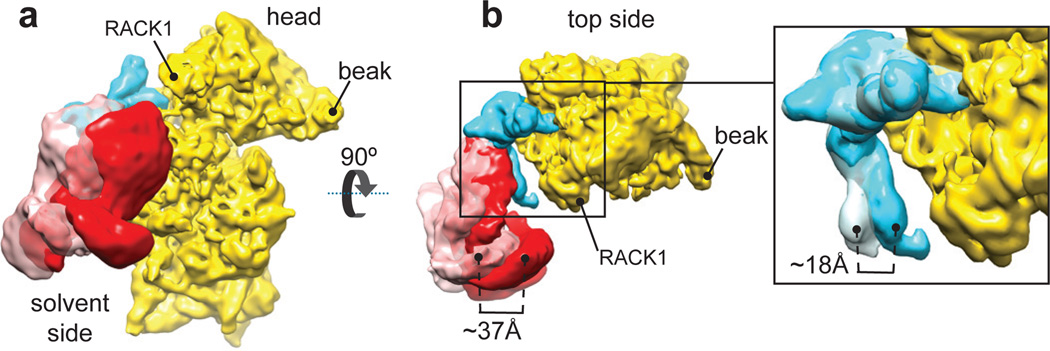
Figure 2. Different orientations of eIF3 and subdomain IIIb in the CSFV ΔII IRES•40S•DHX29 complex.
(a) Solvent-side view of eIF3 in the two most divergent orientations, as it appears in classes 4 (solid red surface) and 6 (transparent pink surface) of the CSFV ΔII-IRES•40S•DHX29•eIF3 complex, bound to the CSFV ΔII-IRES (cyan) on the 40S subunit (yellow). (b, Left). Top view of eIF3 in the two most divergent orientations, bound to the CSFV ΔII-IRES on the 40S subunit. (b, Right) blowup focused on domain IIIb of the CSFV IRES, showing the extent of its reorientation. The brackets display the magnitude of the movement of eIF3 and of IRES domain IIIb in the two most divergent orientations.