Abstract
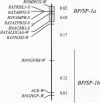
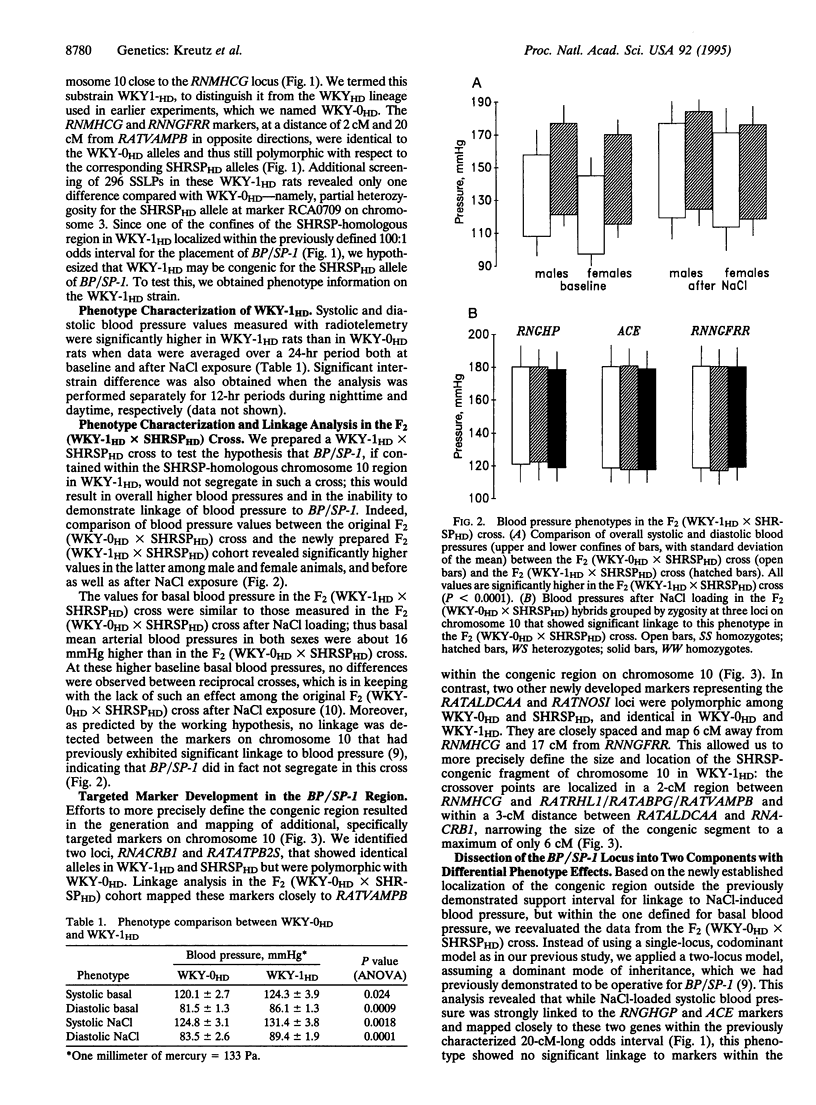
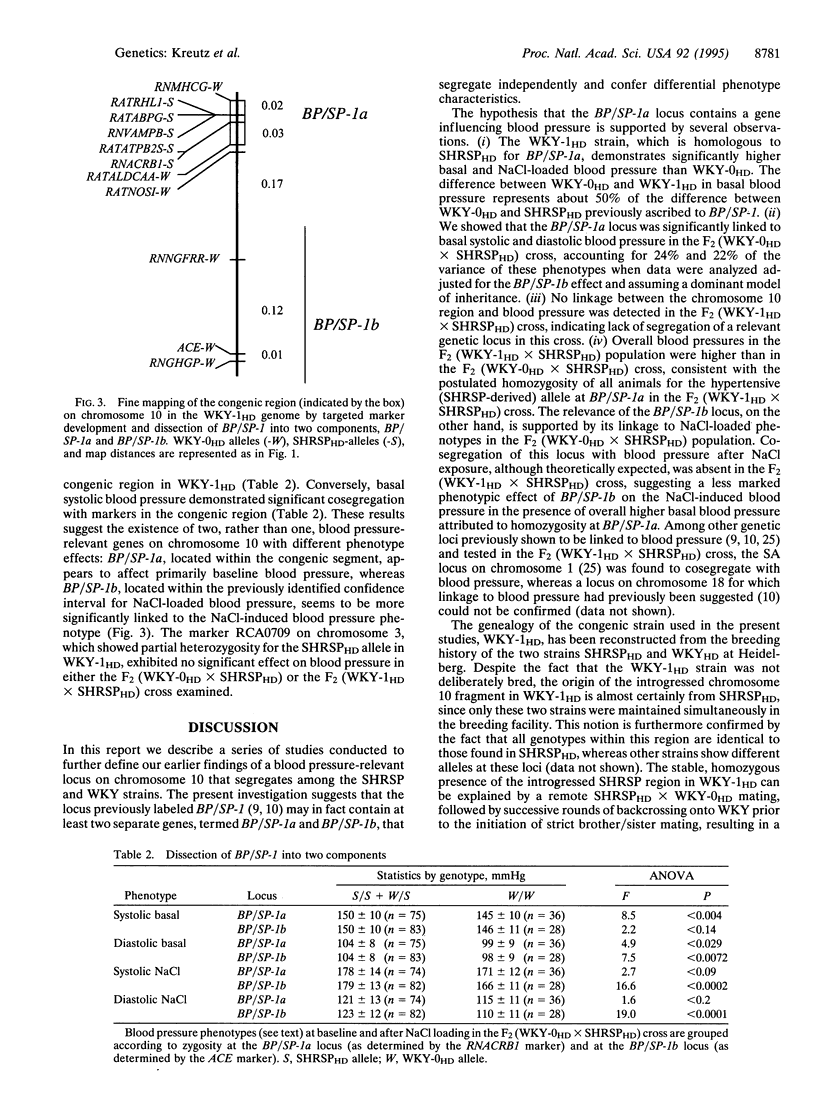
We have previously identified a locus on rat chromosome 10 as carrying a major hypertension gene, BP/SP-1. The 100:1 odds support interval for this gene extended over a 35-centimorgan (cM) region of the chromosome that included the angiotensin I-converting enzyme (ACE) locus as demonstrated in a cross between the stroke-prone spontaneously hypertensive rat (SHRSPHD) and the normotensive Wistar-Kyoto (WKY-0HD) rat. Here we report on the further characterization of BP/SP-1, using a congenic strain, WKY-1HD. WKY-1HD animals carry a 6-cM chromosomal fragment genotypically identical with SHRSPHD on chromosome 10, 26 cM away from the ACE locus. Higher blood pressures in the WKY-1HD strain compared with the WKY-0HD strain, as well as absence of linkage of the chromosome 10 region to blood pressure in an F2 (WKY-1HD x SHRSPHD) population suggested the existence of a quantitative trait locus, termed BP/SP-1a, that lies within the SHRSP-congenic region in WKY-1HD. Linkage analysis in the F2 (WKY-0HD x SHRSPHD) cross revealed that BP/SP-1a is linked to basal blood pressure, whereas a second locus on chromosome 10, termed BP/SP-1b, that maps closer to the ACE locus cosegregates predominantly with blood pressure after exposure to excess dietary NaCl. Thus, we hypothesize that the previously reported effect of BP/SP-1 represents a composite phenotype that can be dissected into at least two specific components on the basis of linkage data and congenic experimentation. One of the loci identified, BP/SP-1a, represents the most precisely mapped locus affecting blood pressure that has so far been characterized by random-marker genome screening.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Buonanno A., Mudd J., Merlie J. P. Isolation and characterization of the beta and epsilon subunit genes of mouse muscle acetylcholine receptor. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 5;264(13):7611–7616. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dannenberg A. L., Drizd T., Horan M. J., Haynes S. G., Leaverton P. E. Progress in the battle against hypertension. Changes in blood pressure levels in the United States from 1960 to 1980. Hypertension. 1987 Aug;10(2):226–233. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.10.2.226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubay C., Vincent M., Samani N. J., Hilbert P., Kaiser M. A., Beressi J. P., Kotelevtsev Y., Beckmann J. S., Soubrier F., Sassard J. Genetic determinants of diastolic and pulse pressure map to different loci in Lyon hypertensive rats. Nat Genet. 1993 Apr;3(4):354–357. doi: 10.1038/ng0493-354. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erdös E. G. The angiotensin I converting enzyme. Fed Proc. 1977 Apr;36(5):1760–1765. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havlik R. J., Garrison R. J., Feinleib M., Kannel W. B., Castelli W. P., McNamara P. M. Blood pressure aggregation in families. Am J Epidemiol. 1979 Sep;110(3):304–312. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a112815. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins M. W., Keller J. B., Metzner H. L., Moore F. E., Ostrander L. D., Jr Studies of blood pressure in Tecumseh, Michigan. II. Antecedents in childhood of high blood pressure in young adults. Hypertension. 1980 Jul-Aug;2(4 Pt 2):117–123. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilbert P., Lindpaintner K., Beckmann J. S., Serikawa T., Soubrier F., Dubay C., Cartwright P., De Gouyon B., Julier C., Takahasi S. Chromosomal mapping of two genetic loci associated with blood-pressure regulation in hereditary hypertensive rats. Nature. 1991 Oct 10;353(6344):521–529. doi: 10.1038/353521a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hussussian C. J., Struewing J. P., Goldstein A. M., Higgins P. A., Ally D. S., Sheahan M. D., Clark W. H., Jr, Tucker M. A., Dracopoli N. C. Germline p16 mutations in familial melanoma. Nat Genet. 1994 Sep;8(1):15–21. doi: 10.1038/ng0994-15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob H. J., Lindpaintner K., Lincoln S. E., Kusumi K., Bunker R. K., Mao Y. P., Ganten D., Dzau V. J., Lander E. S. Genetic mapping of a gene causing hypertension in the stroke-prone spontaneously hypertensive rat. Cell. 1991 Oct 4;67(1):213–224. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90584-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawakami K., Okamoto H., Yagawa Y., Nagano K. Regulation of Na+,K(+)-ATPase. II. Cloning and analysis of the 5'-flanking region of the rat NKAB2 gene encoding the beta 2 subunit. Gene. 1990 Jul 16;91(2):271–274. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90099-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lander E. S., Schork N. J. Genetic dissection of complex traits. Science. 1994 Sep 30;265(5181):2037–2048. doi: 10.1126/science.8091226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathrop G. M., Lalouel J. M. Easy calculations of lod scores and genetic risks on small computers. Am J Hum Genet. 1984 Mar;36(2):460–465. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine R. S., Hennekens C. H., Perry A., Cassady J., Gelband H., Jesse M. J. Genetic variance of blood pressure levels in infant twins. Am J Epidemiol. 1982 Nov;116(5):759–764. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a113465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lifton R. P., Dluhy R. G., Powers M., Rich G. M., Cook S., Ulick S., Lalouel J. M. A chimaeric 11 beta-hydroxylase/aldosterone synthase gene causes glucocorticoid-remediable aldosteronism and human hypertension. Nature. 1992 Jan 16;355(6357):262–265. doi: 10.1038/355262a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindpaintner K., Hilbert P., Ganten D., Nadal-Ginard B., Inagami T., Iwai N. Molecular genetics of the SA-gene: cosegregation with hypertension and mapping to rat chromosome 1. J Hypertens. 1993 Jan;11(1):19–23. doi: 10.1097/00004872-199301000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindpaintner K., Takahashi S., Ganten D. Structural alterations of the renin gene in stroke-prone spontaneously hypertensive rats: examination of genotype-phenotype correlations. J Hypertens. 1990 Aug;8(8):763–773. doi: 10.1097/00004872-199008000-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindpaintner K. What can the molecular genetics of hypertensive rats teach us about the genetics of hypertension in humans? Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 1994 Jan;3(1):30–38. doi: 10.1097/00041552-199401000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukai T., Yatsuki H., Masuko S., Arai Y., Joh K., Hori K. The structure of the brain-specific rat aldolase C gene and its regional expression. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Jan 31;174(2):1035–1042. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)91523-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OKAMOTO K., AOKI K. Development of a strain of spontaneously hypertensive rats. Jpn Circ J. 1963 Mar;27:282–293. doi: 10.1253/jcj.27.282. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnell C. R., Wood J. M. Measurement of blood pressure and heart rate by telemetry in conscious, unrestrained marmosets. Am J Physiol. 1993 May;264(5 Pt 2):H1509–H1516. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1993.264.5.H1509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimkets R. A., Warnock D. G., Bositis C. M., Nelson-Williams C., Hansson J. H., Schambelan M., Gill J. R., Jr, Ulick S., Milora R. V., Findling J. W. Liddle's syndrome: heritable human hypertension caused by mutations in the beta subunit of the epithelial sodium channel. Cell. 1994 Nov 4;79(3):407–414. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90250-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witzemann V., Stein E., Barg B., Konno T., Koenen M., Kues W., Criado M., Hofmann M., Sakmann B. Primary structure and functional expression of the alpha-, beta-, gamma-, delta- and epsilon-subunits of the acetylcholine receptor from rat muscle. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Dec 12;194(2):437–448. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb15637.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood E. R., Berger H., Jr, Sherman P. A., Lapetina E. G. Hepatocytes and macrophages express an identical cytokine inducible nitric oxide synthase gene. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993 Mar 31;191(3):767–774. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1993.1283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuille M. A., Goudie D. R., Affara N. A., Ferguson-Smith M. A. Rapid determination of sequences flanking microsatellites. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Apr 25;19(8):1950–1950. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.8.1950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]