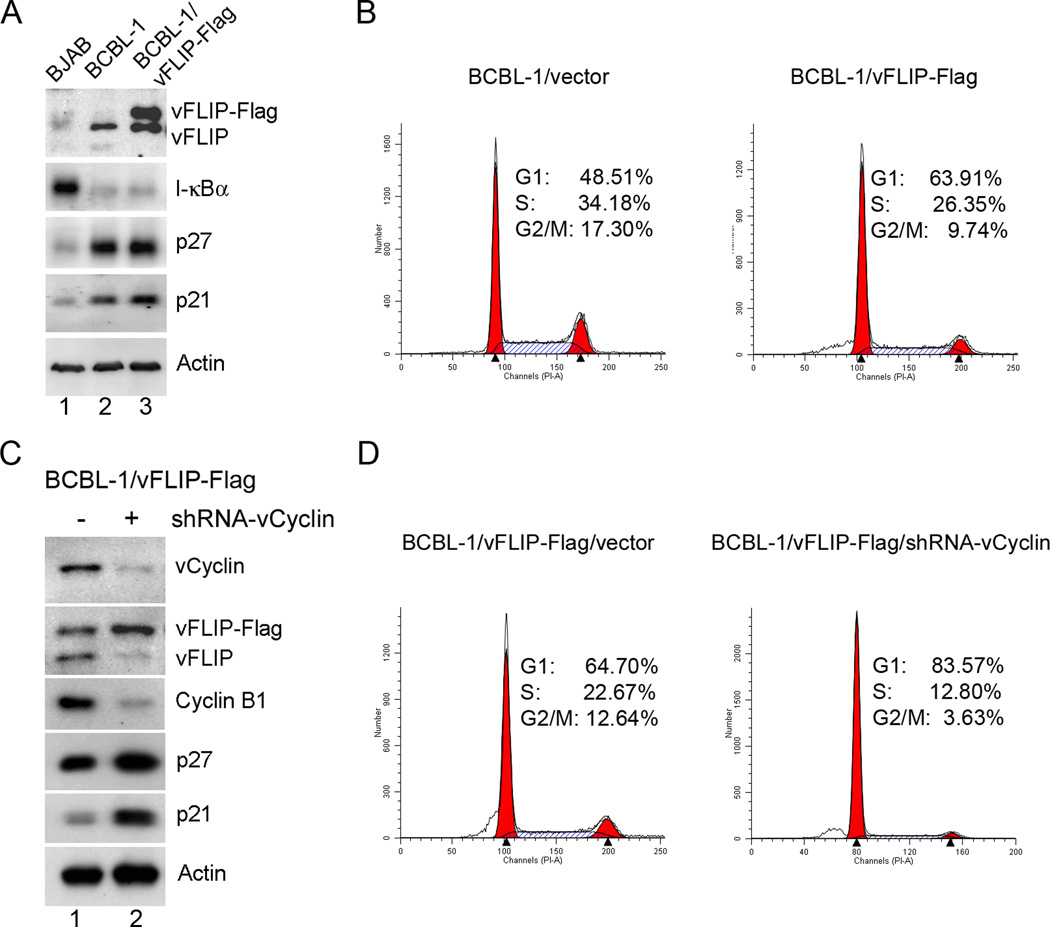
Figure 6. KSHV-transformed BCBL-1 cells that retain vFLIP, but are depleted for vCyclin arrest in G1 phase of the cell cycle.
(A) BCBL-1 cells stably expressing exogenously added vFLIP-Flag were constructed by transduction with LV-vFLIP-Flag-neo, followed by G-418 selection. Immunoblotting was used to detect vFLIP-Flag and endogenous vFLIP expression, as well as the expression of I-κBα, p21, p27, and β-actin (Actin) (lane 3). Human BJAB B cells (lane 1) and LV-neo vector-transduced BCBL-1 cells (lane 2) were used as controls. (B) Flow cytometry histograms of LV-neo and LV-vFLIP-Flag-neo- transduced BCBL-1 cells. Exponentially and asynchronously growing cells were collected and subjected to flow cytometry analysis as in Fig. 1C. (C) The endogenous vCyclin and vFLIP in BCBL-1/vFLIP-Flag cells were knocked down by transduction of LV-shRNA-vCyclin-puro (lane 2). BCBL-1 cells transduced with an empty vector were used as control (lane 1). After 4 days of puromycin selection, cells were harvested for Immunoblotting using the indicated antibodies. (D) Flow cytometry histograms of BCBL-1/vFLIP-Flag cells compared to their vCyclin-depleted counterparts (BCBL-1/vFLIP-Flag/shRNA-vCyclin).