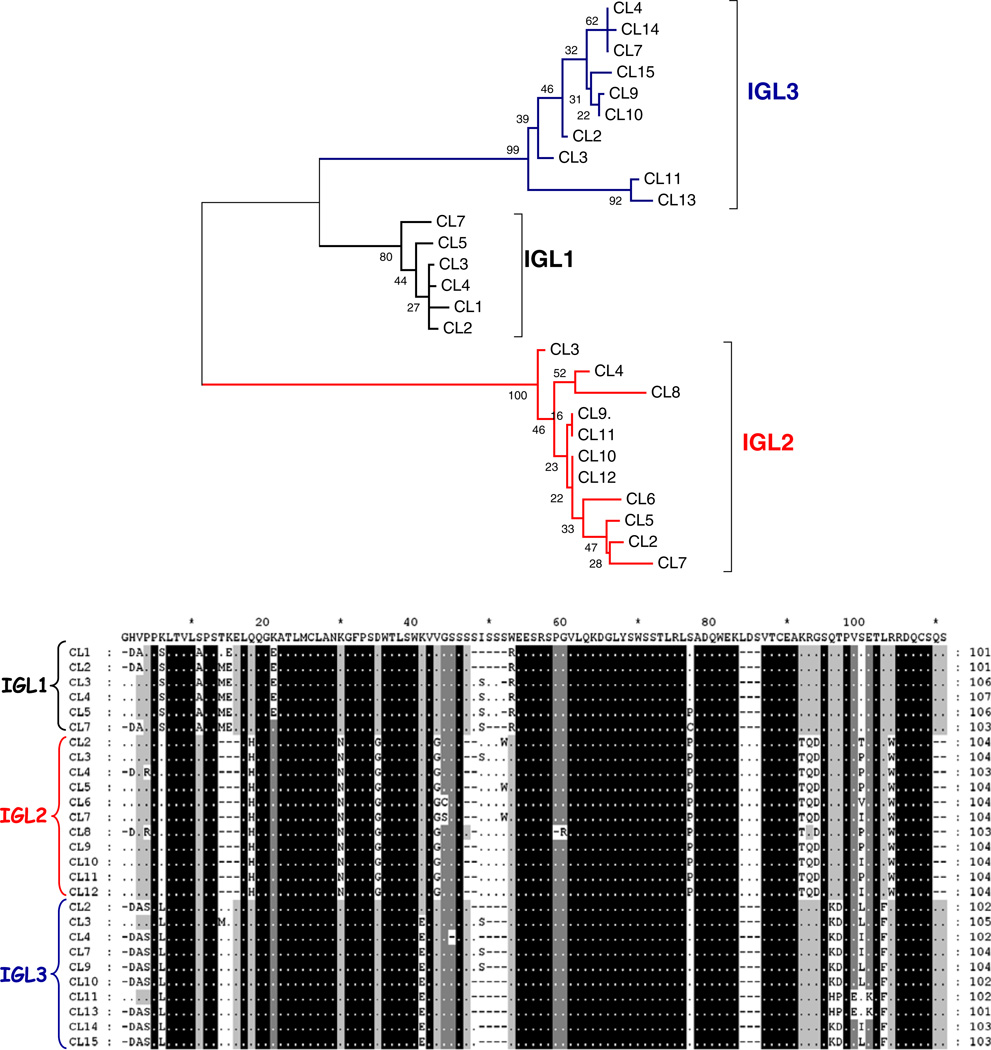
Fig. 4.
Comparisons of medaka CL exons. a An unrooted tree of CL amino acid sequences revealing CL exons clustered into groups that correspond to each locus (IGL1, IGL2, and IGL3). The phylogenetic tree was constructed using the pairwise deletion algorithm, JTT matrix, and differences by sites activated with gamma parameter 2.5. b Different medaka CL segments harbor regions of homology which could be utilized as molecular markers. Arrows indicate regions conserved in members from different CL groups. Among polymorphisms (Ser at position 14; Gln or Glu at 17; a gap at position 20; Phe at 32; Pro at position 34; Asp, Glu, Lys or Arg at position 60; Thr at 65; His at 91 and Phe at 102 position) that have also been utilized to identify the tetrapod C kappa chains (Das et al. 2008), only the Phe at position 32 appears conserved in medaka sequences