Abstract
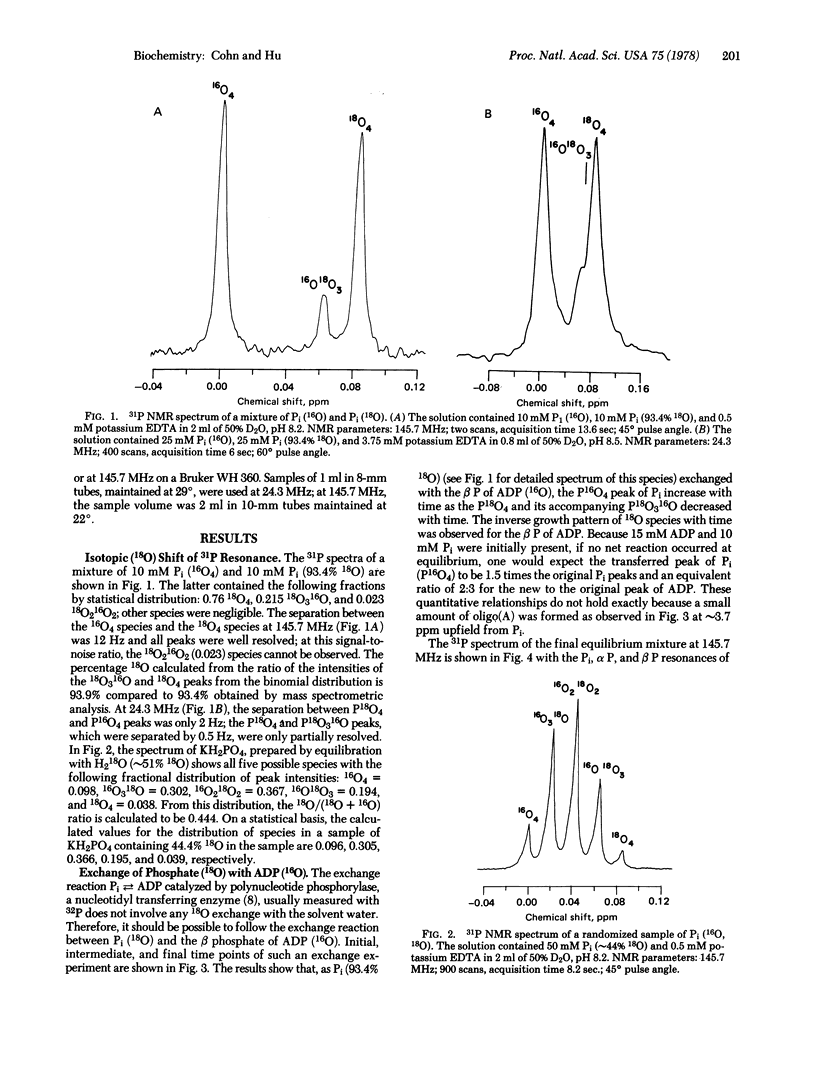
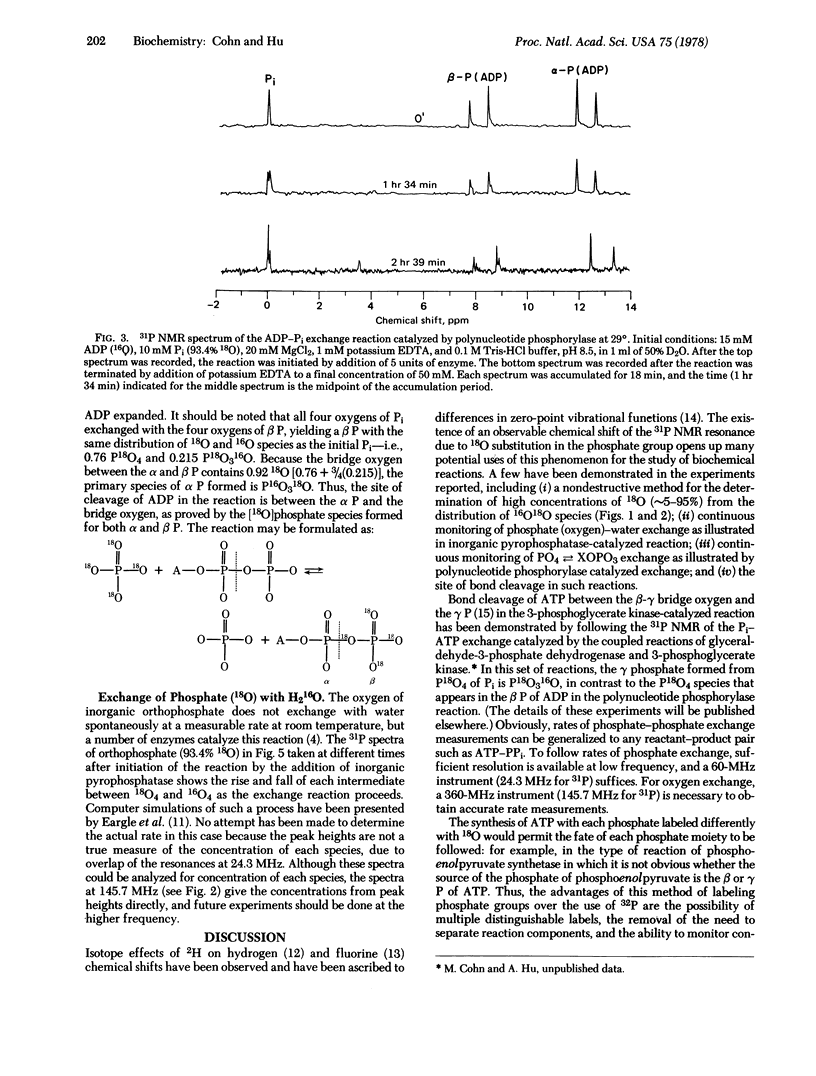
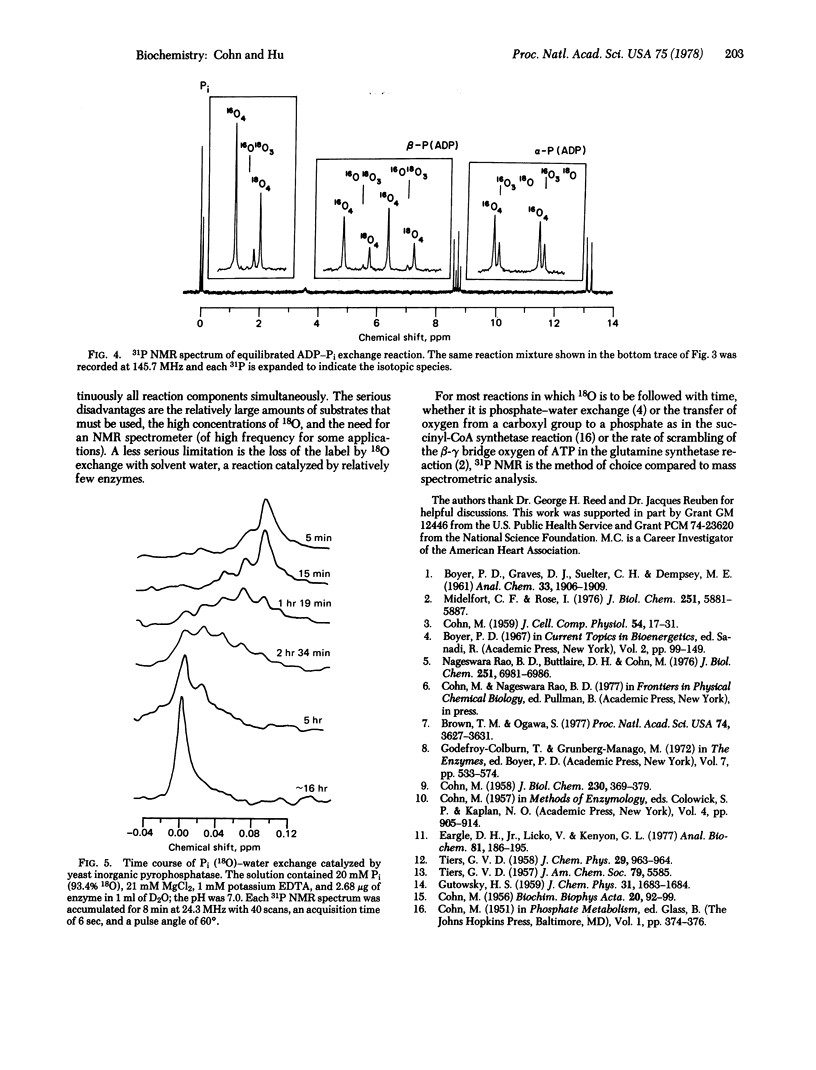
An isotopic shift of the 31P nuclear magnetic resonance due to 18O bonded to phosphorus of 0.0206 ppm has been observed in inorganic orthophosphate and adenine nucleotides. Thus, the separation between the resonances of 31P18O4 and 31P16O4 at 145.7 MHz is 12 Hz and, in a randomized sample containing ∼50% 18O, all five 16O-18O species are resolved and separated from each other by 3 Hz. Not only does this yield the 18O/16O ratio of the phosphate but, more important, the 18O-labeled phosphate in effect can serve as a double label in following phosphate reactions, for oxygen in all cases and for phosphorus, provided the oxygen does not exchange with solvent water. Thus, it becomes possible to follow labeled phosphorus or labeled oxygen continuously as reactions proceed. Rate studies involving (i) phosphorus and (ii) oxygen are illustrated by continuous monitoring of the exchange reactions between (i) the β phosphate of ADP and inorganic phosphate catalyzed by polynucleotide phosphorylase and (ii) inorganic orthophosphate and water catalyzed by yeast inorganic pyrophosphatase. In the ADP—Pi exchange, the Pi (18O4) yielded an α P(16O318O) and a β P(18O4), proving that bond cleavage occurs between the α P and the α-β bridge oxygen. Among the many additional potential uses of this labeling technique and its spectroscopic observation are: (i) different labeling of each phosphate group of ATP, (ii) to follow rate of transfer of 18O from a nonphosphate compound such as a carboxylic acid to a phosphate compound, and (iii) to follow the rate of scrambling (for example, of the β-γ bridge oxygen of ATP to nonbridge β P positions) and simultaneously the rate of exchange of the γ P nonbridge oxygens with solvent water in various ATPase reactions.
Keywords: ADP—Pi exchange, polynucleotide phosphorylase, site of bond cleavage, inorganic pyrophosphatase, oxygen scrambling
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brown T. R., Ogawa S. 31P nuclear magnetic resonance kinetic measurements on adenylatekinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Sep;74(9):3627–3631. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.9.3627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHN M. Mechanisms of enzymic cleavage of some organic phosphates. J Cell Comp Physiol. 1959 Dec;54:17–31. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1030540405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHN M. Phosphate-water exchange reaction catalyzed by inorganic pyrophosphatase of yeast. J Biol Chem. 1958 Jan;230(1):369–379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHN M. Some mechanisms of cleavage of adenosine triphosphate and 1, 3-diphosphoglyceric acid. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1956 Apr;20(1):92–99. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(56)90267-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eargle D. H., Jr, Licko V., Kenyon G. L. Kinetic studies of 18O exchange of inorganic phosphate using mass spectral measurements on the tris-(trimethylsilyl) derivative. Anal Biochem. 1977 Jul;81(1):186–195. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90612-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Midelfort C. F., Rose I. A. A stereochemical method for detection of ATP terminal phosphate transfer in enzymatic reactions. Glutamine synthetase. J Biol Chem. 1976 Oct 10;251(19):5881–5887. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao B. D., Buttlaire D. H., Cohn M. 31P NMR studies of the arginine kinase reaction. Equilibrium constants and exchange rates at stoichiometric enzyme concentration. J Biol Chem. 1976 Nov 25;251(22):6981–6986. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



