Abstract
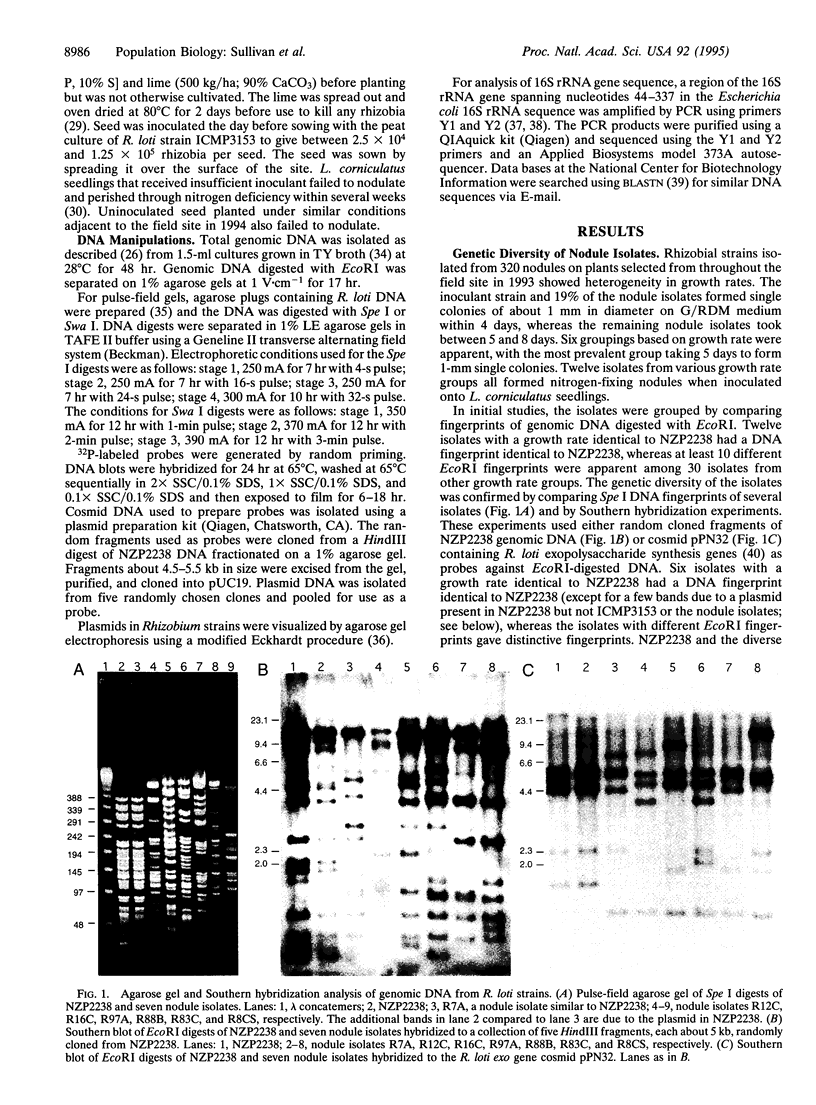
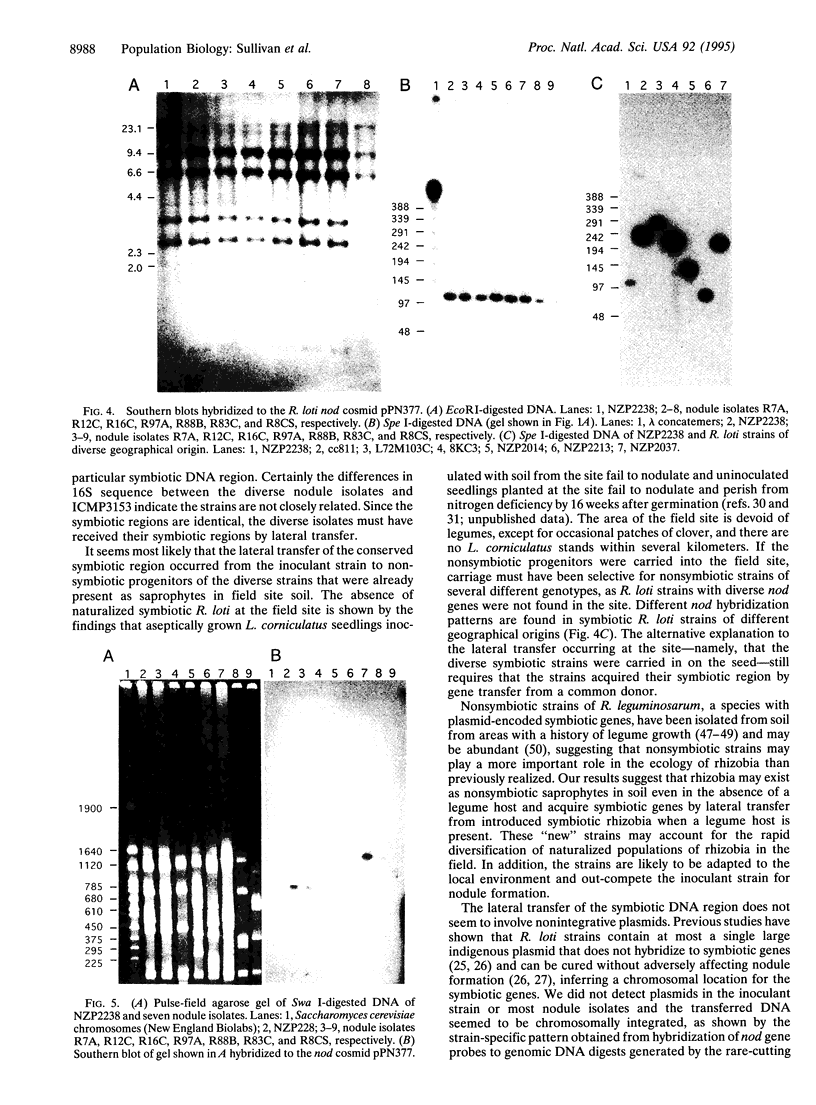
Rhizobia were isolated from nodules off a stand of Lotus corniculatus established with a single inoculant strain, ICMP3153, 7 years earlier in an area devoid of naturalized Rhizobium loti. The isolates showed diversity in growth rate, Spe I fingerprint of genomic DNA, and hybridization pattern to genomic DNA probes. The 19% of isolates that grew at the same rate as strain ICMP3153 were the only isolates that had the same fingerprint as strain ICMP3153. Sequencing of part of the 16S rRNA gene of several diverse isolates confirmed that they were not derived from the inoculant strain. Nevertheless, all non-ICMP3153 strains gave EcoRI and Spe I hybridization patterns identical to ICMP3153 when hybridized to nodulation gene cosmids. Hybridization of digests generated by the very rare cutting enzyme Swa I revealed that the symbiotic DNA region (at least 105 kb) was chromosomally integrated in the strains. The results suggest that the diverse strains arose by transfer of chromosomal symbiotic genes from ICMP3153 to nonsymbiotic rhizobia in the environment.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altschul S. F., Gish W., Miller W., Myers E. W., Lipman D. J. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990 Oct 5;215(3):403–410. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80360-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beringer J. E. R factor transfer in Rhizobium leguminosarum. J Gen Microbiol. 1974 Sep;84(1):188–198. doi: 10.1099/00221287-84-1-188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borges K. M., Bergquist P. L. A rapid method for preparation of bacterial chromosomal DNA in agarose plugs using Thermus Rt41A proteinase. Biotechniques. 1992 Feb;12(2):222–223. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chua K. Y., Pankhurst C. E., Macdonald P. E., Hopcroft D. H., Jarvis B. D., Scott D. B. Isolation and characterization of transposon Tn5-induced symbiotic mutants of Rhizobium loti. J Bacteriol. 1985 Apr;162(1):335–343. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.1.335-343.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dowling D. N., Broughton W. J. Competition for nodulation of legumes. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1986;40:131–157. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.40.100186.001023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eardly B. D., Materon L. A., Smith N. H., Johnson D. A., Rumbaugh M. D., Selander R. K. Genetic structure of natural populations of the nitrogen-fixing bacterium Rhizobium meliloti. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Jan;56(1):187–194. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.1.187-194.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eardly B. D., Young J. P., Selander R. K. Phylogenetic position of Rhizobium sp. strain Or 191, a symbiont of both Medicago sativa and Phaseolus vulgaris, based on partial sequences of the 16S rRNA and nifH genes. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 Jun;58(6):1809–1815. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.6.1809-1815.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hotter G. S., Scott D. B. Exopolysaccharide mutants of Rhizobium loti are fully effective on a determinate nodulating host but are ineffective on an indeterminate nodulating host. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jan;173(2):851–859. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.2.851-859.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarvis B. D., Ward L. J., Slade E. A. Expression by Soil Bacteria of Nodulation Genes from Rhizobium leguminosarum biovar trifolii. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Jun;55(6):1426–1434. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.6.1426-1434.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamicker B. J., Brill W. J. Methods To Alter the Recovery and Nodule Location of Bradyrhizobium japonicum Inoculant Strains on Field-Grown Soybeans. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Aug;53(8):1737–1742. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.8.1737-1742.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kündig C., Hennecke H., Göttfert M. Correlated physical and genetic map of the Bradyrhizobium japonicum 110 genome. J Bacteriol. 1993 Feb;175(3):613–622. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.3.613-622.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pankhurst C. E., Broughton W. J., Wieneke U. Transfer of an indigenous plasmid of Rhizobium loti to other rhizobia and Agrobacterium tumefaciens. J Gen Microbiol. 1983 Aug;129(8):2535–2543. doi: 10.1099/00221287-129-8-2535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinero D., Martinez E., Selander R. K. Genetic diversity and relationships among isolates of Rhizobium leguminosarum biovar phaseoli. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Nov;54(11):2825–2832. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.11.2825-2832.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ronson C. W., Nixon B. T., Albright L. M., Ausubel F. M. Rhizobium meliloti ntrA (rpoN) gene is required for diverse metabolic functions. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jun;169(6):2424–2431. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.6.2424-2431.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schofield P. R., Gibson A. H., Dudman W. F., Watson J. M. Evidence for genetic exchange and recombination of Rhizobium symbiotic plasmids in a soil population. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Dec;53(12):2942–2947. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.12.2942-2947.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segovia L., Piñero D., Palacios R., Martínez-Romero E. Genetic structure of a soil population of nonsymbiotic Rhizobium leguminosarum. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Feb;57(2):426–433. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.2.426-433.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. M., Smith N. H., O'Rourke M., Spratt B. G. How clonal are bacteria? Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 May 15;90(10):4384–4388. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.10.4384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Souza V., Eguiarte L., Avila G., Cappello R., Gallardo C., Montoya J., Piñero D. Genetic Structure of Rhizobium etli biovar phaseoli Associated with Wild and Cultivated Bean Plants (Phaseolus vulgaris and Phaseolus coccineus) in Morelos, Mexico. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1994 Apr;60(4):1260–1268. doi: 10.1128/aem.60.4.1260-1268.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Souza V., Nguyen T. T., Hudson R. R., Piñero D., Lenski R. E. Hierarchical analysis of linkage disequilibrium in Rhizobium populations: evidence for sex? Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Sep 1;89(17):8389–8393. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.17.8389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strain S. R., Leung K., Whittam T. S., de Bruijn F. J., Bottomley P. J. Genetic Structure of Rhizobium leguminosarum biovar trifolii and viciae Populations Found in Two Oregon Soils under Different Plant Communities. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1994 Aug;60(8):2772–2778. doi: 10.1128/aem.60.8.2772-2778.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Triplett E. W., Sadowsky M. J. Genetics of competition for nodulation of legumes. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1992;46:399–428. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.46.100192.002151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willems A., Collins M. D. Phylogenetic analysis of rhizobia and agrobacteria based on 16S rRNA gene sequences. Int J Syst Bacteriol. 1993 Apr;43(2):305–313. doi: 10.1099/00207713-43-2-305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woese C. R. Bacterial evolution. Microbiol Rev. 1987 Jun;51(2):221–271. doi: 10.1128/mr.51.2.221-271.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanagi M., Yamasato K. Phylogenetic analysis of the family Rhizobiaceae and related bacteria by sequencing of 16S rRNA gene using PCR and DNA sequencer. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1993 Feb 15;107(1):115–120. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1993.tb06014.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young J. P., Demetriou L., Apte R. G. Rhizobium Population Genetics: Enzyme Polymorphism in Rhizobium leguminosarum from Plants and Soil in a Pea Crop. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Feb;53(2):397–402. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.2.397-402.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young J. P., Downer H. L., Eardly B. D. Phylogeny of the phototrophic rhizobium strain BTAi1 by polymerase chain reaction-based sequencing of a 16S rRNA gene segment. J Bacteriol. 1991 Apr;173(7):2271–2277. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.7.2271-2277.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]