female mice (Taconic Europe, Ll. Skensved, Denmark) were chosen. All procedures of animal work were approved by “The Experimental Animal Inspectorate in Denmark” under The Danish Veterinary and Food Administration, Ministry of Food, Agriculture and Fisheries.
Hair from the back and the abdomen was shaved to avoid autofluorescence during scanning. Cy5-labelled siRNA/chitosan hydrogel formulation in 50 microliter sodium acetate buffer (containing 5 μg siRNA duplex) was subcutaneously injected into the left flank region of mice. The unformulated Cy5-labelled siRNA in PBS with the same volume was administrated as control. The mice were scanned using an IVIS® 200 imaging system (Xenogen, Caliper Life Sciences) before and right after injection followed by 1 hr, 2 hrs, 1 day, 2, 3, 7 and 14 days post injection. The scanning was performed under anesthesia with 2.5% isoflurane. Cy5 excitation (λex = 640 nm) and emission (λem = 700 nm) filters were used. Total emission from inflicted areas (Region of Interest, ROI) of each mouse was quantified using Living Image 4.0 software package. According to the user instruction, the radiant efficiency (RE) of injection sites was measured (photons/sec/cm2/sr)/ (μW/cm2), which is presented radiance/illumination power density [33,34].
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Authors’ contributions
ZM designed and carried out all the experiments. CY carried out the hydrogel preparation and joined most of experiments. WS analyzed the data and drafted the manuscript. QW participated in the design of the study. JK analyzed the data and revised the manuscript. SG drafted and revised the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Supplementary Material
RANK gene knockdown efficiency. Three siRNA against murine RANK (siRNA1, siRNA2 and siRNA3) were transfected in triplicate into RAW264.7 cells using TransIT-TKO reagent. Untreated cells (UTR) or cells transfected with siRNA against EGFP (siR-EGFP) and siR-NC were included as controls. Cells were harvested 48 hrs post transfection and RANK mRNA levels were evaluated by quantitative RT-PCR. Data were presented as mean ± SD (n = 3). * siRNA was selected for further experiment.
Analysis of siRNA released from chitosan hydrogel. The Cy3-labled siRNA was encapsulated in chitosan hydrogel (n = 3) and incubated in PBS for 2h at 37°C, the PBS solution was collected and half of the solution (release solution) was centrifuged through a filter device. The Cy3 fluorescent intensity of filtered solution was measured and normalized to input solution. Unformulated free Cy3-siRNA (free siRNA) was applied as control.
Contributor Information
Zhiwei Ma, Email: zhiweimafmmu@163.com.
Chuanxu Yang, Email: chuanxuyang@inano.au.dk.
Wen Song, Email: songwenfmmu@hotmail.com.
Qintao Wang, Email: qintaowang@hotmail.com.
Jørgen Kjems, Email: jk@mb.au.dk.
Shan Gao, Email: shg@mb.au.dk.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from the Nature Science Foundation of China (NSFC 81271137) and the Lundbeck Foundation - Lundbeck Foundation Nanomedicine Center for Individualized Management of Tissue Damage and Regeneration. We thank San Hein for his supervision of chitosan preparation and Menglin Chen for her kindly help in hydrogel release test in vitro. We thank Rita Rosendahl and Claus Bus for their excellent technical assistance, as well as Frederik Dagnæs-Hansen for his arrangement of animal works.
References
- Koide M, Kinugawa S, Takahashi N, Udagawa N. Osteoclastic bone resorption induced by innate immune responses. Periodontol 2000. 2010;54:235–246. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0757.2010.00355.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez-Fraga M, Martinez T, Jimenez A. RNA interference technologies and therapeutics: from basic research to products. BioDrugs. 2009;23:305–332. doi: 10.2165/11318190-000000000-00000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sotillo E, Thomas-Tikhonenko A. Shielding the messenger (RNA): microRNA-based anticancer therapies. Pharmacol Ther. 2011;131:18–32. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2011.04.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez-Alegre P. Therapeutic RNA interference for neurodegenerative diseases: from promise to progress. Pharmacol Ther. 2007;114:34–55. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2007.01.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lupberger J, Brino L, Baumert TF. RNAi: a powerful tool to unravel hepatitis C virus-host interactions within the infectious life cycle. J Hepatol. 2008;48:523–525. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2007.12.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laroui H, Theiss AL, Yan Y, Dalmasso G, Nguyen HT, Sitaraman SV, Merlin D. Functional TNFalpha gene silencing mediated by polyethyleneimine/TNFalpha siRNA nanocomplexes in inflamed colon. Biomaterials. 2011;32:1218–1228. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2010.09.062. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard KA, Paludan SR, Behlke MA, Besenbacher F, Deleuran B, Kjems J. Chitosan/siRNA nanoparticle-mediated TNF-alpha knockdown in peritoneal macrophages for anti-inflammatory treatment in a murine arthritis model. Mol Ther. 2009;17:162–168. doi: 10.1038/mt.2008.220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nawroth I, Alsner J, Behlke MA, Besenbacher F, Overgaard J, Howard KA, Kjems J. Intraperitoneal administration of chitosan/DsiRNA nanoparticles targeting TNFalpha prevents radiation-induced fibrosis. Radiother Oncol. 2010;97:143–148. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2010.09.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroeder A, Levins CG, Cortez C, Langer R, Anderson DG. Lipid-based nanotherapeutics for siRNA delivery. J Intern Med. 2010;267:9–21. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2796.2009.02189.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duceppe N, Tabrizian M. Advances in using chitosan-based nanoparticles for in vitro and in vivo drug and gene delivery. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2010;7:1191–1207. doi: 10.1517/17425247.2010.514604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard KA, Rahbek UL, Liu X, Damgaard CK, Glud SZ, Andersen MO, Hovgaard MB, Schmitz A, Nyengaard JR, Besenbacher F, Kjems J. RNA interference in vitro and in vivo using a novel chitosan/siRNA nanoparticle system. Mol Ther. 2006;14:476–484. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2006.04.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holzerny P, Ajdini B, Heusermann W, Bruno K, Schuleit M, Meinel L, Keller M. Biophysical properties of chitosan/siRNA polyplexes: profiling the polymer/siRNA interactions and bioactivity. J Control Release. 2012;157:297–304. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2011.08.023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldrick P. The safety of chitosan as a pharmaceutical excipient. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol. 2010;56:290–299. doi: 10.1016/j.yrtph.2009.09.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramakrishnan S. Hydrogel-siRNA for cancer therapy. Cancer Biol Ther. 2011;11:849–851. doi: 10.4161/cbt.11.9.15465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jo S, Kim S, Cho TH, Shin E, Hwang SJ, Noh I. Effects of recombinant human bone morphogenic protein-2 and human bone marrow-derived stromal cells on in vivo bone regeneration of chitosan-poly(ethylene oxide) hydrogel. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2013;101:892–901. doi: 10.1002/jbm.a.34354. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakavala SR, Patel NG, Pate NV, Thakkar VT, Patel KV, Gandhi TR. Development and in vivo evaluation of silver sulfadiazine loaded hydrogel consisting polyvinyl alcohol and chitosan for severe burns. J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 2012;4:S54–S56. doi: 10.4103/0975-7406.94131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ahmadi R, de Bruijn JD. Biocompatibility and gelation of chitosan-glycerol phosphate hydrogels. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2008;86:824–832. doi: 10.1002/jbm.a.31676. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoemann CD, Chenite A, Sun J, Hurtig M, Serreqi A, Lu Z, Rossomacha E, Buschmann MD. Cytocompatible gel formation of chitosan-glycerol phosphate solutions supplemented with hydroxyl ethyl cellulose is due to the presence of glyoxal. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2007;83:521–529. doi: 10.1002/jbm.a.31365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruel-Gariepy E, Chenite A, Chaput C, Guirguis S, Leroux J. Characterization of thermosensitive chitosan gels for the sustained delivery of drugs. Int J Pharm. 2000;203:89–98. doi: 10.1016/s0378-5173(00)00428-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim S, Nishimoto SK, Bumgardner JD, Haggard WO, Gaber MW, Yang Y. A chitosan/beta-glycerophosphate thermo-sensitive gel for the delivery of ellagic acid for the treatment of brain cancer. Biomaterials. 2010;31:4157–4166. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2010.01.139. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang L, Stegemann JP. Thermogelling chitosan and collagen composite hydrogels initiated with beta-glycerophosphate for bone tissue engineering. Biomaterials. 2010;31:3976–3985. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2010.01.131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng YH, Yang SH, Lin FH. Thermosensitive chitosan-gelatin-glycerol phosphate hydrogel as a controlled release system of ferulic acid for nucleus pulposus regeneration. Biomaterials. 2011;32:6953–6961. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2011.03.065. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seth S, Johns R, Templin MV. Delivery and biodistribution of siRNA for cancer therapy: challenges and future prospects. Ther Deliv. 2012;3:245–261. doi: 10.4155/tde.11.155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manaka T, Suzuki A, Takayama K, Imai Y, Nakamura H, Takaoka K. Local delivery of siRNA using a biodegradable polymer application to enhance BMP-induced bone formation. Biomaterials. 2011;32:9642–9648. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2011.08.026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito T, Tabata Y. Preparation of gelatin hydrogels incorporating small interfering RNA for the controlled release. J Drug Target. 2012;20:864–872. doi: 10.3109/1061186X.2012.725170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krebs MD, Jeon O, Alsberg E. Localized and sustained delivery of silencing RNA from macroscopic biopolymer hydrogels. J Am Chem Soc. 2009;131:9204–9206. doi: 10.1021/ja9037615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han HD, Mora EM, Roh JW, Nishimura M, Lee SJ, Stone RL, Bar-Eli M, Lopez-Berestein G, Sood AK. Chitosan hydrogel for localized gene silencing. Cancer Biol Ther. 2011;11:839–845. doi: 10.4161/cbt.11.9.15185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akncbay H, Senel S, Ay ZY. Application of chitosan gel in the treatment of chronic periodontitis. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2007;80:290–296. doi: 10.1002/jbm.b.30596. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee KY, Ha WS, Park WH. Blood compatibility and biodegradability of partially N-acylated chitosan derivatives. Biomaterials. 1995;16:1211–1216. doi: 10.1016/0142-9612(95)98126-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onishi H, Machida Y. Biodegradation and distribution of water-soluble chitosan in mice. Biomaterials. 1999;20:175–182. doi: 10.1016/s0142-9612(98)00159-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomihata K, Ikada Y. In vitro and in vivo degradation of films of chitin and its deacetylated derivatives. Biomaterials. 1997;18:567–575. doi: 10.1016/s0142-9612(96)00167-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lim SM, Song DK, Oh SH, Lee-Yoon DS, Bae EH, Lee JH. In vitro and in vivo degradation behavior of acetylated chitosan porous beads. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2008;19:453–466. doi: 10.1163/156856208783719482. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iversen F, Yang C, Dagnaes-Hansen F, Schaffert DH, Kjems J, Gao S. Optimized siRNA-PEG conjugates for extended blood circulation and reduced urine excretion in mice. Theranostics. 2013;3:201–209. doi: 10.7150/thno.5743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nawroth I, Alsner J, Deleuran BW, Dagnaes-Hansen F, Yang C, Horsman MR, Overgaard J, Howard KA, Kjems J, Gao S. Peritoneal macrophages mediated delivery of chitosan/siRNA nanoparticle to the lesion site in a murine radiation-induced fibrosis model. Acta Oncol (Stockholm, Sweden) 2013;52:1730–1738. doi: 10.3109/0284186X.2012.726373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
RANK gene knockdown efficiency. Three siRNA against murine RANK (siRNA1, siRNA2 and siRNA3) were transfected in triplicate into RAW264.7 cells using TransIT-TKO reagent. Untreated cells (UTR) or cells transfected with siRNA against EGFP (siR-EGFP) and siR-NC were included as controls. Cells were harvested 48 hrs post transfection and RANK mRNA levels were evaluated by quantitative RT-PCR. Data were presented as mean ± SD (n = 3). * siRNA was selected for further experiment.
Analysis of siRNA released from chitosan hydrogel. The Cy3-labled siRNA was encapsulated in chitosan hydrogel (n = 3) and incubated in PBS for 2h at 37°C, the PBS solution was collected and half of the solution (release solution) was centrifuged through a filter device. The Cy3 fluorescent intensity of filtered solution was measured and normalized to input solution. Unformulated free Cy3-siRNA (free siRNA) was applied as control.


