Abstract
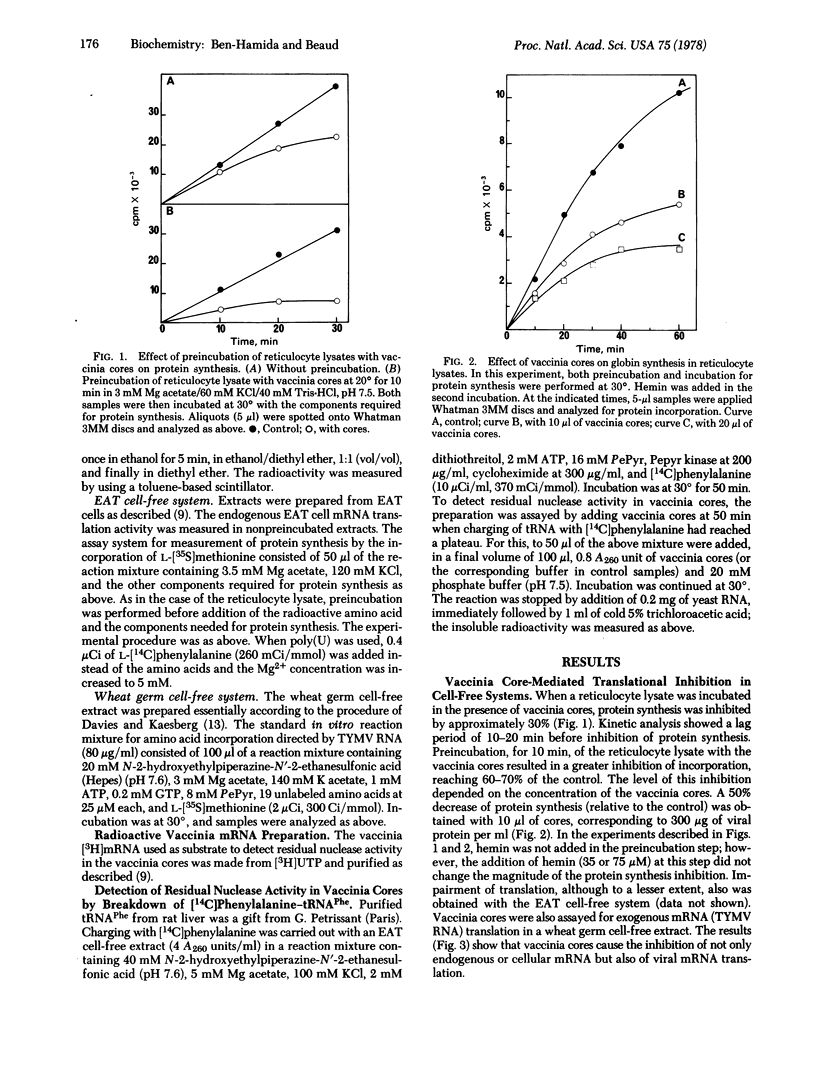
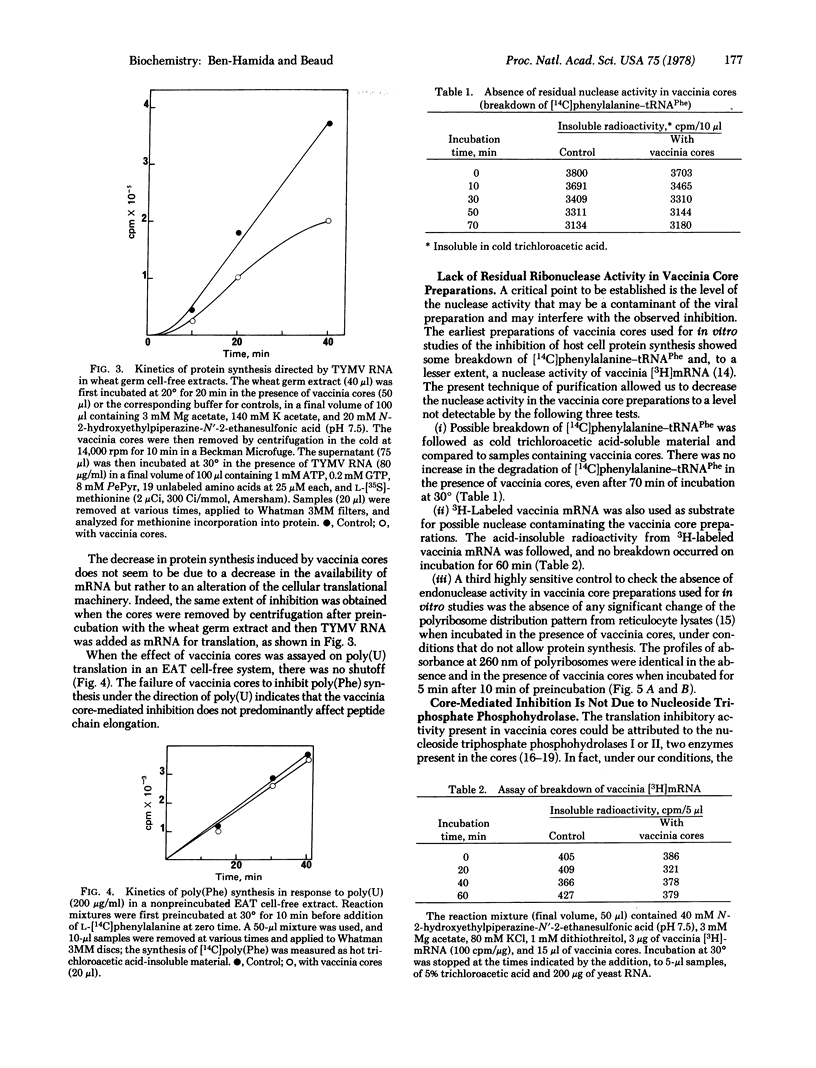
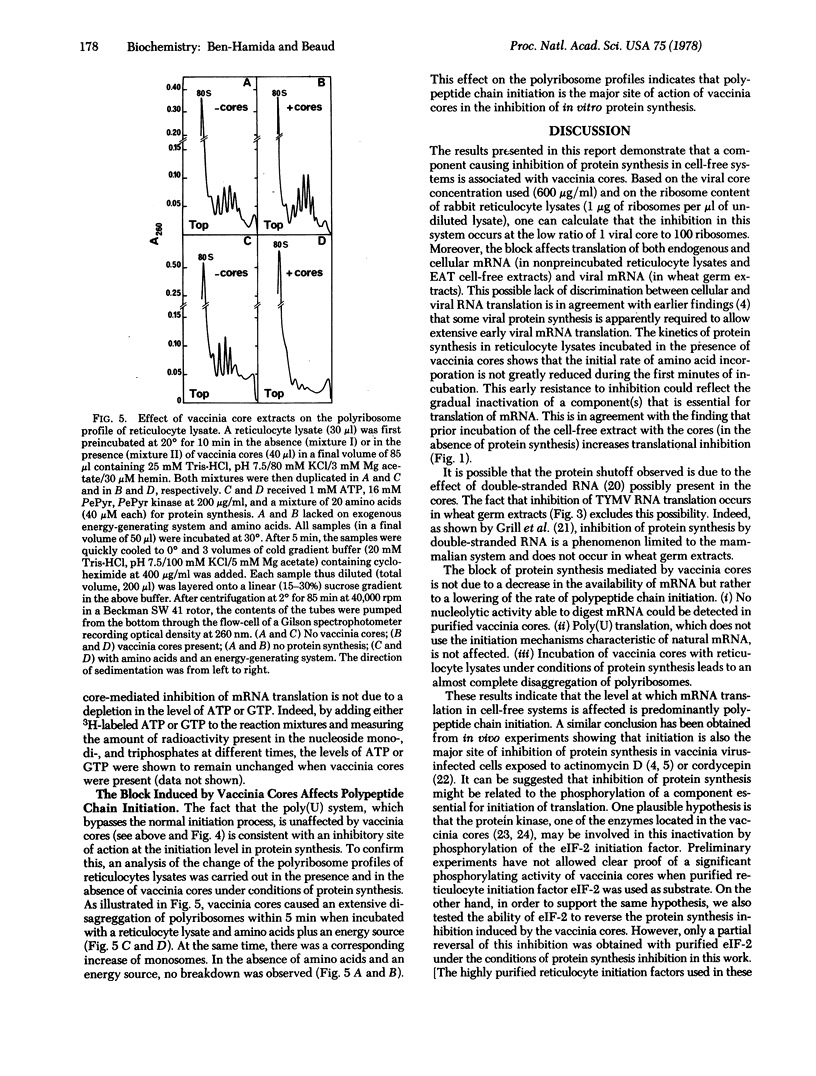
The mechanism of the shutoff of cellular protein synthesis in vaccinia virus-infected cells has been investigated by using in vitro systems. Purified vaccinia cores cause inhibition of endogenous mRNA translation in nonpreincubated reticulocyte lysates and Ehrlich ascites tumor cell-free systems. Translation of viral mRNA from turnip yellow mosaic virus is also impaired in wheat germ cell-free extracts. The block induced by vaccinia cores in protein synthesis is not due to a decrease in the availability of mRNA but rather to an alteration of the cellular translational machinery. No nucleolytic activity able of digesting mRNA could be detected in purified vaccinia cores with three sensitive tests. There is a lack of inhibition in the poly(Phe)-poly(U) system, which bypasses the normal initiation process. An almost complete disaggregation of polyribosomes in the reticulocyte lysate appears when vaccinia cores are present. These results indicate that mRNA translation in a cell-free system is affected predominantly at the level of polypeptide chain initiation.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Balanian R. Structural and functional alterations in cultured cells infected with cytocidal viruses. Prog Med Virol. 1975;19:40–83. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clemens M. J., Pain V. M., Henshaw E. C., London I. M. Characterization of a macromolecular inhibitor of polypeptide chain initiation from Ehrlich ascites tumor cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Sep 20;72(2):768–775. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(76)80105-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DALES S. The uptake and development of vaccinia virus in strain L cells followed with labeled viral deoxyribonucleic acid. J Cell Biol. 1963 Jul;18:51–72. doi: 10.1083/jcb.18.1.51. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies J. W., Kaesberg P. Translation of virus mRNA: synthesis of bacteriophage Q beta proteins in a cell-free extract from wheat embryo. J Virol. 1973 Dec;12(6):1434–1441. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.6.1434-1441.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Easterbrook K. B. Controlled degradation of vaccinia virions in vitro: an electron microscopic study. J Ultrastruct Res. 1966 Mar;14(5):484–496. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(66)80077-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrenfeld E., Hunt T. Double-stranded poliovirus RNA inhibits initiation of protein synthesis by reticulocyte lysates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 May;68(5):1075–1078. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.5.1075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esteban M., Metz D. H. Early virus protein synthesis in vaccinia virus-infected cells. J Gen Virol. 1973 May;19(2):201–206. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-19-2-201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold P. H., Dales S. Localization of nucleotide phosphohydrolase activity within vaccinia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Jul;60(3):845–852. doi: 10.1073/pnas.60.3.845. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grill L. K., Sun J. D., Kandel J. Effect of double stranded RNA on protein synthesis in an in vitro wheat germ embryo system. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Nov 8;73(1):149–156. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90509-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holloway P. W. A simple procedure for removal of Triton X-100 from protein samples. Anal Biochem. 1973 May;53(1):304–308. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90436-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Housman D., Jacobs-Lorena M., Rajbhandary U. L., Lodish H. F. Initiation of haemoglobin synthesis by methionyl-tRNA. Nature. 1970 Aug 29;227(5261):913–918. doi: 10.1038/227913a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JOKLIK W. K. THE INTRACELLULAR UNCOATING OF POXVIRUS DNA. I. THE FATE OF RADIOACTIVELY-LABELED RABBITPOX VIRUS. J Mol Biol. 1964 Feb;8:263–276. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(64)80136-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaureguiberry G., Ben-Hamida F., Chapeville F., Beaud G. Messenger activity of RNA transcribed in vitro by DNA-RNA polymerase associated to vaccinia virus cores. J Virol. 1975 Jun;15(6):1467–1474. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.6.1467-1474.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaerlein M., Horak I. Phosphorylation of ribosomal proteins in HeLa cells infected with vaccinia virus. Nature. 1976 Jan 15;259(5539):150–151. doi: 10.1038/259150a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleiman J. H., Moss B. Purification of a protein kinase and two phosphate acceptor proteins from vaccinia virions. J Biol Chem. 1975 Apr 10;250(7):2420–2429. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss B. Inhibition of HeLa cell protein synthesis by the vaccinia virion. J Virol. 1968 Oct;2(10):1028–1037. doi: 10.1128/jvi.2.10.1028-1037.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munyon W., Paoletti E., Ospina J., Grace J. T., Jr Nucleotide phosphohydrolase in purified vaccinia virus. J Virol. 1968 Mar;2(3):167–172. doi: 10.1128/jvi.2.3.167-172.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paolette E., Rosemond-Hornbeak H., Moss B. Two nucleid acid-dependent nucleoside triphosphate phosphohydrolases from vaccinia virus. Purification and characterization. J Biol Chem. 1974 May 25;249(10):3273–3280. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paoletti E., Moss B. Protein kinase and specific phosphate acceptor proteins associated with vaccinia virus cores. J Virol. 1972 Sep;10(3):417–424. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.3.417-424.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paoletti E., Moss B. Two nucleic acid-dependent nucleoside triphosphate phosphohydrolases from vaccinia virus. Nucleotide substrate and polynucleotide cofactor specificities. J Biol Chem. 1974 May 25;249(10):3281–3286. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosemond-Hornbeak H., Moss B. Inhibition of host protein synthesis by vaccinia virus: fate of cell mRNA and synthesis of small poly (A)-rich polyribonucleotides in the presence of actinomycin D. J Virol. 1975 Jul;16(1):34–42. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.1.34-42.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHATKIN A. J. ACTINOMYCIN D AND VACCINIA VIRUS INFECTION OF HELA CELLS. Nature. 1963 Jul 27;199:357–358. doi: 10.1038/199357a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



