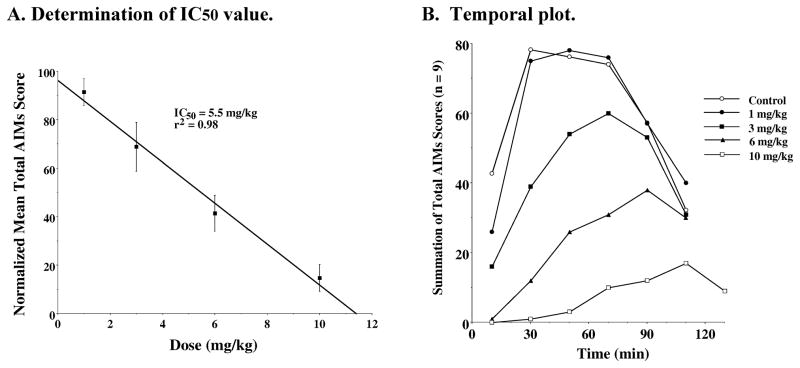
Figure 10. Dose Response Dependence of WC 44 for the Attenuation of Total AIM scores.
A. Determination of IC50 value: Unilaterally lesioned rats were injected (i.p.) with varying doses of WC 44 (0 to 10 mg/kg) followed immediately with a constant dose of L-dopa and benserazide (8 mg/kg each). The percent of the mean total AIMs score ± S.E.M. (n ≥ 9) relative to vehicle controls as a function the dose of WC 44 is shown. The mean values ± S.E.M. for the normalized total AIMs values as a function of WC 44 concentrations are as follows: a) 1 mg/kg, 91.4 ± 5.5, b) 3.0 mg/kg, 68.8 ± 10.1, c) 6 mg/kg, 41.4 ± 7.4 and d) 10 mg/kg, 14.6 ± 5.5. The calculated IC50 value for this data was found to be 5.5 mg/kg using a linear regression analysis (r2 = 0.98). B. Temporal plot: The variation in the total AIMs score as a function of time is shown using zero time pretreatment with an i.p. injection of WC 44 at 10 mg/kg (□), 6 mg/kg (▲), 3 mg/kg (■), 1 mg/kg (●) or vehicle control (❍). Animals were also injected (i.p.) with 8 mg/kg L-dopa and benserazide. Each point is the summation of total AIMs score for a total of 9 animals at each observation time point for each dose of WC 44. The temporal plot for the vehicle control curve is the mean value for all four experiments.