Abstract
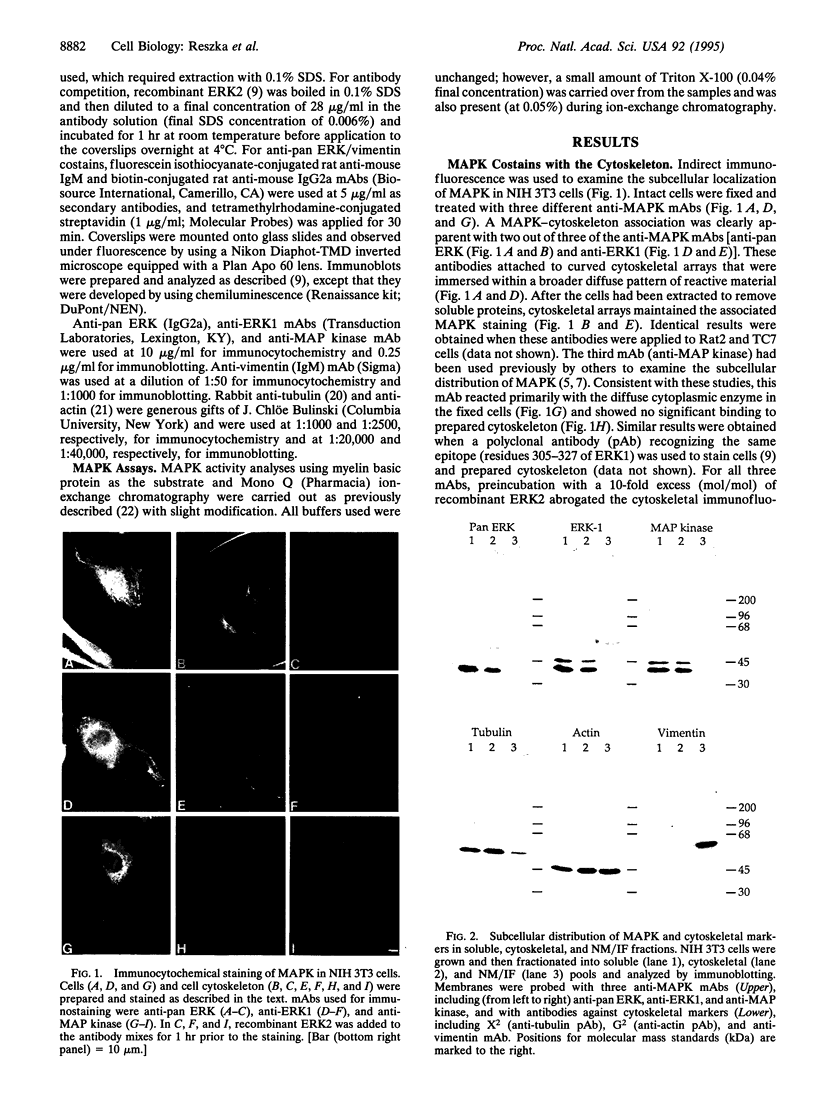
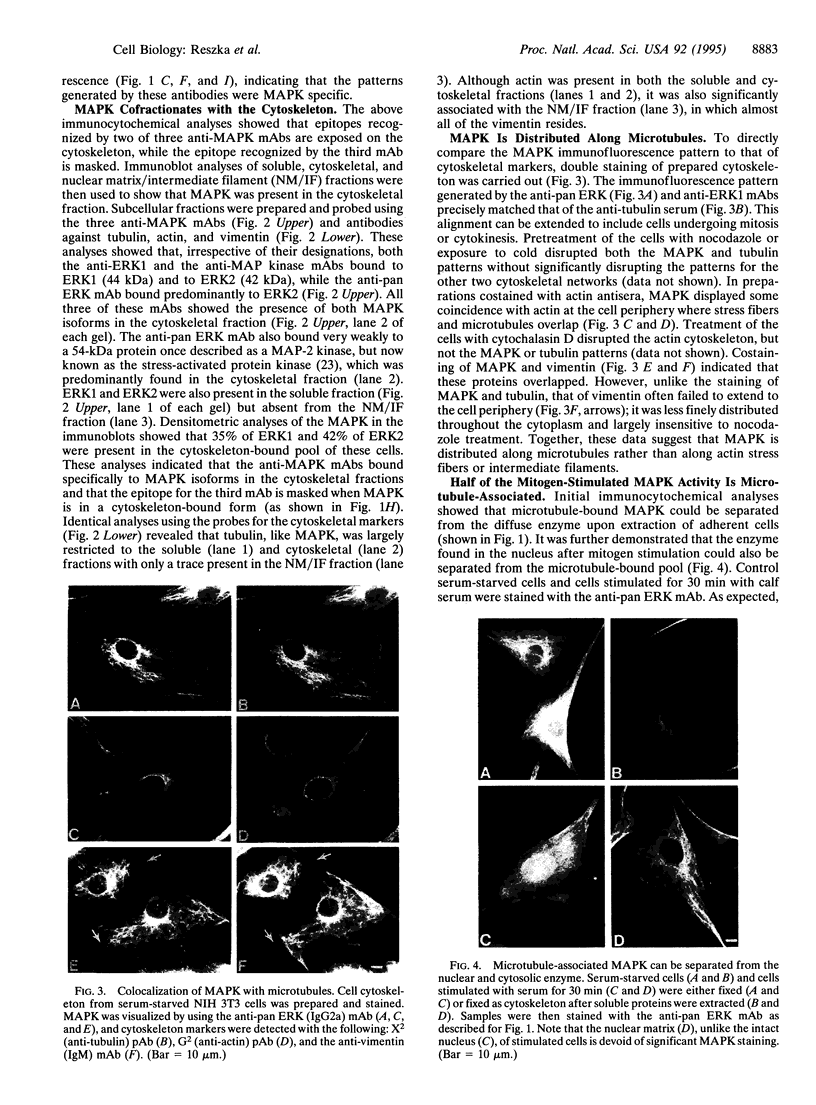
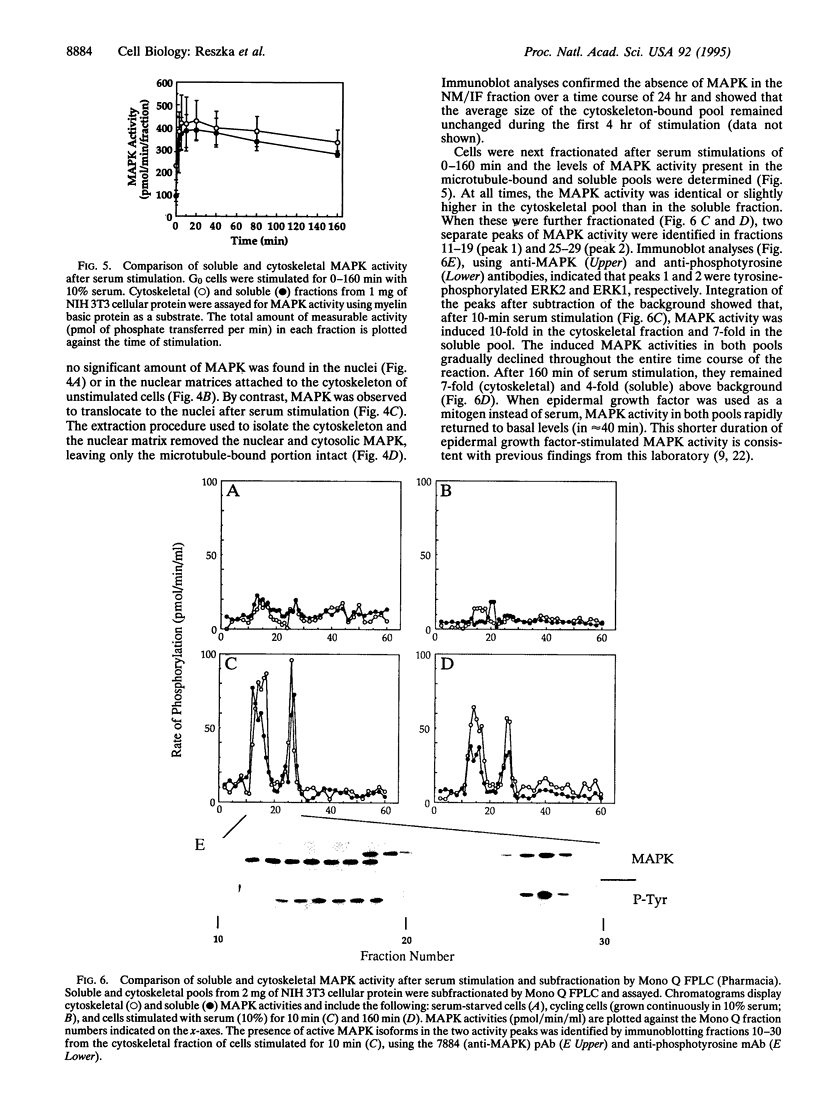
Using indirect immunofluorescence microscopy and biochemical techniques, we have determined that approximately one-third of the total mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) is associated with the microtubule cytoskeleton in NIH 3T3 mouse fibroblasts. This population of enzyme can be separated from the soluble form that is found distributed throughout the cytosol and is also present in the nucleus after mitogen stimulation. The microtubule-associated enzyme pool constitutes half of all detectable MAPK activity after mitogenic stimulation. These findings extend the known in vivo associations of MAPK with microtubules to include the entire microtubule cytoskeleton of proliferating cells, and they suggest that a direct association of MAPK with microtubules may be in part responsible for the observed correlations between MAPK activities and cytoskeletal alteration.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahn N. G., Weiel J. E., Chan C. P., Krebs E. G. Identification of multiple epidermal growth factor-stimulated protein serine/threonine kinases from Swiss 3T3 cells. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 15;265(20):11487–11494. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blenis J. Signal transduction via the MAP kinases: proceed at your own RSK. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 1;90(13):5889–5892. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.13.5889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunet A., Pagès G., Pouysségur J. Constitutively active mutants of MAP kinase kinase (MEK1) induce growth factor-relaxation and oncogenicity when expressed in fibroblasts. Oncogene. 1994 Nov;9(11):3379–3387. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Q., Kinch M. S., Lin T. H., Burridge K., Juliano R. L. Integrin-mediated cell adhesion activates mitogen-activated protein kinases. J Biol Chem. 1994 Oct 28;269(43):26602–26605. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen R. H., Sarnecki C., Blenis J. Nuclear localization and regulation of erk- and rsk-encoded protein kinases. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Mar;12(3):915–927. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.3.915. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Childs T. J., Watson M. H., Sanghera J. S., Campbell D. L., Pelech S. L., Mak A. S. Phosphorylation of smooth muscle caldesmon by mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase and expression of MAP kinase in differentiated smooth muscle cells. J Biol Chem. 1992 Nov 15;267(32):22853–22859. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connolly J. A., Kalnins V. I., Cleveland D. W., Kirschner M. W. Immunoflourescent staining of cytoplasmic and spindle microtubules in mouse fibroblasts with antibody to tau protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jun;74(6):2437–2440. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.6.2437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowley S., Paterson H., Kemp P., Marshall C. J. Activation of MAP kinase kinase is necessary and sufficient for PC12 differentiation and for transformation of NIH 3T3 cells. Cell. 1994 Jun 17;77(6):841–852. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90133-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis R. J. The mitogen-activated protein kinase signal transduction pathway. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jul 15;268(20):14553–14556. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drechsel D. N., Hyman A. A., Cobb M. H., Kirschner M. W. Modulation of the dynamic instability of tubulin assembly by the microtubule-associated protein tau. Mol Biol Cell. 1992 Oct;3(10):1141–1154. doi: 10.1091/mbc.3.10.1141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiore R. S., Bayer V. E., Pelech S. L., Posada J., Cooper J. A., Baraban J. M. p42 mitogen-activated protein kinase in brain: prominent localization in neuronal cell bodies and dendrites. Neuroscience. 1993 Jul;55(2):463–472. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(93)90516-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez F. A., Seth A., Raden D. L., Bowman D. S., Fay F. S., Davis R. J. Serum-induced translocation of mitogen-activated protein kinase to the cell surface ruffling membrane and the nucleus. J Cell Biol. 1993 Sep;122(5):1089–1101. doi: 10.1083/jcb.122.5.1089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grinstein S., Furuya W. Chemoattractant-induced tyrosine phosphorylation and activation of microtubule-associated protein kinase in human neutrophils. J Biol Chem. 1992 Sep 5;267(25):18122–18125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gundersen G. G., Kalnoski M. H., Bulinski J. C. Distinct populations of microtubules: tyrosinated and nontyrosinated alpha tubulin are distributed differently in vivo. Cell. 1984 Oct;38(3):779–789. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90273-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta S. K., Gallego C., Johnson G. L., Heasley L. E. MAP kinase is constitutively activated in gip2 and src transformed rat 1a fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 25;267(12):7987–7990. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoshi M., Ohta K., Gotoh Y., Mori A., Murofushi H., Sakai H., Nishida E. Mitogen-activated-protein-kinase-catalyzed phosphorylation of microtubule-associated proteins, microtubule-associated protein 2 and microtubule-associated protein 4, induces an alteration in their function. Eur J Biochem. 1992 Jan 15;203(1-2):43–52. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb19825.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaken S., Leach K., Klauck T. Association of type 3 protein kinase C with focal contacts in rat embryo fibroblasts. J Cell Biol. 1989 Aug;109(2):697–704. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.2.697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jameson L., Caplow M. Modification of microtubule steady-state dynamics by phosphorylation of the microtubule-associated proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3413–3417. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyriakis J. M., Banerjee P., Nikolakaki E., Dai T., Rubie E. A., Ahmad M. F., Avruch J., Woodgett J. R. The stress-activated protein kinase subfamily of c-Jun kinases. Nature. 1994 May 12;369(6476):156–160. doi: 10.1038/369156a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenormand P., Sardet C., Pagès G., L'Allemain G., Brunet A., Pouysségur J. Growth factors induce nuclear translocation of MAP kinases (p42mapk and p44mapk) but not of their activator MAP kinase kinase (p45mapkk) in fibroblasts. J Cell Biol. 1993 Sep;122(5):1079–1088. doi: 10.1083/jcb.122.5.1079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandelkow E. M., Drewes G., Biernat J., Gustke N., Van Lint J., Vandenheede J. R., Mandelkow E. Glycogen synthase kinase-3 and the Alzheimer-like state of microtubule-associated protein tau. FEBS Lett. 1992 Dec 21;314(3):315–321. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)81496-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noguchi T., Metz R., Chen L., Mattéi M. G., Carrasco D., Bravo R. Structure, mapping, and expression of erp, a growth factor-inducible gene encoding a nontransmembrane protein tyrosine phosphatase, and effect of ERP on cell growth. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Sep;13(9):5195–5205. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.9.5195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn M., Weber K. The display of microtubules in transformed cells. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):561–571. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90257-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otey C. A., Kalnoski M. H., Lessard J. L., Bulinski J. C. Immunolocalization of the gamma isoform of nonmuscle actin in cultured cells. J Cell Biol. 1986 May;102(5):1726–1737. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.5.1726. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray L. B., Sturgill T. W. Rapid stimulation by insulin of a serine/threonine kinase in 3T3-L1 adipocytes that phosphorylates microtubule-associated protein 2 in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(6):1502–1506. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.6.1502. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sano M., Kitajima S. Activation of microtubule-associated protein kinase in PC12D cells in response to both fibroblast growth factor and epidermal growth factor and concomitant stimulation of the outgrowth of neurites. J Neurochem. 1992 Mar;58(3):837–844. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1992.tb09333.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlaepfer D. D., Hanks S. K., Hunter T., van der Geer P. Integrin-mediated signal transduction linked to Ras pathway by GRB2 binding to focal adhesion kinase. Nature. 1994 Dec 22;372(6508):786–791. doi: 10.1038/372786a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seger R., Seger D., Reszka A. A., Munar E. S., Eldar-Finkelman H., Dobrowolska G., Jensen A. M., Campbell J. S., Fischer E. H., Krebs E. G. Overexpression of mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase (MAPKK) and its mutants in NIH 3T3 cells. Evidence that MAPKK involvement in cellular proliferation is regulated by phosphorylation of serine residues in its kinase subdomains VII and VIII. J Biol Chem. 1994 Oct 14;269(41):25699–25709. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seth A., Gonzalez F. A., Gupta S., Raden D. L., Davis R. J. Signal transduction within the nucleus by mitogen-activated protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1992 Dec 5;267(34):24796–24804. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun H., Charles C. H., Lau L. F., Tonks N. K. MKP-1 (3CH134), an immediate early gene product, is a dual specificity phosphatase that dephosphorylates MAP kinase in vivo. Cell. 1993 Nov 5;75(3):487–493. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90383-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verlhac M. H., Kubiak J. Z., Clarke H. J., Maro B. Microtubule and chromatin behavior follow MAP kinase activity but not MPF activity during meiosis in mouse oocytes. Development. 1994 Apr;120(4):1017–1025. doi: 10.1242/dev.120.4.1017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verlhac M. H., de Pennart H., Maro B., Cobb M. H., Clarke H. J. MAP kinase becomes stably activated at metaphase and is associated with microtubule-organizing centers during meiotic maturation of mouse oocytes. Dev Biol. 1993 Aug;158(2):330–340. doi: 10.1006/dbio.1993.1192. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zheng C. F., Guan K. L. Cytoplasmic localization of the mitogen-activated protein kinase activator MEK. J Biol Chem. 1994 Aug 5;269(31):19947–19952. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]








