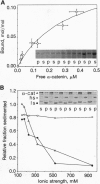
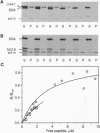
Abstract
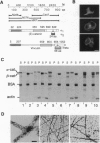
Calcium-dependent homotypic cell-cell adhesion, mediated by molecules such as E-cadherin, guides the establishment of classical epithelial cell polarity and contributes to the control of migration, growth, and differentiation. These actions involve additional proteins, including alpha- and beta-catenin (or plakoglobin) and p120, as well as linkage to the cortical actin cytoskeleton. The molecular basis for these interactions and their hierarchy of interaction remain controversial. We demonstrate a direct interaction between F-actin and alpha (E)-catenin, an activity not shared by either the cytoplasmic domain of E-cadherin or beta-catenin. Sedimentation assays and direct visualization by transmission electron microscopy reveal that alpha 1(E)-catenin binds and bundles F-actin in vitro with micromolar affinity at a catenin/G-actin monomer ratio of approximately 1:7 (mol/mol). Recombinant human beta-catenin can simultaneously bind to the alpha-catenin/actin complex but does not bind actin directly. Recombinant fragments encompassing the amino-terminal 228 residues of alpha 1(E)-catenin or the carboxyl-terminal 447 residues individually bind actin in cosedimentation assays with reduced affinity compared with the full-length protein, and neither fragment bundles actin. Except for similarities to vinculin, neither region contains sequences homologous to established actin-binding proteins. Collectively these data indicate that alpha 1 (E)-catenin is a novel actin-binding and -bundling protein and support a model in which alpha 1(E)-catenin is responsible for organizing and tethering actin filaments at the zones of E-cadherin-mediated cell-cell contact.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aberle H., Butz S., Stappert J., Weissig H., Kemler R., Hoschuetzky H. Assembly of the cadherin-catenin complex in vitro with recombinant proteins. J Cell Sci. 1994 Dec;107(Pt 12):3655–3663. doi: 10.1242/jcs.107.12.3655. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker T. A., Grossman A. D., Gross C. A. A gene regulating the heat shock response in Escherichia coli also affects proteolysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(21):6779–6783. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.21.6779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cepek K. L., Shaw S. K., Parker C. M., Russell G. J., Morrow J. S., Rimm D. L., Brenner M. B. Adhesion between epithelial cells and T lymphocytes mediated by E-cadherin and the alpha E beta 7 integrin. Nature. 1994 Nov 10;372(6502):190–193. doi: 10.1038/372190a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedlander D. R., Mège R. M., Cunningham B. A., Edelman G. M. Cell sorting-out is modulated by both the specificity and amount of different cell adhesion molecules (CAMs) expressed on cell surfaces. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(18):7043–7047. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.18.7043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gumbiner B. M., McCrea P. D. Catenins as mediators of the cytoplasmic functions of cadherins. J Cell Sci Suppl. 1993;17:155–158. doi: 10.1242/jcs.1993.supplement_17.22. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartwig J. H., Kwiatkowski D. J. Actin-binding proteins. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1991 Feb;3(1):87–97. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(91)90170-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinck L., Nelson W. J., Papkoff J. Wnt-1 modulates cell-cell adhesion in mammalian cells by stabilizing beta-catenin binding to the cell adhesion protein cadherin. J Cell Biol. 1994 Mar;124(5):729–741. doi: 10.1083/jcb.124.5.729. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinck L., Näthke I. S., Papkoff J., Nelson W. J. Beta-catenin: a common target for the regulation of cell adhesion by Wnt-1 and Src signaling pathways. Trends Biochem Sci. 1994 Dec;19(12):538–542. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(94)90057-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huxley H. E., Brown W. The low-angle x-ray diagram of vertebrate striated muscle and its behaviour during contraction and rigor. J Mol Biol. 1967 Dec 14;30(2):383–434. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(67)80046-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. P., Craig S. W. F-actin binding site masked by the intramolecular association of vinculin head and tail domains. Nature. 1995 Jan 19;373(6511):261–264. doi: 10.1038/373261a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemler R. From cadherins to catenins: cytoplasmic protein interactions and regulation of cell adhesion. Trends Genet. 1993 Sep;9(9):317–321. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(93)90250-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy S. P., Warren S. L., Forget B. G., Morrow J. S. Ankyrin binds to the 15th repetitive unit of erythroid and nonerythroid beta-spectrin. J Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;115(1):267–277. doi: 10.1083/jcb.115.1.267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebart M. C., Méjean C., Casanova D., Audemard E., Derancourt J., Roustan C., Benyamin Y. Characterization of the actin binding site on smooth muscle filamin. J Biol Chem. 1994 Feb 11;269(6):4279–4284. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsudaira P. Modular organization of actin crosslinking proteins. Trends Biochem Sci. 1991 Mar;16(3):87–92. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(91)90039-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNeill H., Ryan T. A., Smith S. J., Nelson W. J. Spatial and temporal dissection of immediate and early events following cadherin-mediated epithelial cell adhesion. J Cell Biol. 1993 Mar;120(5):1217–1226. doi: 10.1083/jcb.120.5.1217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menkel A. R., Kroemker M., Bubeck P., Ronsiek M., Nikolai G., Jockusch B. M. Characterization of an F-actin-binding domain in the cytoskeletal protein vinculin. J Cell Biol. 1994 Sep;126(5):1231–1240. doi: 10.1083/jcb.126.5.1231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mische S. M., Mooseker M. S., Morrow J. S. Erythrocyte adducin: a calmodulin-regulated actin-bundling protein that stimulates spectrin-actin binding. J Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;105(6 Pt 1):2837–2845. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.6.2837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagafuchi A., Takeichi M. Transmembrane control of cadherin-mediated cell adhesion: a 94 kDa protein functionally associated with a specific region of the cytoplasmic domain of E-cadherin. Cell Regul. 1989 Nov;1(1):37–44. doi: 10.1091/mbc.1.1.37. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagafuchi A., Takeichi M., Tsukita S. The 102 kd cadherin-associated protein: similarity to vinculin and posttranscriptional regulation of expression. Cell. 1991 May 31;65(5):849–857. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90392-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson W. J., Hammerton R. W. A membrane-cytoskeletal complex containing Na+,K+-ATPase, ankyrin, and fodrin in Madin-Darby canine kidney (MDCK) cells: implications for the biogenesis of epithelial cell polarity. J Cell Biol. 1989 Mar;108(3):893–902. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.3.893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson W. J., Hammerton R. W., Wang A. Z., Shore E. M. Involvement of the membrane-cytoskeleton in development of epithelial cell polarity. Semin Cell Biol. 1990 Oct;1(5):359–371. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozawa M., Ringwald M., Kemler R. Uvomorulin-catenin complex formation is regulated by a specific domain in the cytoplasmic region of the cell adhesion molecule. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(11):4246–4250. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.11.4246. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds A. B., Daniel J., McCrea P. D., Wheelock M. J., Wu J., Zhang Z. Identification of a new catenin: the tyrosine kinase substrate p120cas associates with E-cadherin complexes. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Dec;14(12):8333–8342. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.12.8333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rimm D. L., Kebriaei P., Morrow J. S. Molecular cloning reveals alternative splice forms of human alpha(E)-catenin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1994 Sep 30;203(3):1691–1699. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1994.2381. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rimm D. L., Morrow J. S. Molecular cloning of human E-cadherin suggests a novel subdivision of the cadherin superfamily. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1994 May 16;200(3):1754–1761. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1994.1656. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rimm D. L., Sinard J. H., Morrow J. S. Reduced alpha-catenin and E-cadherin expression in breast cancer. Lab Invest. 1995 May;72(5):506–512. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozycki M. D., Myslik J. C., Schutt C. E., Lindberg U. Structural aspects of actin-binding proteins. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1994 Feb;6(1):87–95. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(94)90121-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. B., Johnson K. S. Single-step purification of polypeptides expressed in Escherichia coli as fusions with glutathione S-transferase. Gene. 1988 Jul 15;67(1):31–40. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90005-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeichi M. Cadherin cell adhesion receptors as a morphogenetic regulator. Science. 1991 Mar 22;251(5000):1451–1455. doi: 10.1126/science.2006419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandekerckhove J., Vancompernolle K. Structural relationships of actin-binding proteins. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1992 Feb;4(1):36–42. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(92)90056-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Way M., Pope B., Weeds A. Molecular biology of actin binding proteins: evidence for a common structural domain in the F-actin binding sites of gelsolin and alpha-actinin. J Cell Sci Suppl. 1991;14:91–94. doi: 10.1242/jcs.1991.supplement_14.19. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wollner D. A., Krzeminski K. A., Nelson W. J. Remodeling the cell surface distribution of membrane proteins during the development of epithelial cell polarity. J Cell Biol. 1992 Feb;116(4):889–899. doi: 10.1083/jcb.116.4.889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]