Abstract
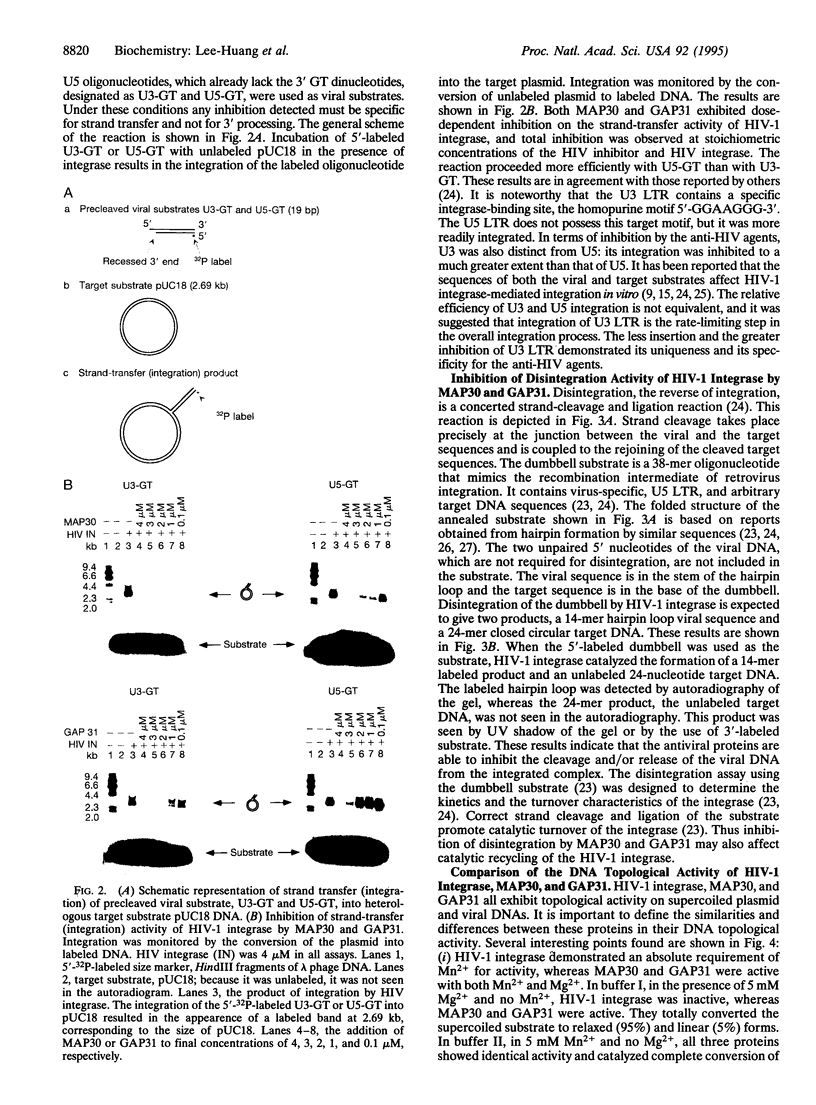
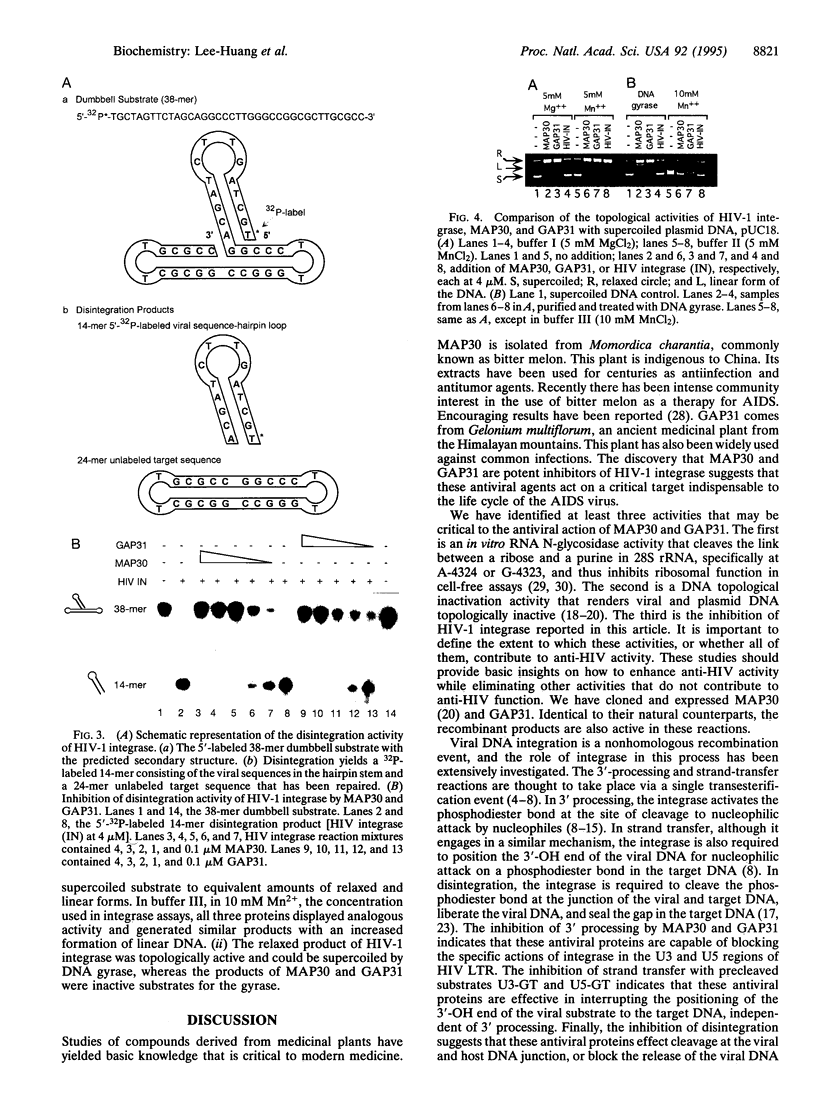
MAP30 (Momordica anti-HIV protein of 30 kDa) and GAP31 (Gelonium anti-HIV protein of 31 kDa) are anti-HIV plant proteins that we have identified, purified, and cloned from the medicinal plants Momordica charantia and Gelonium multiflorum. These antiviral agents are capable of inhibiting infection of HIV type 1 (HIV-1) in T lymphocytes and monocytes as well as replication of the virus in already-infected cells. They are not toxic to normal uninfected cells because they are unable to enter healthy cells. MAP30 and GAP31 also possess an N-glycosidase activity on 28S ribosomal RNA and a topological activity on plasmid and viral DNAs including HIV-1 long terminal repeats (LTRs). LTRs are essential sites for integration of viral DNA into the host genome by viral integrase. We therefore investigated the effect of MAP30 and GAP31 on HIV-1 integrase. We report that both of these antiviral agents exhibit dose-dependent inhibition of HIV-1 integrase. Inhibition was observed in all of the three specific reactions catalyzed by the integrase, namely, 3' processing (specific cleavage of the dinucleotide GT from the viral substrate), strand transfer (integration), and "disintegration" (the reversal of strand transfer). Inhibition was studied by using oligonucleotide substrates with sequences corresponding to the U3 and U5 regions of HIV LTR. In the presence of 20 ng of viral substrate, 50 ng of target substrate, and 4 microM integrase, total inhibition was achieved at equimolar concentrations of the integrase and the antiviral proteins, with EC50 values of about 1 microM. Integration of viral DNA into the host chromosome is a vital step in the replicative cycle of retroviruses, including the AIDS virus. The inhibition of HIV-1 integrase by MAP30 and GAP31 suggests that impediment of viral DNA integration may play a key role in the anti-HIV activity of these plant proteins.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Antao V. P., Lai S. Y., Tinoco I., Jr A thermodynamic study of unusually stable RNA and DNA hairpins. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Nov 11;19(21):5901–5905. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.21.5901. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blommers M. J., Walters J. A., Haasnoot C. A., Aelen J. M., van der Marel G. A., van Boom J. H., Hilbers C. W. Effects of base sequence on the loop folding in DNA hairpins. Biochemistry. 1989 Sep 5;28(18):7491–7498. doi: 10.1021/bi00444a049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown P. O., Bowerman B., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M. Retroviral integration: structure of the initial covalent product and its precursor, and a role for the viral IN protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(8):2525–2529. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown P. O. Integration of retroviral DNA. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1990;157:19–48. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-75218-6_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bushman F. D., Craigie R. Activities of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) integration protein in vitro: specific cleavage and integration of HIV DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 15;88(4):1339–1343. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.4.1339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bushman F. D., Engelman A., Palmer I., Wingfield P., Craigie R. Domains of the integrase protein of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 responsible for polynucleotidyl transfer and zinc binding. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 15;90(8):3428–3432. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.8.3428. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bushman F. D., Fujiwara T., Craigie R. Retroviral DNA integration directed by HIV integration protein in vitro. Science. 1990 Sep 28;249(4976):1555–1558. doi: 10.1126/science.2171144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bushman F. Targeting retroviral integration. Science. 1995 Mar 10;267(5203):1443–1444. doi: 10.1126/science.7878462. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow S. A., Brown P. O. Substrate features important for recognition and catalysis by human immunodeficiency virus type 1 integrase identified by using novel DNA substrates. J Virol. 1994 Jun;68(6):3896–3907. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.6.3896-3907.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow S. A., Vincent K. A., Ellison V., Brown P. O. Reversal of integration and DNA splicing mediated by integrase of human immunodeficiency virus. Science. 1992 Feb 7;255(5045):723–726. doi: 10.1126/science.1738845. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craigie R. Hotspots and warm spots: integration specificity of retroelements. Trends Genet. 1992 Jun;8(6):187–190. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(92)90223-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craigie R., Mizuuchi K., Bushman F. D., Engelman A. A rapid in vitro assay for HIV DNA integration. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 May 25;19(10):2729–2734. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.10.2729. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dyda F., Hickman A. B., Jenkins T. M., Engelman A., Craigie R., Davies D. R. Crystal structure of the catalytic domain of HIV-1 integrase: similarity to other polynucleotidyl transferases. Science. 1994 Dec 23;266(5193):1981–1986. doi: 10.1126/science.7801124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endo Y., Tsurugi K. RNA N-glycosidase activity of ricin A-chain. Mechanism of action of the toxic lectin ricin on eukaryotic ribosomes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 15;262(17):8128–8130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelman A., Mizuuchi K., Craigie R. HIV-1 DNA integration: mechanism of viral DNA cleavage and DNA strand transfer. Cell. 1991 Dec 20;67(6):1211–1221. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90297-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farnet C. M., Haseltine W. A. Determination of viral proteins present in the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 preintegration complex. J Virol. 1991 Apr;65(4):1910–1915. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.4.1910-1915.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foà-Tomasi L., Campadelli-Fiume G., Barbieri L., Stirpe F. Effect of ribosome-inactivating proteins on virus-infected cells. Inhibition of virus multiplication and of protein synthesis. Arch Virol. 1982;71(4):323–332. doi: 10.1007/BF01315062. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goff S. P. Genetics of retroviral integration. Annu Rev Genet. 1992;26:527–544. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.26.120192.002523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalpana G. V., Marmon S., Wang W., Crabtree G. R., Goff S. P. Binding and stimulation of HIV-1 integrase by a human homolog of yeast transcription factor SNF5. Science. 1994 Dec 23;266(5193):2002–2006. doi: 10.1126/science.7801128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirchner J., Connolly C. M., Sandmeyer S. B. Requirement of RNA polymerase III transcription factors for in vitro position-specific integration of a retroviruslike element. Science. 1995 Mar 10;267(5203):1488–1491. doi: 10.1126/science.7878467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kulkosky J., Katz R. A., Merkel G., Skalka A. M. Activities and substrate specificity of the evolutionarily conserved central domain of retroviral integrase. Virology. 1995 Jan 10;206(1):448–456. doi: 10.1016/s0042-6822(95)80060-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kulkosky J., Skalka A. M. Molecular mechanism of retroviral DNA integration. Pharmacol Ther. 1994;61(1-2):185–203. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(94)90062-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leavitt A. D., Rose R. B., Varmus H. E. Both substrate and target oligonucleotide sequences affect in vitro integration mediated by human immunodeficiency virus type 1 integrase protein produced in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Virol. 1992 Apr;66(4):2359–2368. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.4.2359-2368.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee-Huang S., Huang P. L., Chen H. C., Huang P. L., Bourinbaiar A., Huang H. I., Kung H. F. Anti-HIV and anti-tumor activities of recombinant MAP30 from bitter melon. Gene. 1995 Aug 19;161(2):151–156. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(95)00186-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee-Huang S., Huang P. L., Nara P. L., Chen H. C., Kung H. F., Huang P., Huang H. I., Huang P. L. MAP 30: a new inhibitor of HIV-1 infection and replication. FEBS Lett. 1990 Oct 15;272(1-2):12–18. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80438-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee-Huang S., Kung H. F., Chen H. C., Huang P. L., Rybak S. M., Huang P. L., Bourinbaiar A. S., Musayev F., Liaw Y. C. Crystallization and preliminary X-ray analysis of GAP 31. A protein which inhibits the life cycle of HIV-1. J Mol Biol. 1994 Jul 1;240(1):92–94. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1994.1421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee-Huang S., Kung H. F., Huang P. L., Bourinbaiar A. S., Morell J. L., Brown J. H., Huang P. L., Tsai W. P., Chen A. Y., Huang H. I. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) inhibition, DNA-binding, RNA-binding, and ribosome inactivation activities in the N-terminal segments of the plant anti-HIV protein GAP31. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Dec 6;91(25):12208–12212. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.25.12208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee-Huang S., Kung H. F., Huang P. L., Huang P. L., Li B. Q., Huang P., Huang H. I., Chen H. C. A new class of anti-HIV agents: GAP31, DAPs 30 and 32. FEBS Lett. 1991 Oct 7;291(1):139–144. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)81122-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panganiban A. T., Temin H. M. The retrovirus pol gene encodes a product required for DNA integration: identification of a retrovirus int locus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(24):7885–7889. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.24.7885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul W. E. Reexamining AIDS research priorities. Science. 1995 Feb 3;267(5198):633–636. doi: 10.1126/science.7839138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakai H., Kawamura M., Sakuragi J., Sakuragi S., Shibata R., Ishimoto A., Ono N., Ueda S., Adachi A. Integration is essential for efficient gene expression of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. J Virol. 1993 Mar;67(3):1169–1174. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.3.1169-1174.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman P. A., Dickson M. L., Fyfe J. A. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 integration protein: DNA sequence requirements for cleaving and joining reactions. J Virol. 1992 Jun;66(6):3593–3601. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.6.3593-3601.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman P. A., Fyfe J. A. Human immunodeficiency virus integration protein expressed in Escherichia coli possesses selective DNA cleaving activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(13):5119–5123. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.13.5119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent K. A., Ellison V., Chow S. A., Brown P. O. Characterization of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 integrase expressed in Escherichia coli and analysis of variants with amino-terminal mutations. J Virol. 1993 Jan;67(1):425–437. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.1.425-437.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vink C., Oude Groeneger A. M., Plasterk R. H. Identification of the catalytic and DNA-binding region of the human immunodeficiency virus type I integrase protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Mar 25;21(6):1419–1425. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.6.1419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vink C., van Gent D. C., Elgersma Y., Plasterk R. H. Human immunodeficiency virus integrase protein requires a subterminal position of its viral DNA recognition sequence for efficient cleavage. J Virol. 1991 Sep;65(9):4636–4644. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.9.4636-4644.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]