Abstract
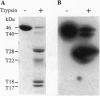
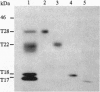
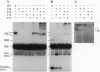
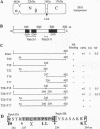
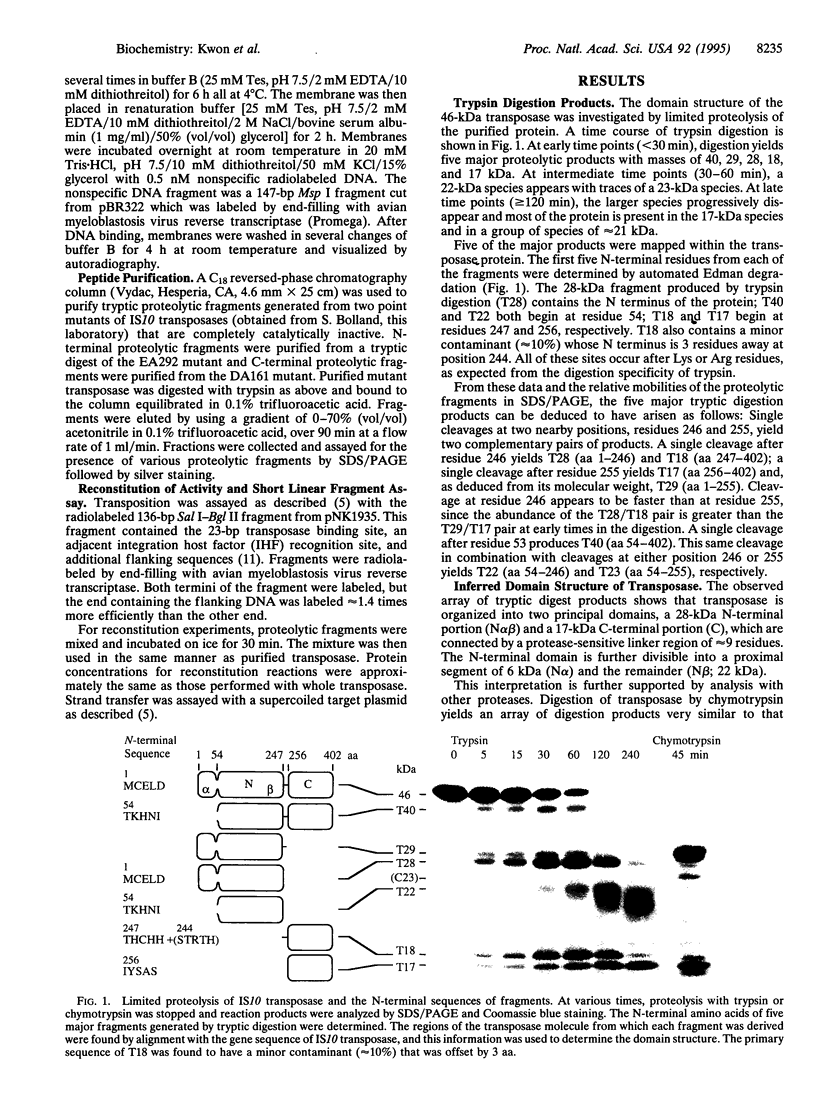
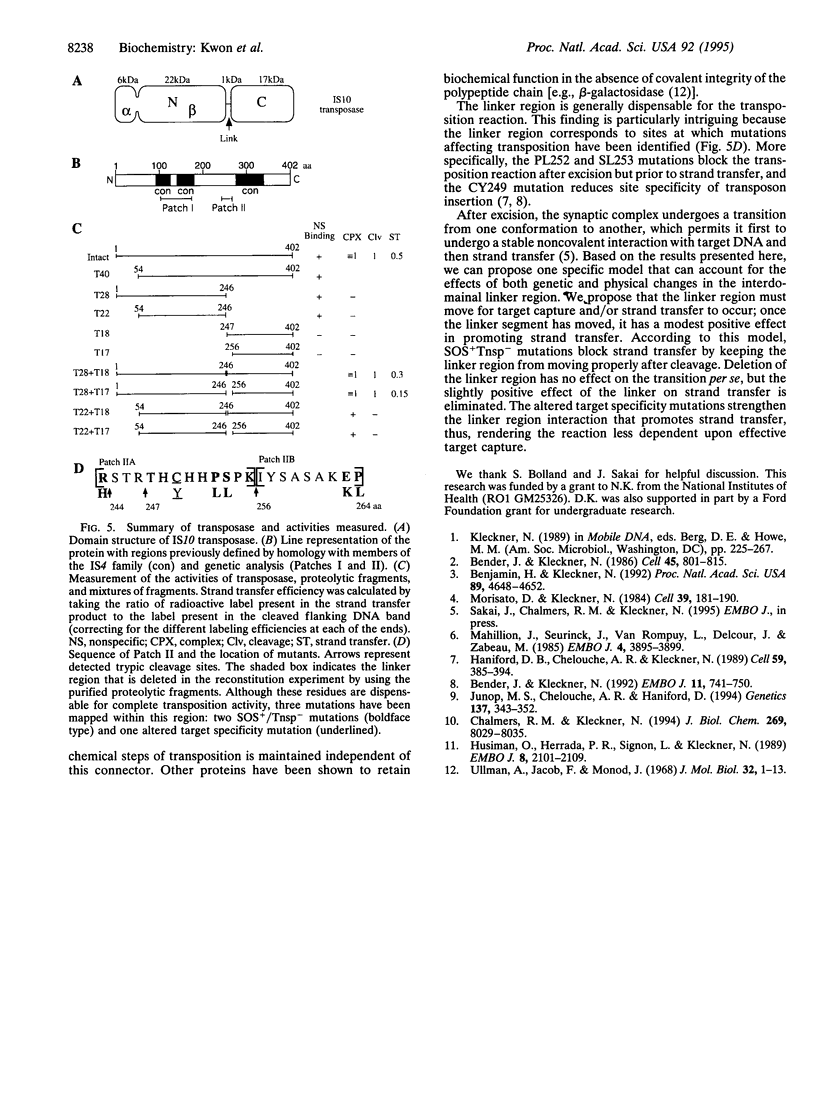
All of the DNA cleavage and strand transfer events required for transposition of insertion sequence IS10 are carried out by a 46-kDa IS10-encoded transposase protein. Limited proteolysis demonstrates that transposase has two principal structural domains, a 28-kDa N-terminal domain (N alpha beta; aa 1-246) and a 17-kDa C-terminal domain (C; aa 256-402). The two domains are connected by a 1-kDa proteolytic-sensitive linker region (aa 247-255). The N-terminal domain N alpha beta can be further subdivided into domains N alpha and N beta by a weaker protease-sensitive site located 6 kDa (53 aa) from the N terminus. The N beta and N alpha beta fragments are capable of nonspecific DNA binding as determined by Southwestern blot analysis. None of the fragments alone is capable of carrying out the first step of transposition, assembly of a synaptic complex containing a pair of transposon ends. Remarkably, complete transposition activity can be reconstituted by mixing fragment N alpha beta and fragment C, with or without the intervening linker region. We infer that the structural integrity of transposase during the transitions involved in the chemical steps of the transposition reaction is maintained independent of the linker, presumably by direct contacts between and among the principal domains. Reconstitution of activity in the absence of the linker region is puzzling, however, because mutations that block strand transfer or affect insertion specificity alter linker region residues. Additional reconstitution experiments demonstrate that the N alpha region is dispensable for formation of a synaptic complex but is required for complexes to undergo cleavage.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bender J., Kleckner N. Genetic evidence that Tn10 transposes by a nonreplicative mechanism. Cell. 1986 Jun 20;45(6):801–815. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90555-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bender J., Kleckner N. IS10 transposase mutations that specifically alter target site recognition. EMBO J. 1992 Feb;11(2):741–750. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05107.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benjamin H. W., Kleckner N. Excision of Tn10 from the donor site during transposition occurs by flush double-strand cleavages at the transposon termini. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 15;89(10):4648–4652. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.10.4648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chalmers R. M., Kleckner N. Tn10/IS10 transposase purification, activation, and in vitro reaction. J Biol Chem. 1994 Mar 18;269(11):8029–8035. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haniford D. B., Chelouche A. R., Kleckner N. A specific class of IS10 transposase mutants are blocked for target site interactions and promote formation of an excised transposon fragment. Cell. 1989 Oct 20;59(2):385–394. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90299-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huisman O., Errada P. R., Signon L., Kleckner N. Mutational analysis of IS10's outside end. EMBO J. 1989 Jul;8(7):2101–2109. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03619.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Junop M. S., Hockman D., Haniford D. B. Intragenic suppression of integration-defective IS10 transposase mutants. Genetics. 1994 Jun;137(2):343–352. doi: 10.1093/genetics/137.2.343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahillon J., Seurinck J., van Rompuy L., Delcour J., Zabeau M. Nucleotide sequence and structural organization of an insertion sequence element (IS231) from Bacillus thuringiensis strain berliner 1715. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 30;4(13B):3895–3899. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04163.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morisato D., Kleckner N. Transposase promotes double strand breaks and single strand joints at Tn10 termini in vivo. Cell. 1984 Nov;39(1):181–190. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90204-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullmann A., Jacob F., Monod J. On the subunit structure of wild-type versus complemented beta-galactosidase of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1968 Feb 28;32(1):1–13. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90140-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]