Abstract
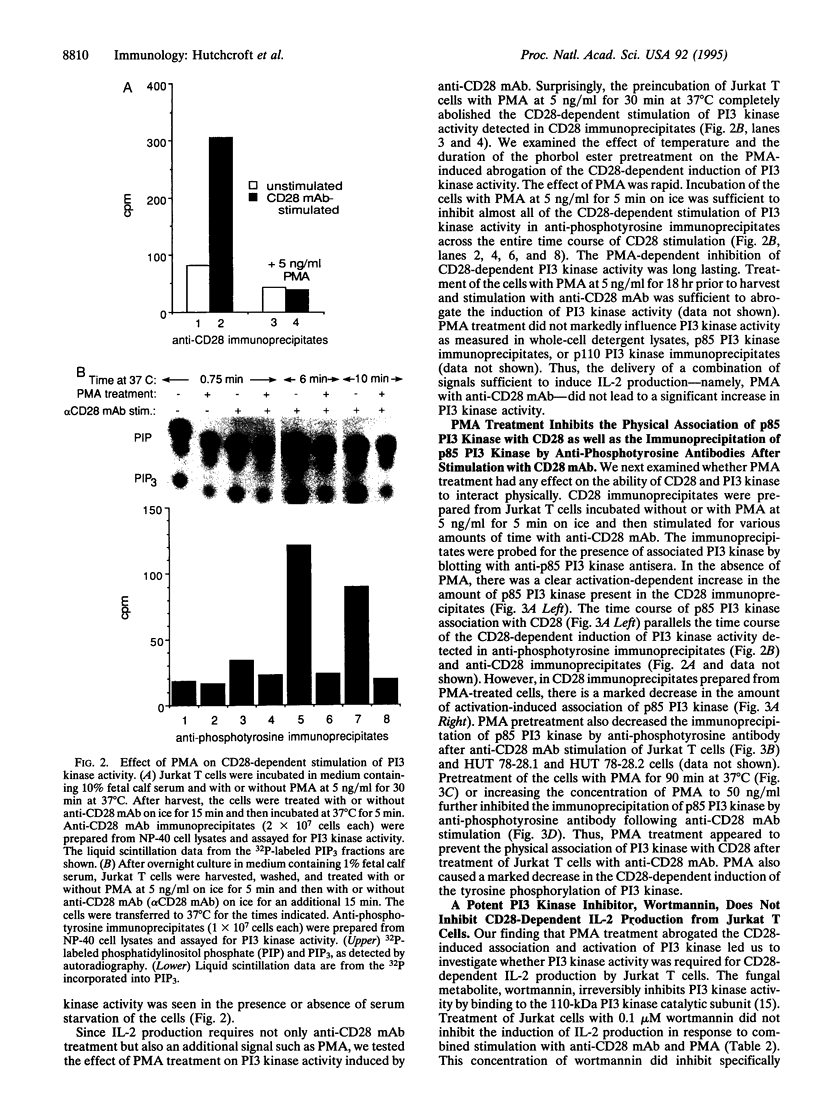
CD28 is a costimulatory receptor found on the surface of most T lymphocytes. Engagement of CD28 induces interleukin 2 (IL-2) production and cell proliferation when combined with an additional signal such as treatment with phorbol ester, an activator of protein kinase C. Recent studies have established that after CD28 ligation, the cytoplasmic domain of CD28 can bind to the 85-kDa subunit of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3 kinase). There is a concomitant increase in PI3 lipid kinase activity that may be important in CD28 signaling. Despite the requirement of phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA) for effector function, we have found, however, that treatment of Jurkat T cells with the phorbol ester PMA dramatically inhibits (i) the association of PI3 kinase with CD28, (ii) the ability of p85 PI3 kinase to be immunoprecipitated by anti-phosphotyrosine antibodies, and (iii) the induction of PI3 kinase activity after stimulation of the cells with the anti-CD28 monoclonal antibody 9.3. These changes occur within minutes of PMA treatment and are persistent. In addition, we have found that wortmannin, a potent inhibitor of PI3 kinase, does not interfere with the induction of IL-2 after stimulation of Jurkat T cells with anti-CD28 monoclonal antibody and PMA. We conclude that PI3 kinase activity may not be required for CD28-dependent IL-2 production from Jurkat T cells in the presence of PMA.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aruffo A., Seed B. Molecular cloning of a CD28 cDNA by a high-efficiency COS cell expression system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8573–8577. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- August A., Dupont B. Activation of src family kinase lck following CD28 crosslinking in the Jurkat leukemic cell line. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1994 Mar 30;199(3):1466–1473. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1994.1396. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- August A., Dupont B. CD28 of T lymphocytes associates with phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. Int Immunol. 1994 May;6(5):769–774. doi: 10.1093/intimm/6.5.769. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- August A., Gibson S., Kawakami Y., Kawakami T., Mills G. B., Dupont B. CD28 is associated with and induces the immediate tyrosine phosphorylation and activation of the Tec family kinase ITK/EMT in the human Jurkat leukemic T-cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Sep 27;91(20):9347–9351. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.20.9347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gmünder H., Lesslauer W. A 45-kDa human T-cell membrane glycoprotein functions in the regulation of cell proliferative responses. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Jul 2;142(1):153–160. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08263.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn W. C., Menzin E., Saito T., Germain R. N., Bierer B. E. The complete sequences of plasmids pFNeo and pMH-Neo: convenient expression vectors for high-level expression of eukaryotic genes in hematopoietic cell lines. Gene. 1993 May 30;127(2):267–268. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(93)90731-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutchcroft J. E., Bierer B. E. Activation-dependent phosphorylation of the T-lymphocyte surface receptor CD28 and associated proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Apr 12;91(8):3260–3264. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.8.3260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapeller R., Cantley L. C. Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. Bioessays. 1994 Aug;16(8):565–576. doi: 10.1002/bies.950160810. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu Y., Phillips C. A., Bjorndahl J. M., Trevillyan J. M. CD28 signal transduction: tyrosine phosphorylation and receptor association of phosphoinositide-3 kinase correlate with Ca(2+)-independent costimulatory activity. Eur J Immunol. 1994 Nov;24(11):2732–2739. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830241124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. Intracellular signaling by hydrolysis of phospholipids and activation of protein kinase C. Science. 1992 Oct 23;258(5082):607–614. doi: 10.1126/science.1411571. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pagès F., Ragueneau M., Rottapel R., Truneh A., Nunes J., Imbert J., Olive D. Binding of phosphatidylinositol-3-OH kinase to CD28 is required for T-cell signalling. Nature. 1994 May 26;369(6478):327–329. doi: 10.1038/369327a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prasad K. V., Cai Y. C., Raab M., Duckworth B., Cantley L., Shoelson S. E., Rudd C. E. T-cell antigen CD28 interacts with the lipid kinase phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase by a cytoplasmic Tyr(P)-Met-Xaa-Met motif. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Mar 29;91(7):2834–2838. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.7.2834. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reif K., Gout I., Waterfield M. D., Cantrell D. A. Divergent regulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase P85 alpha and P85 beta isoforms upon T cell activation. J Biol Chem. 1993 May 25;268(15):10780–10788. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein P. H., Fraser J. D., Weiss A. The cytoplasmic domain of CD28 is both necessary and sufficient for costimulation of interleukin-2 secretion and association with phosphatidylinositol 3'-kinase. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 May;14(5):3392–3402. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.5.3392. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Truitt K. E., Hicks C. M., Imboden J. B. Stimulation of CD28 triggers an association between CD28 and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase in Jurkat T cells. J Exp Med. 1994 Mar 1;179(3):1071–1076. doi: 10.1084/jem.179.3.1071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varticovski L., Druker B., Morrison D., Cantley L., Roberts T. The colony stimulating factor-1 receptor associates with and activates phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase. Nature. 1989 Dec 7;342(6250):699–702. doi: 10.1038/342699a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yano H., Nakanishi S., Kimura K., Hanai N., Saitoh Y., Fukui Y., Nonomura Y., Matsuda Y. Inhibition of histamine secretion by wortmannin through the blockade of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase in RBL-2H3 cells. J Biol Chem. 1993 Dec 5;268(34):25846–25856. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Willebrand M., Baier G., Couture C., Burn P., Mustelin T. Activation of phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase in Jurkat T cells depends on the presence of the p56lck tyrosine kinase. Eur J Immunol. 1994 Jan;24(1):234–238. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830240137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]