Abstract
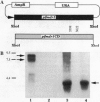
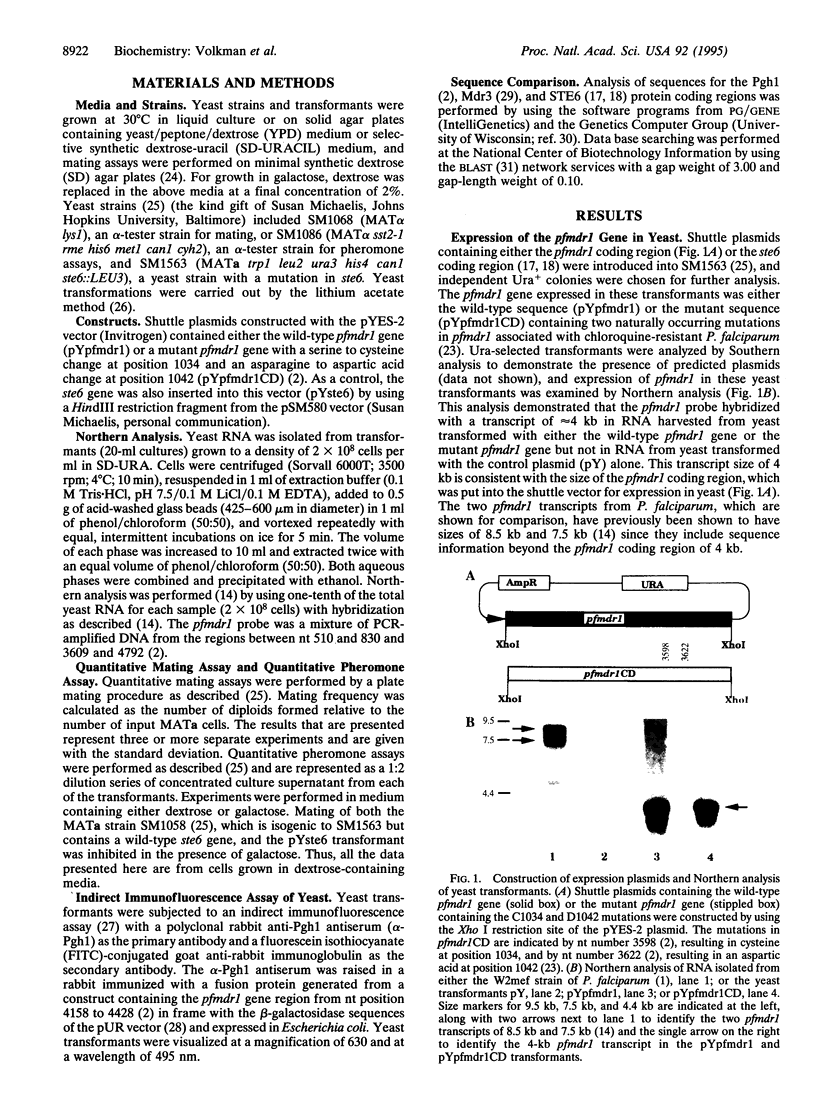
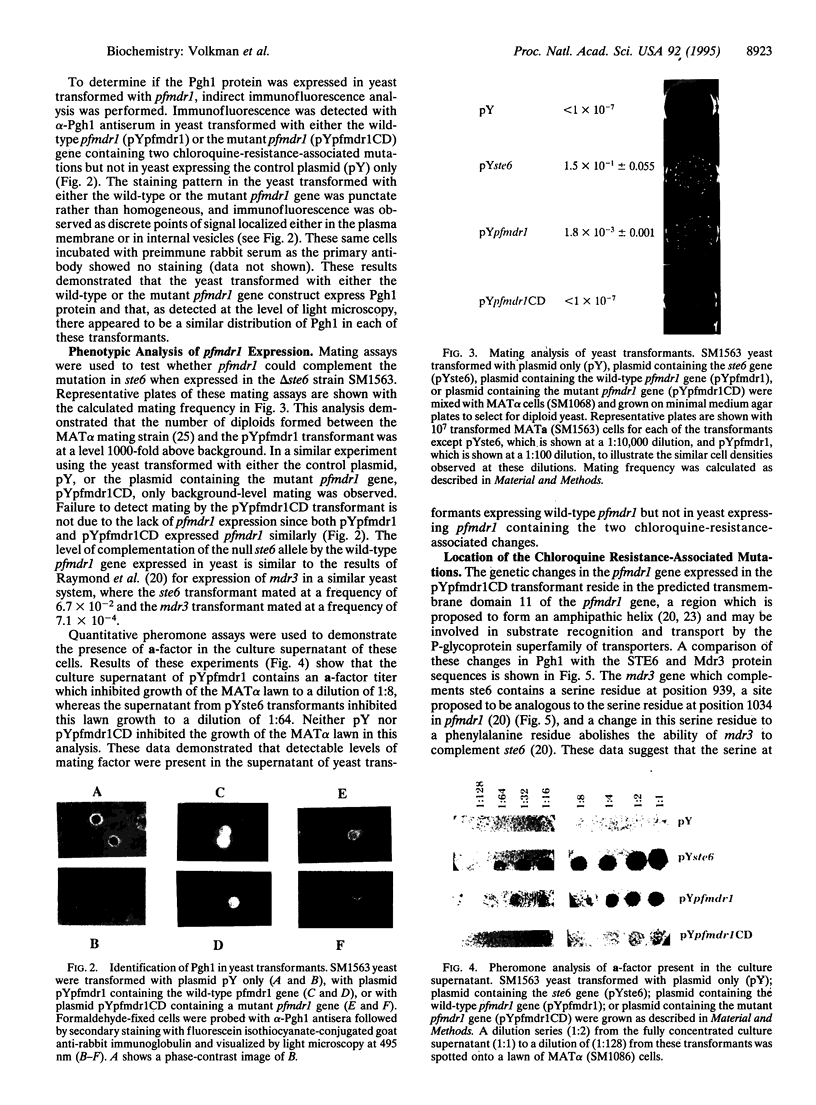
The pfmdr1 gene has been associated with a drug-resistant phenotype in Plasmodium falciparum, and overexpression of pfmdr1 has been associated with mefloquine- and halofantrine-resistant parasites, but little is known about the functional role of pfmdr1 in this process. Here, we demonstrate that the pfmdr1 gene expressed in a heterologous yeast system functions as a transport molecule and complements a mutation in ste6, a gene which encodes a mating pheromone a-factor export molecule. In addition, the pfmdr1 gene containing two mutations which are associated with naturally occurring chloroquine resistance abolishes this mating phenotype, suggesting that these genetic polymorphisms alter this transport function. Our results support the functional role of pfmdr1 as a transport molecule in the mediation of drug resistance and provide an assay system to address the nature of this transport function.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altschul S. F., Gish W., Miller W., Myers E. W., Lipman D. J. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990 Oct 5;215(3):403–410. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80360-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnes D. A., Foote S. J., Galatis D., Kemp D. J., Cowman A. F. Selection for high-level chloroquine resistance results in deamplification of the pfmdr1 gene and increased sensitivity to mefloquine in Plasmodium falciparum. EMBO J. 1992 Aug;11(8):3067–3075. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05378.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berkower C., Michaelis S. Mutational analysis of the yeast a-factor transporter STE6, a member of the ATP binding cassette (ABC) protein superfamily. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(12):3777–3785. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04947.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bray P. G., Boulter M. K., Ritchie G. Y., Howells R. E., Ward S. A. Relationship of global chloroquine transport and reversal of resistance in Plasmodium falciparum. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1994 Jan;63(1):87–94. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(94)90011-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bray P. G., Howells R. E., Ritchie G. Y., Ward S. A. Rapid chloroquine efflux phenotype in both chloroquine-sensitive and chloroquine-resistant Plasmodium falciparum. A correlation of chloroquine sensitivity with energy-dependent drug accumulation. Biochem Pharmacol. 1992 Oct 6;44(7):1317–1324. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(92)90532-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowman A. F., Galatis D., Thompson J. K. Selection for mefloquine resistance in Plasmodium falciparum is linked to amplification of the pfmdr1 gene and cross-resistance to halofantrine and quinine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Feb 1;91(3):1143–1147. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.3.1143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowman A. F., Karcz S., Galatis D., Culvenor J. G. A P-glycoprotein homologue of Plasmodium falciparum is localized on the digestive vacuole. J Cell Biol. 1991 Jun;113(5):1033–1042. doi: 10.1083/jcb.113.5.1033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devault A., Gros P. Two members of the mouse mdr gene family confer multidrug resistance with overlapping but distinct drug specificities. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;10(4):1652–1663. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.4.1652. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dhir R., Grizzuti K., Kajiji S., Gros P. Modulatory effects on substrate specificity of independent mutations at the serine939/941 position in predicted transmembrane domain 11 of P-glycoproteins. Biochemistry. 1993 Sep 14;32(36):9492–9499. doi: 10.1021/bi00087a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foote S. J., Cowman A. F. The mode of action and the mechanism of resistance to antimalarial drugs. Acta Trop. 1994 Mar;56(2-3):157–171. doi: 10.1016/0001-706x(94)90061-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foote S. J., Kyle D. E., Martin R. K., Oduola A. M., Forsyth K., Kemp D. J., Cowman A. F. Several alleles of the multidrug-resistance gene are closely linked to chloroquine resistance in Plasmodium falciparum. Nature. 1990 May 17;345(6272):255–258. doi: 10.1038/345255a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foote S. J., Thompson J. K., Cowman A. F., Kemp D. J. Amplification of the multidrug resistance gene in some chloroquine-resistant isolates of P. falciparum. Cell. 1989 Jun 16;57(6):921–930. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90330-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gietz D., St Jean A., Woods R. A., Schiestl R. H. Improved method for high efficiency transformation of intact yeast cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Mar 25;20(6):1425–1425. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.6.1425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottesman M. M., Pastan I. Biochemistry of multidrug resistance mediated by the multidrug transporter. Annu Rev Biochem. 1993;62:385–427. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.62.070193.002125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gros P., Dhir R., Croop J., Talbot F. A single amino acid substitution strongly modulates the activity and substrate specificity of the mouse mdr1 and mdr3 drug efflux pumps. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 15;88(16):7289–7293. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.16.7289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins C. F. ABC transporters: from microorganisms to man. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1992;8:67–113. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.08.110192.000435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins C. F., Gottesman M. M. Is the multidrug transporter a flippase? Trends Biochem Sci. 1992 Jan;17(1):18–21. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(92)90419-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kajiji S., Talbot F., Grizzuti K., Van Dyke-Phillips V., Agresti M., Safa A. R., Gros P. Functional analysis of P-glycoprotein mutants identifies predicted transmembrane domain 11 as a putative drug binding site. Biochemistry. 1993 Apr 27;32(16):4185–4194. doi: 10.1021/bi00067a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krogstad D. J., Gluzman I. Y., Kyle D. E., Oduola A. M., Martin S. K., Milhous W. K., Schlesinger P. H. Efflux of chloroquine from Plasmodium falciparum: mechanism of chloroquine resistance. Science. 1987 Nov 27;238(4831):1283–1285. doi: 10.1126/science.3317830. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuchler K., Sterne R. E., Thorner J. Saccharomyces cerevisiae STE6 gene product: a novel pathway for protein export in eukaryotic cells. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 20;8(13):3973–3984. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08580.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuchler K., Thorner J. Functional expression of human mdr1 in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 15;89(6):2302–2306. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.6.2302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kölling R., Hollenberg C. P. The ABC-transporter Ste6 accumulates in the plasma membrane in a ubiquitinated form in endocytosis mutants. EMBO J. 1994 Jul 15;13(14):3261–3271. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06627.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin S. K., Oduola A. M., Milhous W. K. Reversal of chloroquine resistance in Plasmodium falciparum by verapamil. Science. 1987 Feb 20;235(4791):899–901. doi: 10.1126/science.3544220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGrath J. P., Varshavsky A. The yeast STE6 gene encodes a homologue of the mammalian multidrug resistance P-glycoprotein. Nature. 1989 Aug 3;340(6232):400–404. doi: 10.1038/340400a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michaelis S. STE6, the yeast a-factor transporter. Semin Cell Biol. 1993 Feb;4(1):17–27. doi: 10.1006/scel.1993.1003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peel S. A., Merritt S. C., Handy J., Baric R. S. Derivation of highly mefloquine-resistant lines from Plasmodium falciparum in vitro. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1993 Mar;48(3):385–397. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1993.48.385. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pringle J. R., Adams A. E., Drubin D. G., Haarer B. K. Immunofluorescence methods for yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1991;194:565–602. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)94043-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raymond M., Gros P., Whiteway M., Thomas D. Y. Functional complementation of yeast ste6 by a mammalian multidrug resistance mdr gene. Science. 1992 Apr 10;256(5054):232–234. doi: 10.1126/science.1348873. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raymond M., Ruetz S., Thomas D. Y., Gros P. Functional expression of P-glycoprotein in Saccharomyces cerevisiae confers cellular resistance to the immunosuppressive and antifungal agent FK520. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Jan;14(1):277–286. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.1.277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rüther U., Müller-Hill B. Easy identification of cDNA clones. EMBO J. 1983;2(10):1791–1794. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01659.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman F. Getting started with yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1991;194:3–21. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)94004-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teem J. L., Berger H. A., Ostedgaard L. S., Rich D. P., Tsui L. C., Welsh M. J. Identification of revertants for the cystic fibrosis delta F508 mutation using STE6-CFTR chimeras in yeast. Cell. 1993 Apr 23;73(2):335–346. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90233-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volkman S. K., Wilson C. M., Wirth D. F. Stage-specific transcripts of the Plasmodium falciparum pfmdr 1 gene. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1993 Feb;57(2):203–211. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(93)90196-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wellems T. E., Panton L. J., Gluzman I. Y., do Rosario V. E., Gwadz R. W., Walker-Jonah A., Krogstad D. J. Chloroquine resistance not linked to mdr-like genes in a Plasmodium falciparum cross. Nature. 1990 May 17;345(6272):253–255. doi: 10.1038/345253a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson C. M., Serrano A. E., Wasley A., Bogenschutz M. P., Shankar A. H., Wirth D. F. Amplification of a gene related to mammalian mdr genes in drug-resistant Plasmodium falciparum. Science. 1989 Jun 9;244(4909):1184–1186. doi: 10.1126/science.2658061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson C. M., Volkman S. K., Thaithong S., Martin R. K., Kyle D. E., Milhous W. K., Wirth D. F. Amplification of pfmdr 1 associated with mefloquine and halofantrine resistance in Plasmodium falciparum from Thailand. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1993 Jan;57(1):151–160. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(93)90252-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Es H. H., Karcz S., Chu F., Cowman A. F., Vidal S., Gros P., Schurr E. Expression of the plasmodial pfmdr1 gene in mammalian cells is associated with increased susceptibility to chloroquine. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Apr;14(4):2419–2428. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.4.2419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Es H. H., Renkema H., Aerts H., Schurr E. Enhanced lysosomal acidification leads to increased chloroquine accumulation in CHO cells expressing the pfmdr1 gene. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1994 Dec;68(2):209–219. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(94)90166-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]