Abstract
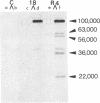
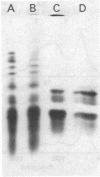
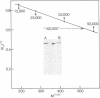
When isolated by means of an anti-polyoma tumor (T) antiserum, the major product from mouse cells productively infected by wild-type polyoma virus is a polypeptide of 100,000 apparent molecular weight as judged by sodium dodecyl sulfate/polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. In cells infected by NG-18, an hr-t mutant carrying a deletion of about 150 base pairs in the early region of the viral DNA, a T antigen species appears that comigrates with that of the wild-type virus. Comparisons of peptides after partial proteolysis reveal no differences between mutant and wild-type products. Both wild-type and mutant 100,000 products can be labeled in vivo with [32P]orthophosphate. An independent and more reliable estimate of the molecular weight of this protein using guanidine/Sepharose chromatography yields a value of 81,000 for both mutant and wild-type species. The apparent identity of wild-type and mutant products indicates that the deletion in NG-18 lies outside of the region encoding this major T antigen species.
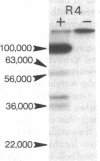
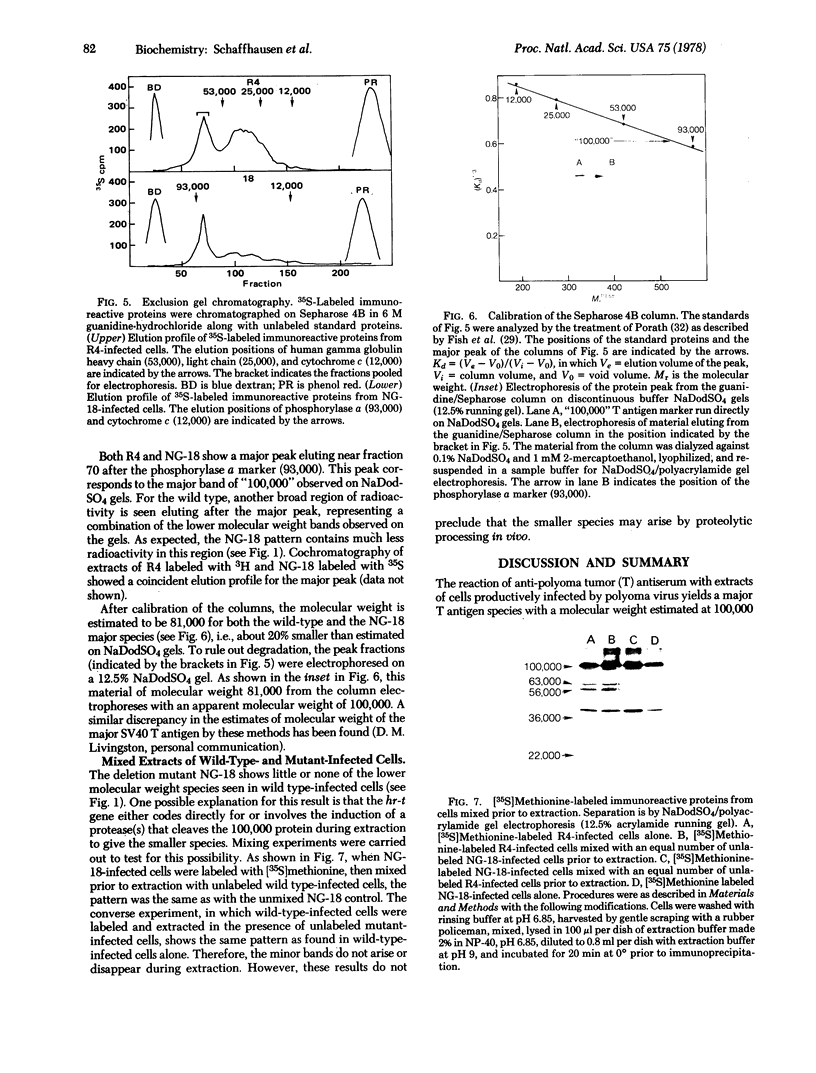
Immunoprecipitates from wild-type infected cells shows four bands in addition to the “100,000” band; these have apparent molecular weights of 63,000, 56,000, 36,000, and 22,000 by sodium dodecyl sulfate/polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis; the 56,000 and 36,000 species are phosphorylated. All four of these lower molecular weight bands are absent or drastically reduced in the immunoprecipitates from NG-18-infected cells.
Keywords: papovavirus, hr-t deletion, nontransforming mutant
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahmad-Zadeh C., Allet B., Greenblatt J., Weil R. Two forms of simian-virus-40-specific T-antigen in abortive and lytic infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Apr;73(4):1097–1101. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.4.1097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLACK P. H., ROWE W. P., TURNER H. C., HUEBNER R. J. A SPECIFIC COMPLEMENT-FIXING ANTIGEN PRESENT IN SV40 TUMOR AND TRANSFORMED CELLS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 Dec;50:1148–1156. doi: 10.1073/pnas.50.6.1148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banker G. A., Cotman C. W. Measurement of free electrophoretic mobility and retardation coefficient of protein-sodium dodecyl sulfate complexes by gel electrophoresis. A method to validate molecular weight estimates. J Biol Chem. 1972 Sep 25;247(18):5856–5861. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll R. B., Smith A. E. Monomer molecular weight of T antigen from simian virus 40-infected and transformed cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jul;73(7):2254–2258. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.7.2254. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckhart W. Complementation between temperature-sensitive (ts) and host range nontransforming (hr-t) mutants of polyoma virus. Virology. 1977 Apr;77(2):589–597. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90484-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feunteun J., Sompayrac L., Fluck M., Benjamin T. Localization of gene functions in polyoma virus DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Nov;73(11):4169–4173. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.11.4169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fish W. W., Mann K. G., Tanford C. The estimation of polypeptide chain molecular weights by gel filtration in 6 M guanidine hydrochloride. J Biol Chem. 1969 Sep 25;244(18):4989–4994. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fluck M. M., Staneloni R. J., Benjamin T. L. Hr-t and ts-a: two early gene functions of polyoma virus. Virology. 1977 Apr;77(2):610–624. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90486-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenblatt J. F., Allet B., Weil R., Ahmad-Zadeh C. Synthesis of the tumour antigen and the major capsid protein of simian virus 40 in a cell-free system derived from Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1976 Dec;108(2):361–379. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(76)80125-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HABEL K. SPECIFIC COMPLEMENT-FIXING ANTIGENS IN POLYOMA TUMORS AND TRANSFORMED CELLS. Virology. 1965 Jan;25:55–61. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(65)90251-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito Y., Spurr N., Dulbecco R. Characterization of polyoma virus T antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Mar;74(3):1259–1263. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.3.1259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jessel D., Landau T., Hudson J., Lalor T., Tenen D., Livingston D. M. Identification of regions of the SV40 genome which contain preferred SV40 T antigen-binding sites. Cell. 1976 Aug;8(4):535–545. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90222-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lagerkvist U., Akesson B., Brändén R. Aminoacyl adenylate, a normal intermediate or a dead end in aminoacylation of transfer ribonucleic acid. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 10;252(3):1002–1006. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oxman M. N., Takemoto K. K., Eckhart W. Polyoma T antigen synthesis by temperature-sensitive mutants of polyoma virus. Virology. 1972 Sep;49(3):675–682. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90524-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POPE J. H., ROWE W. P. DETECTION OF SPECIFIC ANTIGEN IN SV40-TRANSFORMED CELLS BY IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE. J Exp Med. 1964 Aug 1;120:121–128. doi: 10.1084/jem.120.2.121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paulin D., Cuzin F. Polyoma virus T antigen. I. Synthesis of modified heat-labile T angiten in cells transformed with the ts-a mutant. J Virol. 1975 Feb;15(2):393–397. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.2.393-397.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paulin D., Gaudray P., Cuzin F. Purification of polyoma T antigen from transformed cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Aug 18;65(4):1418–1426. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(75)80387-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paulin D., Perreau J., Cuzin F. Immunochemical procedure for partial purification of newly synthesized proteins in polyoma virus-infected mouse cells. J Virol. 1974 Mar;13(3):699–705. doi: 10.1128/jvi.13.3.699-705.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prives C., Gilboa E., Revel M., Winocour E. Cell-free translation of simian virus 40 early messenger RNA coding for viral T-antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):457–461. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed S. I., Ferguson J., Davis R. W., Stark G. R. T antigen binds to simian virus 40 DNA at the origin of replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Apr;72(4):1605–1609. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.4.1605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rundell K., Collins J. K., Tegtmeyer P., Ozer H. L., Lai C. J., Nathans D. Identification of simian virus 40 protein A. J Virol. 1977 Feb;21(2):636–646. doi: 10.1128/jvi.21.2.636-646.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staneloni R. J., Fluck M. M., Benjamin T. L. Host range selection of transformation-defective hr-t mutants of polyoma virus. Virology. 1977 Apr;77(2):598–609. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90485-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tegtmeyer P. Altered patterns of protein synthesis in infection by SV40 mutants. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1975;39(Pt 1):9–15. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.039.01.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tegtmeyer P., Robb J. A., Widmer C., Ozer H. L. Altered protein metabolism in infection by the late tsB11 mutant of simian virus 40. J Virol. 1974 Oct;14(4):997–1007. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.4.997-1007.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tegtmeyer P., Rundell K., Collins J. K. Modification of simian virus 40 protein A. J Virol. 1977 Feb;21(2):647–657. doi: 10.1128/jvi.21.2.647-657.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tenen D. G., Garewal H., Haines L. L., Hudson J., Woodard V., Light S., Livingston D. M. Purification of simian virus 40 tumor antigen from a line of simian virus 40-transformed human cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Sep;74(9):3745–3749. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.9.3745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tenen D. G., Martin R. G., Anderson J., Livingston D. M. Biological and biochemical studies of cells transformed by simian virus 40 temperature-sensitive gene A mutants and A mutant revertants. J Virol. 1977 Apr;22(1):210–218. doi: 10.1128/jvi.22.1.210-218.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WINOCOUR E. Purification of polyoma virus. Virology. 1963 Feb;19:158–168. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(63)90005-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]