Abstract
Background: Nowadays, the most conventional method to quantify physiological amino acids consists in ion exchange chromatography (IEC) followed by post-column ninhydrin derivatization and UV detection at two wavelengths. Unfortunately, the technique presents some drawbacks such as long run time, large sample volume, and specific costs associated to the maintenance of a dedicated instrument. Therefore, we aimed to switch towards a mass spectrometry approach.
Methods: We have tested the aTRAQ kit for Amino Acid Analysis of Physiological Fluids (AB Sciex), affording the selective quantification of about 40 amino acids, and present here the results of our assessments.
Results: Outlined accuracy profiles for each amino acid demonstrated very reliable data. A good linearity was observed from 1 to 1,000 μmol/L. Results comparison with IEC showed a right concordance. Reference intervals established were very similar to those obtained by IEC and patients suffering from inborn error of metabolism have been readily identified.
Conclusions: The present approach offers a valid alternative to the IEC method, with several advantages: lower sample volume, run time reduction, and improved specificity. However, the aTRAQ method requires minute data reviewing, expending the overall time of procedure. Finally, financial and practical considerations of both techniques have to be counterbalanced before engaging any transition.
Electronic supplementary material: The online version of this chapter (doi:10.1007/8904_2013_265) contains supplementary material, which is available to authorized users.
Introduction
Amino acid disorders represent an important field in the wide classification of inborn errors of metabolism (WHO 2010). Such conditions result from a defect in the metabolic pathways of amino acids, leading to the accumulation of the corresponding metabolite in plasma, urine, cerebrospinal, amniotic fluid, or other biological matrix.
Besides the conventional 20 proteinogenic amino acids, several nonstandard amino acids hold critical physiological functions. Some of them are the result of posttranslational protein modification (i.e., hydroxyproline), which is an essential process for the function or regulation of proteins, while others are intermediates of metabolic pathways (i.e., urea cycle intermediates) and they also act as neurotransmitters (i.e., GABA). Acknowledging the central role of amino acids in protein synthesis and metabolism homeostasis, profiling of these markers has became a noticeable tool in the identification and follow-up of primary disorders. The biochemical findings that may be present in amino acid disorders include metabolic acidosis, hyperammonemia, hypoglycemia with appropriate or increased ketosis, multi-system disorder, developmental delay, encephalopathy, coma, or death.
Amino acids are not only associated with inborn errors of metabolism, they are also sensitive markers of the nutritional state and of the function of various organs such as the liver, the kidneys, the intestine, or the muscles. These dysfunctions generate subtle alterations in amino acid concentrations; therefore, accuracy of the amino acid analysis is a crucial matter in order to interpret these changes.
In those contexts’ workup, the most conventional method for amino acid quantification consists in ion exchange chromatography (IEC) followed by post-column ninhydrin derivatization and UV detection at two wavelengths. Actually, amino acid analyzers have been used since more than 50 years in biochemical laboratories and still are considered as a reference method (Dietzen et al. 2008; Duran 2008). Notwithstanding, the technology suffers some drawbacks; chromatographic separation lasts about 150 min and requires high sample volumes (>100 μL). In addition, running analysis on dedicated instruments, requiring expensive maintenance costs, depicts another leading concern.
Considering the disadvantages of IEC technique and owning a triple quadrupole mass spectrometer for the newborn screening of inborn errors of metabolism, we wanted to evaluate a mass spectrometry approach. Nowadays, identification and quantification of amino acids by mass spectrometry are rather uncommon in clinical laboratories. Only a few methods have already been developed and validated and are based either on native (Piraud et al. 2003, 2005; Waterval et al. 2009) or on derivatized (Dettmer et al. 2012; Dietzen et al. 2008; Harder et al. 2011; Held et al. 2011) metabolites identification.
Based on this perception, we have tested the aTRAQ kit for Amino Acid Analysis of Physiological Fluids (AB Sciex), affording the selective quantification of about 40 amino acids. We report here the results of our assessment, based on plasma, urine, and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) samples.
Material and Methods
Chemicals
aTRAQ kit for Amino Acid Analysis of Physiological Fluids was provided by AB Sciex. Mixes of amino acid standards (reference numbers A6407 and A6282), glutamine and sodium chloride (NaCl) were obtained from Sigma. Bovine serum albumin (BSA) was purchased at Roche.
Samples
Five-point calibration curves were prepared by diluting amino acid standard mixes and glutamine in 75 g/L BSA, isotonized with 0.9 g/L NaCl. Final calibration concentrations were the following: 1,000, 250, 100, 50, and 10 μmol/L for all amino acids, except for cystine whose concentrations were 500, 125, 50, 25, and 5 μmol/L.
Validation samples were prepared in the same way with final concentrations at 1,000, 200, 75, 20, 5, and 1 μmol/L for all amino acids, except for cystine whose concentrations were 500, 100, 37.5, 10, 2.5, and 0.5 μmol/L. Samples from the ERNDIM Amino Acids Scheme have also been used for method validation; target concentrations used corresponded to the consensus mean concentrations of all participating laboratories.
Plasma, urine, and CSF samples were gathered from normal individuals.
Sample Derivatization
Conceptually, amino groups are labeled with tags of varying isotope patterns. The label consists of a reporter group (with the masses m/z 113 or 121), a neutral linker, and an amino-reactive group (N–hydroxysuccinimide ester). The 121-labeling reagent is used to derivatize the amino acids in the sample, whereas the 113-labeling reagent is employed to provide a 113-labeled standard mix containing 42 analytes for absolute quantification.
Briefly, sample (40 μL) proteins were precipitated with 10 % sulfosalicylic acid (10 μL) containing 400 μmol/L norleucine. After vortexing and centrifugation, the supernatant (10 μL) was mixed with 40 μL labeling buffer containing norvaline. At this moment, part of the mixture (20 μL) can be set aside if allo-isoleucine quantification is necessary. To 10 μL of this reaction mix, 5 μL of isopropanol diluted aTRAQ Δ8-reagent was added. After 30-min incubation at room temperature, 5 μL of hydroxylamine was added and homogenized mixture was incubated 15 min at room temperature. Then, 32 μL of reconstituted aTRAQ Internal Standard solution was added to the reaction mixture. If allo-isoleucine testing is mandated, 5 μL of underivatized mix, saved from the second step, is added. The specimen is then partly concentrated under nitrogen for 15 min. Finally, half-evaporated samples were diluted 10 times with milli-Q water before injection.
Allo-isoleucine coelutes with isoleucine when labeled with the aTRAQ Δ8-reagent. Therefore, for confirmation and follow-up of maple urine syrup disease (MSUD) patients, allo-isoleucine is quantified in its underivatized form, which is then chromatographically well separated from isoleucine.
Separation and Detection
Derivatized samples (1 μL) were introduced into a TQ5500 tandem mass spectrometer (AB Sciex) using a Prominence AR HPLC system (Shimadzu).
Tagged amino acids were chromatographically separated on the AB Sciex C18 column at 50 °C. The column dimension was 15 cm long, with a 4.6 mm inner diameter. A binary gradient of water (mobile phase A) and methanol (mobile phase B), both containing 0.1 % formic and 0.01 % heptafluorobutyric acids, was flowing through the system at 0.8 mL/min. The percentage of mobile phase B was gradually increased from 2 % to 90 % in 13 min, followed by a 5-min re-equilibration step.
Acquisition in the mass spectrometer was achieved by multiple reaction monitoring (MRM) using the scheduled MRM algorithm (See Supplemental Data Table 1). This latter functionality eliminates the requirement of multi-period experiments by monitoring each transition only across its expected elution time. MRM transitions are then organized automatically, optimizing dwell time, cycle time, and detection window.
Data recording and treatment were performed with the v.1.6 Analyst software (AB Sciex).
Quantification
As recommended by manufacturer, quantification was achieved dividing the analyte area by the IS area and then multiplying by the IS concentration. To evaluate the performance of such calibration protocol, we compared concentrations estimated by this internal quantification method with results calculated by a five-point external calibration curve.
Analytical Validation
The method was validated using accuracy profiles based on β-expectation tolerance intervals for the total error measurement and assessing the measurements’ uncertainty (Gustavo Gonzales and Angeles Herrador 2006; Hubert et al. 2004; Hubert et al. 2007a, b; Rozet et al. 2006). For this purpose, five measurements of each validation samples have been analyzed in five independent series, and before each run, a calibration curve was tested twice. Computing of validation data was ensured using the v3.0 Enoval validation software (http://www.arlenda.com).
Method Comparison
Comparison was done between the MS method and the ion exchange chromatography (IEC) amino acid analyzer. Five independent measurements of 4 ERNDIM Amino Acids Scheme samples, covering the main part of the physiological range, have been carried out. The ERNDIM “IEC with Ninhydrin and one Internal Standard” method has been considered for this purpose, and the IEC target result used for method comparison is therefore the consensus mean of more than 100 laboratories.
Slope and intercept were estimated by Passing and Bablok regression with Medcalc v12.1 software.
Reference Ranges
Normal population values have been set up for plasma, urine, and CSF on several age categories: 0–2 years, 2–12 years, and >12 years. Intervals, proceeding from about 20 to 30 samples in each age class, have been generated using nonparametric analysis and represent the central 90 % (5–95 %) of the populations evaluated.
Clinical Evaluation
Samples (urine and plasma) from patients with confirmed inborn error of metabolism have been tested. The assessment included urines from homozygote cystinuria, Non ketotic hyperglycinemia, tyrosinemia I, and cystathioninuria. Plasmas from treated phenylketonuria, maple syrup urine disease, and ornithinemia patients have also been tested.
Results
Internal Versus External Calibration
To compare the internal quantification versus the external five-point calibration curve, each back-calculated concentration was normalized, in percentage, against its expected value. These recovery results were then assayed with a one-sample t-test to evaluate whether the average of observations differs significantly from 100 %.
External calibration gave slightly better recovery results for most amino acids. This difference turns out to be very significant for the upper concentration (1,000 μmol/L). Therefore, all further results have been back calculated against this external calibration curve, which was reanalyzed twice before each run. Additionally, opting for this quantification way helps to decrease the batch-to-batch variability (Held et al. 2011).
Method Capacities
An approach using accuracy profiles based on tolerance intervals for the total error measurement, including both bias and standard deviation for intermediate precision, was applied to demonstrate the method capability. Method is considered as valid within the range for which the accuracy profile is fully included inside the accuracy acceptance limits, set at ±30 % for upper concentrations (>75 μmol/L) and at ±50 % for lower concentrations (≤75 μmol/L). The β-expectation tolerance interval, which describes a region where, on average, a proportion β of future measurements will fall, was fixed at 5 %. This proceeding gives the guarantee that each further measurement of unknown samples will be included within the tolerance limits at the fixed level and thus within the acceptance limits.
Accuracy profiles have been generated for all amino acids, and a profile example is provided in Fig. 1. Based on these profiles, the lower limit of quantitation (LLOQ) is defined as the smallest quantity of each amino acid that fits within acceptance range (Fig. 2 and Supplemental Data Table 2).
Fig. 1.
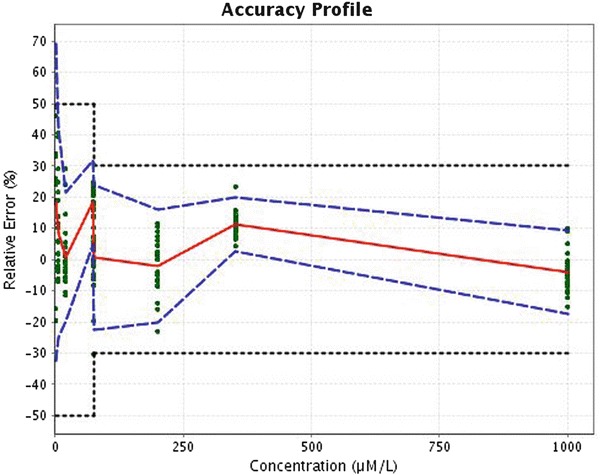
Accuracy profile of phenylalanine. Plain red line is the relative bias, dashed blue lines are the β-expectation tolerance limit (β = 5 %), and dotted black curves represent the acceptance limit (±50 % for the concentration smaller than 75 μmol/L and ±30 % for concentration equal or greater than this value). The dots represent the relative back-calculated concentrations of the validation standards and are plotted according to their targeted concentration
Fig. 2.
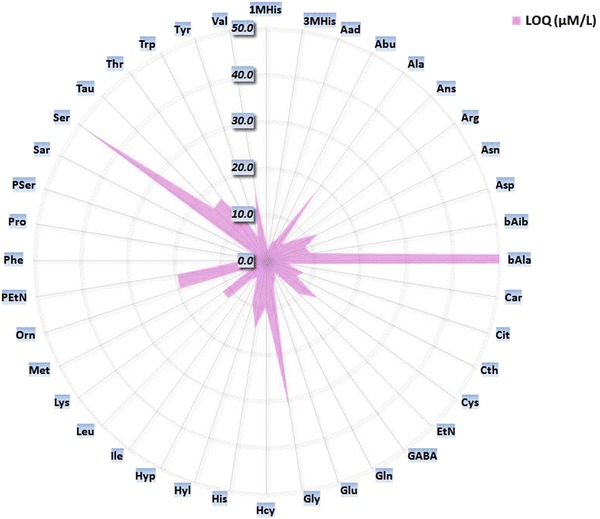
Radar chart of calculated LLOQ, based on the accuracy profile approach
Accuracy profile can be used as a visual decision tool to assess the validity of an analytical method. However, as for every graphical representation, this visual interpretation is partly subjective. Therefore, different “desirability” indexes have been considered: dosing range index, precision index, and trueness index (Rozet et al. 2007). The dosing range index is defined as the ratio between the length of interval in which the method is considered as valid and the length of the interval between the highest and lowest concentration levels investigated during the validation. The precision index corresponds to the ratio between the area defined within the acceptance limits and the limits of β-expectation tolerance interval, and the area bounded by the upper and lower acceptance limits, for which the method is considered as valid. The trueness index is defined as 1 minus the ratio between the sum of the square of the observed bias at each concentration level and the sum of the square of the maximum tolerated bias at each concentration level, for which the method is considered as valid. All these three indexes vary from 0 to 1; the better is the method for a criteria, the closer to one is the corresponding index (See Supplemental Data Statistic) (Rozet et al. 2007).
A synthetic radar chart of each index has been built for each amino acid (Fig. 3). Dosing range of bAla, Pser, and Sar are narrower than for other amino acids. For Sar, this can be explained by the saturation of the instrument detector at higher concentrations (1,000 μmol/L). Nevertheless, clinical impact of such phenomenon is reduced; physiological concentrations of the analyte are far below. Additionally, intra- and inter-run coefficients of variation are presented under a usual way in Table 1. Finally, bAla, EtN, and PSer show the worst precision index with highest coefficient of variation.
Fig. 3.
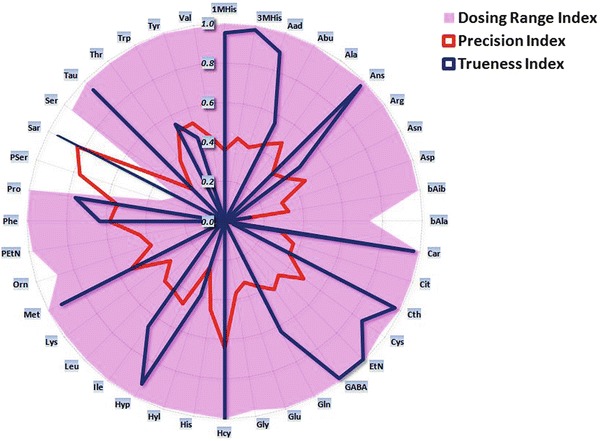
Radar chart of each amino acid indexes. Indexes vary from 0 to 1; the better is the method for a criteria, the closer to one is the corresponding index. Compared to the other analytes, dosing range for Asp, Glu, Pser, and Sar are reduced, the instrument detector saturating at higher concentrations
Table 1.
Intra- and inter-run variation for two levels of concentration
| Concentration level – 20 μmol/L | Concentration level – 200 μmol/L | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cystine – 10 μmol/L | Cystine – 100 μmol/L | |||
| Intra-run coefficient of variation (%) | Inter-run coefficient of variation (%) | Intra-run coefficient of variation (%) | Inter-run coefficient of variation (%) | |
| 1MHis | 10.55 | 11.43 | 7.88 | 7.99 |
| 3MHis | 9.11 | 9.36 | 8.54 | 8.54 |
| Aad | 10.93 | 11.17 | 8.16 | 8.16 |
| Abu | 8.85 | 11.48 | 8.41 | 9.30 |
| Ala | 10.66 | 11.84 | 9.42 | 9.42 |
| Ans | 10.78 | 11.47 | 7.70 | 8.31 |
| Arg | 11.45 | 13.11 | 9.05 | 9.40 |
| Asn | 10.01 | 10.01 | 7.27 | 7.43 |
| Asp | 18.72 | 18.72 | 6.96 | 6.96 |
| bAib | 11.46 | 12.19 | 7.84 | 7.99 |
| bAla | 26.84 | 41.24 | 8.38 | 9.02 |
| Car | 12.31 | 12.31 | 8.70 | 8.70 |
| Cit | 9.78 | 10.26 | 9.14 | 9.64 |
| Cth | 14.54 | 15.55 | 8.91 | 9.44 |
| Cys | 11.81 | 12.94 | 6.71 | 9.00 |
| EtN | 7.99 | 15.81 | 16.21 | 16.21 |
| GABA | 9.82 | 11.32 | 7.19 | 7.19 |
| Gln | 10.83 | 10.85 | 7.42 | 7.42 |
| Glu | 12.49 | 13.06 | 7.15 | 7.68 |
| Gly | 9.85 | 18.13 | 10.31 | 10.31 |
| Hcy | 5.02 | 38.29 | 17.16 | 17.16 |
| His | 9.61 | 9.61 | 10.92 | 10.92 |
| Hyl | 14.30 | 14.30 | 10.07 | 10.36 |
| Hyp | 12.14 | 13.05 | 3.93 | 4.39 |
| Ile | 12.55 | 12.55 | 8.67 | 8.72 |
| Leu | 15.02 | 15.02 | 7.79 | 7.85 |
| Lys | 10.73 | 11.99 | 9.00 | 9.00 |
| Met | 9.49 | 10.67 | 8.09 | 8.09 |
| Orn | 14.47 | 16.49 | 7.61 | 7.72 |
| PEtN | 11.51 | 13.92 | 7.09 | 7.25 |
| Phe | 9.28 | 9.71 | 8.57 | 8.57 |
| Pro | 8.84 | 9.24 | 5.82 | 5.82 |
| PSer | 28.71 | 28.71 | 10.50 | 10.50 |
| Sar | 10.53 | 11.25 | 8.25 | 8.25 |
| Ser | 16.16 | 18.77 | 9.06 | 9.06 |
| Tau | 7.23 | 14.42 | 3.53 | 8.36 |
| Thr | 9.52 | 10.24 | 7.15 | 8.47 |
| Trp | 7.87 | 9.59 | 7.54 | 7.78 |
| Tyr | 12.04 | 14.47 | 10.76 | 10.76 |
| Val | 10.51 | 10.91 | 9.27 | 9.41 |
MS Versus IEC
Results of method comparison are presented in Table 2. For all amino acids tested, slopes and intercepts are very close to 1 and 0, respectively.
Table 2.
Method comparison: IEC versus MS method. Slope and intercept were calculated by means of a nonparametric Passing and Bablok regression
| Slope | Slope 95 % CIa | Intercept | Intercept 95 % CIa | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3MHis | 1.01 | 0.938 to 1.362 | 3.19 | −3.863 to 5.464 |
| Abu | 1.17 | 1.105 to 1.252 | −2.94 | −5.209 to 0.857 |
| Ala | 1.05 | 1.016 to 1.085 | −7.32 | −20.1 to 2.336 |
| Arg | 1.06 | 1.045 to 1.083 | −0.92 | −5.514 to 1.503 |
| Asn | 1.19 | 1.151 to 1.279 | 5.70 | −5.066 to 9.417 |
| Asp | 0.99 | 0.927 to 1.071 | 1.06 | −2.051 to 2.432 |
| Cit | 0.96 | 0.938 to 1.008 | 1.88 | 0.449 to 3.583 |
| Cth | 1.12 | 1.005 to 1.156 | 0.55 | −0.428 to 1.388 |
| Cys | 1.08 | 1.011 to 1.167 | −3.07 | −6.464 to 0.94 |
| Gln | 0.92 | 0.803 to 1.083 | 3.72 | −33.91 to 9.132 |
| Glu | 1.08 | 1.041 to 1.132 | 3.38 | −2.056 to 6.867 |
| Gly | 0.98 | 0.928 to 1.058 | 1.28 | −15.09 to 1.45 |
| His | 1.01 | 0.98 to 1.071 | −0.12 | −5.099 to 2.776 |
| Hpro | 1.14 | 1.097 to 1.223 | −0.39 | −4.912 to 2.063 |
| Ile | 1.09 | 0.995 to 1.188 | 1.19 | −2.022 to 5.713 |
| Leu | 1.11 | 1.001 to 1.094 | 1.16 | −5.852 to 6.11 |
| Lys | 1.02 | 1.001 to 1.094 | −4.87 | −11.99 to 0.824 |
| Met | 1.08 | 1.072 to 1.173 | 0.20 | −5.297 to 0.879 |
| Orn | 1.03 | 0.986 to 1.097 | −5.23 | −12.84 to 0.285 |
| Phe | 1.18 | 1.051 to 1.294 | −4.46 | −10.86 to 3.971 |
| Pro | 1.18 | 1.141 to 1.226 | 6.21 | 0.419 to 9.499 |
| Ser | 1.15 | 1.087 to 1.246 | 1.06 | −5.565 to 4.681 |
| Tau | 1.08 | 1.022 to 1.154 | −10.95 | −21.82 to 2.961 |
| Thr | 1.01 | 0.965 to 1.105 | 4.28 | −4.631 to 9.206 |
| Trp | 1.02 | 0.928 to 1.124 | 3.40 | −5.842 to 2.067 |
| Tyr | 1.00 | 0.927 to 1.05 | 0.64 | −3.441 to 7.371 |
| Val | 1.07 | 1.035 to 1.117 | −3.31 | −22.83 to 4.374 |
a95 % CI = Confidence interval at 95 % for slope and intercept, respectively
Normal Population Values
Reference intervals have been established on plasma, urine, and CSF samples collected from normal controls (Table 3). For each, ranges were defined to cover the central 90 % of the measured values, and for plasma and urine matrices, three age classes have been considered.
Table 3.
Amino acid reference ranges on plasma, urine, and CSF matrices
| Plasma | Urine | CSF | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0–2 years | 2–12 years | >= 12 years | 0–2 years | 2–12 years | >= 12 years | / | |
| μmol/L | μmol/L | μmol/L | mM/M Creat. | mM/M Creat. | mM/M Creat. | μmol/L | |
| 1MHis | 0.1–3.7 | 0.2–15.7 | 0.5–14 | 2.7–18.9 | 2.7–208 | 3.6–137 | 0–0.9 |
| 3MHis | 1.4–5.7 | 1.3–7.1 | 2.4–8 | 7.4–37.5 | 12.5–35.4 | 10.2–25.7 | 0.1–0.4 |
| Aad | 0.6–1.8 | 0.3–1.6 | 0.4–2 | 0.9–46.3 | 1.4–13.3 | 0.7–7.4 | 0–0.3 |
| Abu | 3.1–16.7 | 7.6–28 | 4.4–36.3 | 0.4–7.4 | 0.6–4.9 | 0.4–2.4 | 1.3–4 |
| Ala | 122–426 | 111–518 | 153–592 | 32.1–235 | 16.8–129 | 7.4–53.8 | 19–32.5 |
| Ans | 0–0.9 | 0–1.1 | 0–0.7 | 0–8.3 | 0–41.8 | 0–19.2 | 0–12 |
| Arg | 14.4–164 | 18.4–102 | 11.2–128 | 0.7–43.3 | 6.1–61.7 | 1.1–11.6 | 10.8–27 |
| Asaa | 0.3–7.8 | 0–13.7 | 0–12.5 | 0–18.2 | 1.1–4.2 | 0.5–3 | 0.4–6.7 |
| Asn | 27.1–123 | 28.4–102 | 22.7–115 | 3.3–136 | 8.4–48 | 3.5–36.6 | 6.6–12.1 |
| Asp | 6.1–69.4 | 4.6–60.3 | 4.4–65 | 0.8–20.3 | 0.3–9.4 | 0.3–4.6 | 1–11.6 |
| bAib | 0.8–31.8 | 0.5–3.3 | 0.3–2.9 | 3–98.1 | 2.6–107.2 | 1.5–27.6 | 0–0.2 |
| bAla | 17.2–67.3 | 15.8–49.9 | 18.5–60.7 | 1.5–116 | 0.3–15.9 | 0.2–13.7 | 17–41.4 |
| Car | 0–2.2 | 0–0.4 | 0–0.5 | 1.3–62 | 2–43.1 | 0.2–12.1 | 0–0.1 |
| Cit | 7.9–33.6 | 8.4–40.7 | 13.5–63.3 | 0.3–18.5 | 0.3–2.1 | 0.1–1.7 | 1.9–20 |
| Cth | 0.3–29.9 | 0.1–1.2 | 0.1–1.5 | 0.7–13 | 0.3–5 | 0.3–4.4 | 0.1–0.5 |
| Cys | 6.4–124 | 0.9–39.1 | 7.3–58.5 | 2.5–91.7 | 2.1–9.8 | 1.7–10 | 0–1 |
| EtN | 3.8–46.6 | 4.1–21.9 | 3.8–24.6 | 12.3–149 | 21.7–69.3 | 15.1–34.8 | 4.7–41.3 |
| GABA | 0.2–57.7 | 0.2–4.7 | 0.2–6.5 | 0.2–5.3 | 0.2–1.3 | 0.1–0.7 | 0.2–2.1 |
| Gln | 336–691 | 300–688 | 296–884 | 3–357 | 32–134 | 15–90 | 374–836 |
| Glu | 38–353 | 35–288 | 41.9–236 | 2.5–42.6 | 1.3–37.5 | 0.9–10.7 | 0.9–12 |
| Gly | 113–458 | 164.7–402 | 94.9–463 | 79.2–1,057 | 66–417 | 43–360 | 9.3–34 |
| Hcita | 0.1–0.7 | 0–0.8 | 0.1–0.7 | 0.3–29.4 | 1–8.1 | 0.8–3.9 | 0.1–0.4 |
| Hcy | 0–26.3 | 0–0.4 | 0–0.3 | 0–1.8 | 0–0.2 | 0–0.2 | 0–0.5 |
| His | 35–117 | 34.2–114 | 35.4–136.2 | 46–379 | 34.8–290 | 18–125 | 9.2–25.3 |
| Hyl | 0.1–110 | 0.1–86.4 | 0–103.2 | 1.1–40.3 | 0.5–11 | 0.1–1.7 | 0.1–2 |
| Hyp | 10.8–76.2 | 8.7–31.9 | 4.8–34.6 | 1.4–233 | 0.4–4.2 | 0.1–2.3 | 0.3–1.8 |
| Ile | 30.3–129 | 24.7–94.7 | 28.3–167.8 | 1–12 | 1–4.2 | 0.2–2.6 | 3.2–12.9 |
| Leu | 44.9–198 | 44.5–158 | 61.2–203.8 | 0.6–21.1 | 2.1–9.9 | 0.3–6.6 | 5–10 |
| Lys | 64.5–375 | 75.5–228 | 105–253 | 2–274 | 4.7–105 | 1.9–23.5 | 6.3–28.6 |
| Met | 9.4–67.6 | 9.3–31 | 9.6–44.4 | 0.2–5.1 | 0.5–2.3 | 0–1.3 | 1.5–4.2 |
| Orn | 19.9–181 | 23.4–165 | 42.8–186 | 1.5–52.8 | 0.9–5.4 | 0.6–2.6 | 4.5–10 |
| PEtN | 0–6 | 0–3.8 | 0.2–2.3 | 1.8–28.5 | 2.5–22.1 | 0.6–4.9 | 0.8–5.6 |
| Phe | 25.5–131 | 27.7–95.8 | 23.5–104 | 1.4–38.2 | 4.2–19 | 1.9–10.1 | 6.3–13.5 |
| Pro | 74.9–276 | 89.2–286 | 85.8–327.8 | 1.9–97.2 | 0.6–9.5 | 0.3–5 | 1.4–5.3 |
| PSer | 0–0.4 | 0–0.4 | 0–0.4 | 0–1.2 | 0–0.3 | 0–0.2 | 0–0.3 |
| Sar | 0.4–3 | 0.8–4.7 | 0.5–2.7 | 0.2–12.4 | 0–1.2 | 0–1.3 | 0–0.2 |
| Ser | 62–253 | 61.8–230 | 53.7–216 | 5.3–302 | 26.4–90.6 | 11.1–52.6 | 25.3–67.1 |
| Tau | 34.8–309 | 34.9–266 | 30.3–223 | 6–546 | 14.6–349 | 4.5–140 | 4.5–10.1 |
| Thr | 41.7–252 | 51–167 | 58.3–206 | 4.8–171 | 7.5–40.5 | 4.5–35 | 15.3–36.1 |
| Trp | 17.1–87.3 | 15.1–58.4 | 24.6–85.7 | 2.2–33.7 | 4–21.1 | 2.4–11 | 1.3–3.2 |
| Tyr | 24–154 | 27.3–92.1 | 34–101 | 1.3–76.2 | 6.2–45.5 | 2.8–17.9 | 6.9–17.8 |
| Val | 72.6–277 | 94.8–261 | 99.2–329 | 1.2–24.7 | 3.1–12 | 1–7.9 | 8.3–21.5 |
aAsa and Hcit concentrations were calculated based upon the corresponding IS concentrations, as they were not included in the five-point external calibration curve
In urine, the concentration of each amino acid was normalized against creatinine and then expressed in mmol/mol of creatinine. As previously described (Illsinger et al. 2010), large variations in amino acid concentrations are observed in urine of newborns, reflecting the variability of renal tubular function in the first months of life (Rossi et al. 1994).
Medical Valuation
Samples, collected from confirmed IEM patients, revealed positive results, according to their respective pathology (Table 4).
Table 4.
Amino acid concentrations measured in different IEM
| IEM | Matrix | Amino acid | Concentration (age-related normal range) |
|---|---|---|---|
| MSUD | Plasma | Leu | 491 μmol/L (61,0–341,0) |
| allo-Ilea | 115 μmol/L | ||
| PKU | Plasma | Phe | 1,230 μmol/L (23,5–104,0) |
| Ornithinemia | Plasma | Orn | 660 μmol/L (42.8–346.2) |
| Treated tyrosinemia type I | Urine | Tyr | 86,8 mM/M creatinine (2,8–17,9) |
| NKHGb | Urine | Gly | 3971 mM/M creatinine (66,0–416,7) |
| Cystinuria | Urine | Arg | 157,6 mM/M creatinine (6,1–61,7) |
| Cys | 93,1 mM/M creatinine (2,1–9,8) | ||
| Lys | 551,0 mM/M creatinine (4,7–105,0) | ||
| Orn | 148,8 mM/M creatinine (0,9–5,4) | ||
| Cystathioninuria | Urine | Cth | 208 mM/M creatinine (0,3–4,4) |
aallo-Isoleucine
bNon ketotic hyperglycinemia
Discussion
We present here an exhaustive assessment of the aTRAQ kit for Amino Acid Analysis of Physiological Fluids, using a total error approach. To our knowledge, this is the first validation report of amino acid profiling through the use of accuracy profile.
Based on the most recent manufacturer’s recommendations, a few modifications have been appended to the original protocol for sample preparation. These improvements are the consequence of some troubles reported by customers in methionine quantification with the native procedure.
The first amelioration referred to the addition of the aTRAQ Internal Standard solution before the evaporation step, and not after as required in the initial method. During this dryness stage, an oxidation phenomenon occurs, which mainly affects methionine and cystathionine. As internal standards were initially added after this step, they were not subjected to this degradation, and Met and Cth were then underestimated. Therefore, adding the Internal Standard solution before desiccation equally affects the metabolites to be quantified and their corresponding internal standards.
After hydroxylamine pipetting, an additional 15-min incubation step at room temperature was initiated. The phenolic group of tyrosine is also slowly and partially labeled by the aTRAQ Δ8-reagent. Hydroxylamine solution is used to remove this extra label, but as internal standard is added before the drying step, the concentration of hydroxylamine is reduced compared to the original protocol. This dilution slows down the reaction removing the unwanted tag and, therefore, an extra incubation time is required.
Finally, the evaporation step under nitrogen stream was reduced to the half mixture volume, and not to dryness as requested by the original proceeding. Indeed, extended drying can result in excessive methionine oxidation.
This latter protocol gives satisfaction for amino acids profiling. Sulfur-containing amino acids generate adequate results with reliable recoveries for Met and Cth. β-Alanine is poorly reproducible on lower concentrations. Because of detector saturation at higher concentrations, the limit of quantification of sarcosine was fixed at 272 μmol/L. Finally, phosphoserine gave precise but inaccurate results at higher concentrations (>341 μmol). Reference medical ranges are equivalent with published intervals (Duran 2008). Results comparison with IEC showed a right concordance, and patients affected by IEM have been readily identified.
Conclusion
The presented method is focused on the targeted identification of about 40 amino acids. The application has been evaluated and offers a valid alternative in a clinical context. Furthermore, the present approach offers certain advantage compared to the IEC method: lower sample volume, time run reduction, and better specificity. Additionally, the use of labeled internal standards for each amino acid confers reliable quantitative results. Neglecting maintenance costs of a devoted IEC-instrument, analytical running expenses are similar between the two methods.
Nevertheless, not everything is idyllic. Although chromatography time drops down from 180 to 18 min, the aTRAQ method requires much more of that time difference for extraction, derivatization, and data processing, this latter step being labor intensive. In addition, some specific ninhydrin-reactive species (i.e., aspartylglucosamine or pipecolic acid), which may be identified with any IEC amino acid analyzer, will remain undetectable with the MRM approach. Nonetheless, implementation of additional analytes in the MS acquisition method should be a future concern. Besides, this latter consideration depicts a certain advantage of the MS technology, as these “extra-analytes” should not involve exclusively ninhydrin-responsive compounds.
Aware that the sensitivity of ultimate generation mass spectrometer is far below major physiological amino acid concentrations, we demonstrate here that these technological advances, which are fundamental for traces detection (on the order of picomol/L or lower), are not incompatible with the reliable quantification of elevated amino acid concentrations (i.e., >100 μmol/L). Therefore, running methods requiring very high sensitivity can be easily combined with less sensitive protocols on the same instruments.
Finally, the aTRAQ kit is a very good alternative to the IEC method, but financial and practical considerations of both technologies have to be counterbalanced before engaging any transition.
Electronic Supplementary Material
Article aTRAQ - Supplemental Data (DOCX 97KB)
Abbreviations
- 1MHis
1-Methylhistidine
- 3MHis
3-Methylhistidine
- Aad
Alpha-Aminoadipate
- Abu
Alpha-Aminobutyrate
- Ala
Alanine
- Ans
Anserine
- Arg
Arginine
- Asa
Argininosuccinate
- Asn
Asparagine
- Asp
Aspartate
- bAib
Beta-Aminoisobutyrate
- bAla
Beta-Alanine
- BSA
Bovine Serum Albumin
- Car
Carnosine
- Cit
Citrulline
- Cth
Cystathionine
- Cys
Cystine
- ERNDIM
European Research Network for evaluation and improvement of screening Diagnosis and treatment of Inherited disorders of Metabolism
- EtN
Ethanolamine
- GABA
Gamma Aminobutyrate
- Gln
Glutamine
- Glu
Glutamate
- Gly
Glycine
- Hcit
Homocitrulline
- Hcy
Homocystine
- His
Histidine
- HPLC
High Pressure Liquid Chromatography
- Hyl
Hydroxylysine
- Hyp
Hydroxyproline
- IEC
Ion Exchange Chromatography
- IEM
Inborn Error of Metabolism
- Ile
Isoleucine
- IS
Internal Standard
- Leu
Leucine
- Lys
Lysine
- Met
Methionine
- MRM
Multiple Reaction Monitoring
- MS
Mass Spectrometry
- Nle
Norleucine
- Nva
Norvaline
- Orn
Ornithine
- PEtN
Phosphoethanolamine
- Phe
Phenylalanine
- Pro
Proline
- PSer
Phosphoserine
- Sar
Sarcosine
- Ser
Serine
- Tau
Taurine
- Thr
Threonine
- Trp
Tryptophane
- Tyr
Tyrosine
- Val
Valine
Synopsis
Validation of the aTRAQ assay for Amino Acid Analysis in Physiological Fluids.
Compliance with Ethics Guidelines
Disclosure
Romain FILEE, Roland SCHOOS, and François BOEMER declare no conflict of interest.
Grant/Funding Support
None.
Footnotes
Competing interests: None declared
Contributor Information
François Boemer, Email: F.Boemer@chu.ulg.ac.be.
Collaborators: Johannes Zschocke and K Michael Gibson
References
- Dettmer K, Stevens AP, Fagerer SR, Kaspar H, Oefner PJ. Amino acid analysis in physiological samples by GC-MS with propyl chloroformate derivatization and iTRAQ-LC-MS/MS. Methods Mol Biol. 2012;828:165–181. doi: 10.1007/978-1-61779-445-2_15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietzen DJ, Weindel AL, Carayannopoulos MO, et al. Rapid comprehensive amino acid analysis by liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry: comparison to cation exchange with post-column ninhydrin detection. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom (RCM) 2008;22:3481–3488. doi: 10.1002/rcm.3754. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duran M. Amino acids. In: Blau N, Duran M, Gibson KM, editors. Laboratory guide to the methods in biochemical genetics. Berlin: Springer; 2008. pp. 53–89. [Google Scholar]
- Gustavo Gonzales A, Angeles Herrador M. Accuracy profiles from uncertainty measurements. Talanta. 2006;70:896–901. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2006.02.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harder U, Koletzko B, Peissner W. Quantification of 22 plasma amino acids combining derivatization and ion-pair LC-MS/MS. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2011;879:495–504. doi: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2011.01.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Held PK, White L, Pasquali M. Quantitative urine amino acid analysis using liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry and aTRAQ reagents. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2011;879:2695–2703. doi: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2011.07.030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubert P, Nguyen-Huu JJ, Boulanger B, et al. Harmonization of strategies for the validation of quantitative analytical procedures. A SFSTP proposal–part I. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2004;36:579–586. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2004.07.027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubert P, Nguyen-Huu JJ, Boulanger B, et al. Harmonization of strategies for the validation of quantitative analytical procedures. A SFSTP proposal–part II. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2007;45:70–81. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2007.06.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubert P, Nguyen-Huu JJ, Boulanger B, et al. Harmonization of strategies for the validation of quantitative analytical procedures. A SFSTP proposal–part III. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2007;45:82–96. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2007.06.032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Illsinger S, Schmidt KH, Lucke T, Vaske B, Bohnhorst B, Das AM. Plasma and urine amino acid pattern in preterm infants on enteral nutrition: impact of gestational age. Amino Acids. 2010;38:959–972. doi: 10.1007/s00726-009-0305-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piraud M, Vianey-Saban C, Petritis K, et al. ESI-MS/MS analysis of underivatised amino acids: a new tool for the diagnosis of inherited disorders of amino acid metabolism. Fragmentation study of 79 molecules of biological interest in positive and negative ionisation mode. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom (RCM) 2003;17:1297–1311. doi: 10.1002/rcm.1054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piraud M, Vianey-Saban C, Bourdin C, et al. A new reversed-phase liquid chromatographic/tandem mass spectrometric method for analysis of underivatised amino acids: evaluation for the diagnosis and the management of inherited disorders of amino acid metabolism. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom (RCM) 2005;19:3287–3297. doi: 10.1002/rcm.2197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossi R, Danzebrink S, Linnenburger K, et al. Assessment of tubular reabsorption of sodium, glucose, phosphate and amino acids based on spot urine samples. Acta Paediatr. 1994;83:1282–1286. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1994.tb13017.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozet E, Morello R, Lecomte F, et al. Performances of a multidimensional on-line SPE-LC-ECD method for the determination of three major catecholamines in native human urine: validation, risk and uncertainty assessments. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2006;844:251–260. doi: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2006.07.060. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozet E, Wascotte V, Lecouturier N, et al. Improvement of the decision efficiency of the accuracy profile by means of a desirability function for analytical methods validation. Application to a diacetyl-monoxime colorimetric assay used for the determination of urea in transdermal iontophoretic extracts. Anal Chim Acta. 2007;591:239–247. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2007.04.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waterval WA, Scheijen JL, Ortmans-Ploemen MM, Habets-van der Poel CD, Bierau J. Quantitative UPLC-MS/MS analysis of underivatised amino acids in body fluids is a reliable tool for the diagnosis and follow-up of patients with inborn errors of metabolism. Clin Chim Acta; Int J Clin Chem. 2009;407:36–42. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2009.06.023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHO (2010) International statistical classification of diseases and related health problems. WHO. http://apps.who.int/classifications/icd10 [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Article aTRAQ - Supplemental Data (DOCX 97KB)


