Abstract
A centrosome consists of two barrel-shaped centrioles embedded in a matrix of proteins known as the pericentriolar material (PCM). The PCM serves as a platform for protein complexes that regulate organelle trafficking, protein degradation and spindle assembly. Perhaps most important for cell division, the PCM concentrates tubulin and serves as the primary organizing centre for microtubules in metazoan somatic cells. Thus, similar to other well-described organelles, such as the nucleus and mitochondria, the cell has compartmentalized a multitude of vital biochemical reactions in the PCM. However, unlike these other organelles, the PCM is not membrane bound, but rather a dynamic collection of protein complexes and nucleic acids that constitute the organelle's interior and determine its boundary. How is the complex biochemical machinery necessary for the myriad centrosome functions concentrated and maintained in the PCM? Recent advances in proteomics and RNAi screening have unveiled most of the key PCM components and hinted at their molecular interactions ( table 1). Now we must understand how the interactions between these molecules contribute to the mesoscale organization and the assembly of the centrosome. Among outstanding questions are the intrinsic mechanisms that determine PCM shape and size, and how it functions as a biochemical reaction hub.
Keywords: pericentriolar material, centrosome, organelle scaling, microtubule-organizing centre
1. Pericentriolar material structure
Decades of research have pursued atomic-level resolution of the underlying pericentriolar material (PCM) structure with little avail. This is probably owing to limitations in methodology, but also to the fact that the PCM does not behave like most ordered proteinacious assemblies. In the earliest electron micrographs depicting centrosomes in situ, the PCM appeared as a densely stained amorphous mass that surrounded the highly structured centrioles [1]. Electron microscopy (EM) micrographs of centrosomes isolated from mammalian cells did little to resolve the amorphous mass any further, although these experiments definitively showed that microtubules (MTs) originate from the PCM (figure 1) [2] and that PCM integrity is sensitive to chelating divalent cations [9].
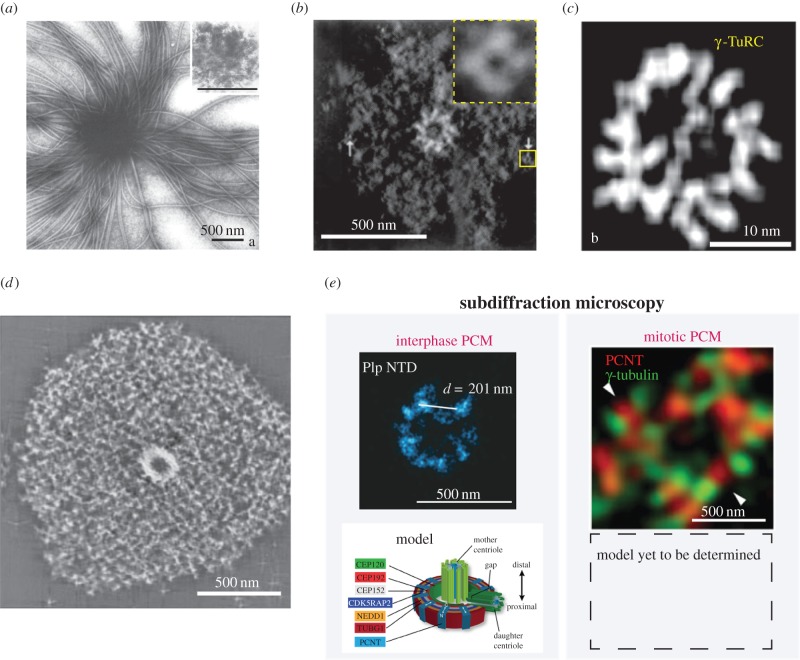
Figure 1.
Structural organization of the PCM. (a) Negative stain electron micrograph of a centrosome isolated from Chinese hamster ovary cells. One hundred and twenty-five MTs emanate from the densely staining centre. (Adapted from [2].) (b) Structure of a purified Drosophila centrosome as revealed by electron tomography. A ninefold radially symmetric centriole can be seen at the centre surrounded by PCM. The inset shows a magnified view of a ring-like complex found within the PCM. These complexes measured 25–30 nm in diameter and were determined to contain γ-tubulin. (Adapted from [3].) (c) The γ-TuRC was later isolated from Drosophila cells and analysed by electron tomography. (Adapted from [4].) (d) Harsh treatment of Spisula centrosomes with potassium iodide revealed 12–15 nm wide filaments running throughout the PCM, leading to the hypothesis that a lattice-like network forms the structural foundation of the PCM. (Adapted from [5].) (e) The development of subdiffraction microscopy techniques allowed high precision localization of proteins within the PCM. The first picture depicts the localization of PCNT-like protein (D-PLP) in Drosophila cells determined with stochastic optical reconstruction microscopy (STORM). Comparison of the localization of numerous proteins revealed that the interphase PCM contains ordered subdomains of defined size. However, the expansive PCM that exists during mitosis is less ordered. Localization of PCNT and γ-tubulin in human cells using three-dimensional SIM is shown. (Adapted from [6–8].)
The resolution required to distinguish subdomains within the PCM would not be achieved until the implementation of EM tomography. Using this approach, in combination with immunolabelling, Moritz et al. [3] could discern gamma-tubulin-containing ring structures 25–30 nm in diameter within PCM from isolated Drosophila melanogaster centrosomes [3]. Higher resolution structures of immunoprecipitated Drosophila γ-tubulin ring complexes (γ-TuRCs) confirmed the 25–30 nm diameter of these rings and showed that they cap the minus ends of PCM-derived MTs [4]. Similar ring structures were observed in centrosomes isolated from surf clam oocytes and, intriguingly, were stripped away after exposure to potassium iodide, leaving behind an underlying skeletonized lattice of 12–15 nm wide filaments [5]. Unlike the untreated centrosomes, the salt-stripped centrosomes could not nucleate MTs. Interestingly, the ring structures reappeared and MT nucleation could be restored if the salt-stripped centrosomes were incubated in oocyte extract. Taken together, the findings from these studies hinted that the PCM comprises a porous structural scaffold onto which γ-tubulin and other soluble components from the cytoplasm are loaded.
Concurrently, scientists sought to determine the identities and biochemical properties of the proteins that construct the PCM scaffold, or the so-called ‘centromatrix’. Researchers took advantage of the curious fact that auto-immune sera taken from scleroderma patients reacted widely with centrosomes and, thus, could be used as a robust label for specific centrosome proteins in western blot and immunofluorescence assays [10]. Use of these sera revealed that the PCM is a dynamic structure and led to the identification and biochemical characterization of PCM proteins [11]. In this manner, one of the first PCM components, pericentrin (PCNT), was identified, cloned and its necessity for spindle organization described [12]. The discovery of additional core PCM components such as Cep192/SPD-2, CDK5RAP2/Cnn, Cep152/Asterless and SPD-5 in various organisms revealed that the only major similarity among PCM organizing proteins was an abundance of coiled-coil domains [13–18]. The coiled-coil motif consists of intertwined α-helices and is known to mediate protein–protein interactions [19]. Thus, it was proposed that these numerous coiled-coil domains could mediate robust inter-molecular interactions to allow formation of the centromatrix [16,20]. Whether these coiled-coil scaffold proteins per se are sufficient to assemble the centromatrix, and whether their coiled-coil domains are critical for this assembly process, has yet to be determined.
Analysis of purified centrosomes by mass spectrometry and large-scale RNAi and localization screens in Caenorhabditis elegans, Drosophila and human cells unveiled a diverse bounty of centrosome proteins [17,21–25] (table 1). Owing to the diversity and tight clustering of PCM proteins at centrosomes, it is of little surprise that electron microscopy so far could not discern structural information about the PCM. Labelling and observing individual components within the PCM promised to circumvent this problem, but the resolution limitations of conventional light microscopy and immunogold-EM only allowed the localization of the components without generating any meaningful structural insights. However, recent advances in light microscopy technology opened new possibilities for mapping PCM architecture. Four independent studies used subdiffraction light microscopy techniques, such as three-dimensional structured illumination (three-dimensional SIM) and stochastic optical reconstruction microscopy (STORM) to identify the substructures within the PCM [6–8,65]. The authors developed antibodies to label distinct epitopes of different PCM proteins and measured their distances from the outer centriole wall. A key finding was that interphase PCM proteins are distributed in concentric toroids of discrete diameter around centrioles. A subset of proteins, human CDK5RAP2, PCNT, CEP152 and the Drosophila orthologues PCNT-like protein (D-PLP) and Asterless, were shown to exhibit highly extended conformations spanning approximately 100 nm from the centriole wall to the outer toroidal domains of the interphase PCM. In stark contrast, analysis of the same proteins during metaphase revealed no ordered structures or discrete distributions. Interestingly, the co-localization between labelled PCM protein pairs was minimal, indicating that, despite the lack of apparent organization, PCM proteins still occupy distinct domains in the metaphase centrosome [7]. These findings argue that the PCM is first assembled in interphase as an ordered, compact layer immediately surrounding the centrioles that then serves as a foundation for the expansive formation of PCM towards metaphase.
Table 1.
Important proteins for PCM assembly and function. (Key PCM proteins and their homologues from humans, flies and nematodes are grouped based on their general role in PCM biogenesis and function. Scaffold proteins are believed to be involved in forming the foundation of the PCM. The effector proteins are more peripheral factors involved in MT organization. SMC_prok_B: chromosome segregation protein SMC, common bacterial type. PACT_coil_coil: PCNT-AKAP-450 domain of centrosomal targeting protein.)
| Homo sapiens | D. melanogaster | Caenorhabditis elegans | domains | PCM-related phenotypes | reference | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| scaffolds | Cep192 | Spd-2 | SPD-2 | coiled coil, polo-box-binding domain | centriole duplication defect, reduced PCM, PLK-1 targeting to centrosomes lost | [13,26–28] |
| Cep152 | Asl (Asterless) | coiled coil, SMC_prok_B (PFAM) | centriole duplication defect, reduced PCM | [29,14] | ||
| CPAP | SAS-4 | SAS-4 | coiled coil, tubulin binding | centriole duplication defect, reduced PCM | [30,31] | |
| PCNT | D-PLP | coiled coil, centrosome-targeting (PFAM) | reduced PCM | [12,32–34] | ||
| CDK5RAP2 | Cnn (centrosomin) | coiled coil, MT association (PFAM) | reduced PCM, centriole-PCM attachment defect | [15,35–37] | ||
| CG-NAP/AKAP450 | coiled coil, calmodulin-binding domain | centriole duplication defect | [38,39] | |||
| SPD-5 | coiled coil, SMC_prok_B (PFAM) | reduced PCM | [16] | |||
| kinases | Plk1 (polo-like kinase 1) | Plk1 | PLK-1 | kinase, polo-box | reduced PCM, loss of phosphorylation of Cdk5Rap2/CNN, PCNT, and SPD-5 | [40–43] |
| AURKA (Aurora A kinase) | Aurora A | AIR-1 | kinase | centrosome separation defect, loss of effector recruitment (γ-tubulin, D-TACC, MSPS) | [44–46] | |
| phosphatases | PPP2ca | PP2A | LET-92 | phosphatase | centriole duplication defect, loss of MT stability via TPX2 and KLP-7, centrosome–nuclei detachment | [47,48] |
| PPP2r1a | PP2A-B | SUR-6 | regulatory subunit of PP2A | centriole duplication defect | [49] | |
| RSA-1 | regulatory subunit of PP2A | loss of MT stability | [47] | |||
| RSA-2 | regulatory subunit of PP2A | loss of MT stability | [47] | |||
| PP4c | PP4 | PPH4.1 | phosphatase | abberant pericentrin foci, loss of effectors and kinases (α- and γ-tubulin, PLK-1, Aurora A) | [50–53] | |
| effectors | γ-tubulin | γ-tubulin | γ-tubulin | tubulin | impaired spindle assembly, impaired MT nucleation | [3,54–57] |
| TACC2 | D-Tacc | TAC-1 | coiled coil (TACC domain) | loss of effectors (ZYG-9/ZYG-8), loss of MT stability | [58–61] | |
| CKAP5(chTOG) | Msps | ZYG-9 | MT binding, TOG domain | loss of MT stability, loss of centrosome integrity | [61–64] |
2. Formation of the inner pericentriolar material layer
How is the centriole-proximal ground layer laid? Mennella et al. [6] reported that D-PLP is organized with quasi-ninefold symmetry radiating outwards from the centrioles [6]. Furthermore, the outer boundary of the interphase PCM layer approximately matches the length of either D-PLP in fly embryos [6] or PCNT in human cells [7]. One interpretation of these results is that D-PLP and PCNT serve as molecular rulers to set the size of the inner PCM layer. Gopalakrishnan et al. [31] presented data indicating that, in centrosome-free Drosophila embryo extracts, D-PLP forms complexes with SAS-4, Cnn and γ-tubulin, all proteins discovered to occupy concentric toroidal domains within the interphase PCM [31]. These data suggest that the organization and size of the interphase PCM is established through the deposition of pre-assembled complexes of defined stoichiometry and size. This proposed model is intriguing but requires more rigorous biochemical assessment of reconstituted PCM proteins before becoming canonical. Studies in C. elegans indicate that this model may not apply to all systems. In the one-cell embryo, SAS-4-containing centrioles contributed by the sperm are sufficient to organize functional centrosomes even if the maternal pool of SAS-4 has been depleted by RNAi [30]. Thus, it is unlikely that SAS-4 organizes pre-assembled cytoplasmic complexes essential for PCM assembly in worms. Furthermore, mass spectrometry and fluorescence correlation spectroscopy experiments suggest that the core PCM components in C. elegans, SPD-2 and SPD-5, do not interact with each other or with SAS-4 in the cytoplasm, but rather exist as mainly monomeric entities prior to incorporation into the PCM (O. Wueseke 2014, unpublished data). These results argue that PCM assembly through the incorporation of large, pre-assembled units is not a universal mechanism found in all centrosome-containing eukaryotes.
3. Expansion of the pericentriolar material in mitosis
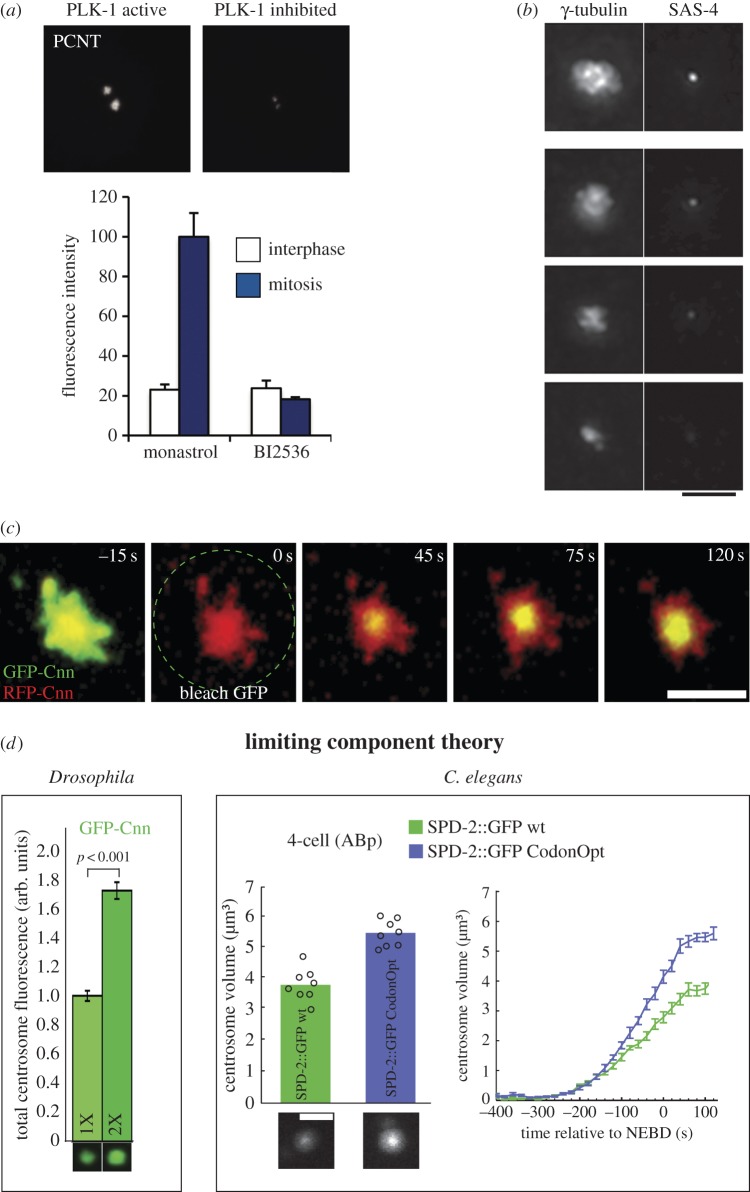
How does the expansive outer PCM layer assemble around the established inner PCM? Decades of cell biology and molecular genetics have indicated that this process of expansion is driven, in part, by kinase-regulated incorporation of core scaffolding proteins, MT-associated proteins (MAPs) and MT nucleating complexes. For instance, inhibition of polo kinase prevents accumulation of γ-tubulin at centrosomes and mitotic PCM expansion in humans, flies and worms (figure 2) [23,40,41,67,68]. Furthermore, polo kinase has been demonstrated to directly phosphorylate the core scaffold proteins pericentein, Cnn and SPD-5, and mutation of polo phosphorylation sites in these proteins precludes PCM assembly ([23,69], J. Woodruff and O. Wueseke 2014, unpublished data). Another important role is played by Aurora A kinase, which is necessary for PCM maturation and function by regulating the recruitment of MT-nucleating complexes and MAPs. For example, inhibition of Aurora A prevents recruitment of γ-tubulin and ZYG-9 (chTOG/Msps) in C. elegans embryos [44] and Msps and D-TACC in Drosophila S2 cells [46]. However, Aurora A inhibition had little effect on SPD-5 localization [16]. These data suggest that PLK-1 drives the assembly of the core structure of the mitotic PCM scaffold, whereas Aurora A stimulates the addition of downstream effector molecules like MAPs to the scaffold.
Figure 2.
Factors regulating PCM growth and final size. (a) Inhibition of PLK-1 kinase activity with the small molecule BI2436 reduces the incorporation of PCNT at centrosomes. Interestingly, inhibition of PLK-1 did not affect PCNT localization to the interphase centrosome. (Adapted from [42].) (b) γ-tubulin staining scales proportionally with the amount of SAS-4 localized to centrioles in C. elegans embryos, suggesting that centriole duplication and size determine PCM growth. Scale bar, 4 μm. (Adapted from [30].) (c) After photo-bleaching, GFP-Cnn first recovers at the centre of the centrosome, near the centrioles and then spreads outward to the periphery in Drosophila cells. This result indicates that Cnn is incorporated immediately around centrioles, suggesting that centrioles play a critical role in converting PCM proteins to an assembly-competent state. Scale bar, 3 μm. (Adapted from [35].) (d) Overexpression of Cnn and SPD-2 increases the final steady-state size of the PCM in Drosophila and C. elegans, respectively. SPD-2 expression levels were increased through a codon-optimization strategy for the C. elegans experiments (SPD-2::GFP CodonOpt, blue bar and line). These results suggest that Cnn and SPD-2 act as limiting components for the formation of PCM. Scale bar, 3 μm. (Adapted from [35,66].)
Interestingly, the requirement for kinase activity to drive PCM expansion can be bypassed in certain non-physiological situations. Overexpression of PCNT or CDK5RAP2 has been shown to artificially promote PCM expansion in interphase-arrested mammalian tissue culture cells. These hypertrophic centrosomes recruit a small amount of γ-tubulin and NEDD1, indicating that they are similar, but not identical, to normal mitotic centrosomes [7,70]. These results hint that the core PCM proteins can self-assemble without external stimulation by mitotic kinases like polo. Under physiological conditions, the effective concentration of the core PCM proteins may be too low to permit spontaneous self-assembly. During mitosis, polo kinase phosphorylation of the core PCM proteins could perhaps stimulate this assembly process. This model is still speculative, but it is consistent with the available data and would allow regulation of PCM assembly in a cell-cycle-dependent fashion.
4. Pericentriolar material disassembly
If phosphorylation of key core scaffold proteins drives PCM assembly and maturation, then it is reasonable to assume that dephosphorylation of these targets contributes to PCM dissolution. Indeed, in metaphase-arrested cells with mature centrosomes, acute inhibition of polo kinase activity promotes the removal of PCNT and γ-tubulin from the centrosome in human cells, indicating the existence of a constantly ongoing dephosphorylation reaction [71]. This result suggests that the cell drives the PCM towards assembly or dissolution by modulating the balance of phosphorylation and dephosphorylation activities inside the PCM. Although this hypothesis is tantalizing, a phosphatase that promotes PCM dissolution has yet to be identified. So far, two major phosphatases have been reported to localize to centrosomes and participate in the regulation of PCM dynamics, namely protein phosphatase 4 (PPH4) and protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A) [47,48,50–52,72]. PPH4 was reported to be required for centrosomal recruitment of Aurora A and γ-tubulin, indicating that it plays a role in centrosome maturation [50–52,72]. PP2A, on the other hand, was found to act on centrosomal effector molecules like the MT-destabilizing kinesin KLP-7 as well as TPX-2 to modulate spindle size in C. elegans [47]. It will be important to determine in the future whether PP2A, PPH4, or any other phosphatase directly influences PCM dissolution, and or de-phosphorylates PLK-1 substrates needed for PCM assembly.
Cortical forces may also tear apart PCM during mitotic exit. After anaphase completion in C. elegans embryos, γ-tubulin::GFP-labelled centrosomes not only become dimmer, indicating the loss of PCM protein, but also rip apart in a cortical-directed manner [66,73]. Elimination of MTs, the dynein heavy chain dhc1, or MT attachment sites on the embryo cortex prevent this dramatic rupturing of PCM [73], implicating a MT motor-driven mechanism for PCM dissolution. Although not essential for PCM disassembly, these MT-dependent cortical forces accelerate the process. One potential explanation is that the rupturing of PCM increases the surface to volume ratio of the PCM, thereby expediting the dephosphorylation reaction. A similar mechanism may also exist in flies. PCM fragments often emerge and radiate away from centrosomes in Drosophila embryos in a process termed ‘flaring’ [74]. Flaring events were shown to be dependent on MTs and reach maximal intensity during telophase and interphase, coordinate with PCM disassembly. Taken together, these findings indicate that the combination of PLK-1 inactivation, phosphatase activity and MT-dependent forces ensure the rapid disassembly of PCM during mitotic exit.
5. Factors regulating pericentriolar material growth kinetics and final size
Like any intracellular organelle, the size of a centrosome is set for any individual cell type. This is especially clear in early C. elegans embryos, where the total amount of centrosome material is constant. Altering the number of centrosomes in a one-cell embryo will change the size of each individual centrosome, but the sum of centrosome volume will remain the same. For example, if a one-cell embryo contains four centrosomes instead of two, then each centrosome will be half the expected size [66,75]. What are the factors that determine PCM expansion and its maximum size? Both centriole-dependent and -independent mechanisms seem to be required.
One mechanism centres around the role of centrioles, as centriolar proteins and overall centriole size were found to affect PCM size. Proper centriole duplication is an essential step towards PCM accumulation around centrioles [76]. In C. elegans two-cell embryos, partial RNAi-depletion of SAS-4 inhibits centriolar duplication to varying degrees and reveals that PCM size directly correlates with the amount of centriole-localized SAS-4 [30]. This result suggests that centrioles directly determine the incorporation rate of PCM components. This idea is supported by photo-bleaching experiments in Drosophila embryos which showed that Cnn incorporates exclusively in the vicinity of centrioles and then migrates outward towards the periphery to form the bulk of the mitotic PCM [35]. Thus, localizing and binding to centrioles may be a universal rate-limiting step for the incorporation of PCM components. Such a mechanism is favourable in that it would also ensure that PCM only forms around centrioles. As SAS-4 is critical for PCM accumulation around centrioles, and that Cnn, D-PLP, γ-tubulin and other PCM proteins have been identified in SAS-4-containing complexes in Drosophila [31], SAS-4 could act as a centriolar tether and a key control point for regulating PCM assembly.
There is also evidence that PCM proteins can assemble independently of the centriole, suggesting that an additional process regulates PCM growth kinetics. For example, overexpression of either Cnn or an Asterless mutant that cannot bind Plk-4 induced the formation of ectopic, acentriolar MT organizing centres in Drosophila [29,77]. Furthermore, in acentriolar mouse oocytes, PCNT forms perinuclear assemblies that localize γ-tubulin and orchestrate MT behaviour similar to mitotic centriolar-nucleated PCM [78,79]. Whether or not other nucleation sites like the surface of the nucleus mimic the role of the centriole in this case, or whether the process does not require a nucleation site at all, remains to be seen. In total, these results argue that PCM itself can stimulate the formation of additional PCM. Such an autocatalytic mechanism would drastically increase the overall incorporation rate of PCM and is probably essential for the C. elegans embryo and other systems that require robust PCM expansion over very short mitotic phases (e.g. in the C. elegans one-cell embryo, the PCM enlarges 60-fold in approx. 8 min) [66]. Systems with smaller final centrosome size or extended mitotic phases might not require such a mechanism to accelerate PCM assembly.
Rates for most biological reactions are directly related to the concentration of the starting material, indicating that PCM growth could be set by concentration, and PCM size set by total amount, of PCM proteins within the cytoplasm. This is certainly the case in the C. elegans embryo, where centrosome size decreases in direct proportion to the cytoplasmic volume, and thus total available PCM components, during development. Moreover, in this system, overexpression of the limiting component SPD-2 increased the rate of PCM growth and its maximum achievable size [66]. Likewise, in Drosophila embryos, increasing the cytoplasmic concentration of Cnn also increased PCM size and growth rate [35]. The fact that recruitment of Cnn to the PCM depends on its interaction with SPD-2 argues that a SPD-2-centred mechanism to regulate PCM growth and size is conserved throughout evolution [35]. Exhaustion of a limiting component could perhaps also explain the characteristic plateau in centrosome size seen during mitosis in both C. elegans and Drosphila embryos [35,66]. Recent experiments on spindle length in Xenopus extracts encased in artificial cells suggest that spindle size is also limited by the availability of certain components like tubulin [80,81]. Thus, a limiting component mechanism could be a general way of setting the size of intracellular organelles in early embryos [75].
6. Outlook
(a). A unified model for pericentriolar material dynamics
The complexity and seemingly disorganized nature of the PCM has made determining its underlying structure and the mechanism of its assembly challenging. As investigations become more sophisticated and more of the complex puzzle is solved, common themes are emerging across the tree of life (figure 3).
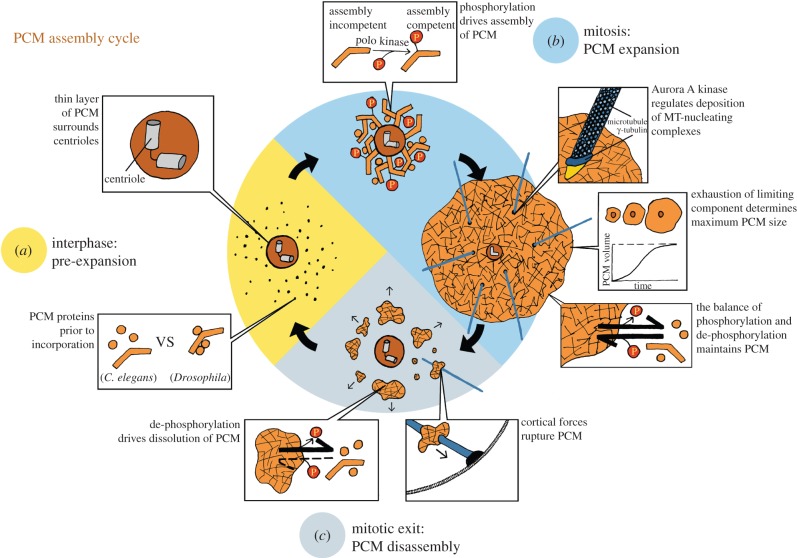
Figure 3.
The PCM assembly cycle in embryonic systems. (a) During interphase, a thin layer of PCM surrounds the centrioles. In the cytoplasm are unincorporated PCM proteins, and there are species-specific differences in their assembly state. In C. elegans, the unincorporated core PCM components are separate entities, whereas in Drosophila, the core PCM proteins may already be pre-assembled into small complexes of defined stoichiometry. (b) As the cell progresses into mitosis, polo kinase phosphorylates the key scaffolding proteins, thereby inducing their incorporation around the established inner PCM layer. This new addition of protein causes the PCM to expand dramatically. As the mitotic PCM expands, Aurora A kinase phosphorylation promotes the deposition of protein complexes that aid in nucleating and stabilizing MTs (blue lines). The steady-state size of the PCM is determined by the total amount of a limiting component and the rates of phosphorylation and de-phosphorylation reactions. (c) Once mitosis is complete, MT-mediated cortical forces rupture the PCM, and protein phosphatases remove polo kinase-derived phosphorylations from the scaffold proteins. These two activities promote rapid disassembly of the mitotic PCM. (Illustration courtesy of Julia Eichhorn.)
Assembly of PCM begins with the deposition of an ordered layer approximately 100 nm thick that encases the centrioles. As the cell cycle advances towards mitosis, polo kinase phosphorylation transforms the cytosolic PCM proteins into assembly-competent building blocks, thus driving their deposition around the already established inner PCM layer. SPD-5, PCNT/D-PLP, Cnn/CDK5RAP2 and Asterless/Cep152 play important scaffolding roles and are presumed to interconnect to form a lattice-like network that establishes the structural foundation of the PCM. Interestingly, based on comparing amino acid sequences across phyla, C. elegans lacks PCNT, Cnn and Asterless, proteins that are essential for PCM formation in Drosophila and humans. Instead, PCM formation in C. elegans depends on the expression of SPD-5, a 135 kDa coiled-coil protein that is not expressed outside of nematodes. Considering that PCNT, Cnn, Asterless and SPD-5 all contain numerous coiled-coil domains, it may be that SPD-5 assumes the function of these proteins in forming the comparatively simplified C. elegans centrosome. Furthermore, like PCNT and Cnn, SPD-5 is a key target of polo kinase and its phosphorylation is essential for PCM expansion (J. Woodruff and O. Wueseke 2014, unpublished data). In vitro comparison of the structures and biochemical activities of purified PCNT, Cnn, Asterless and SPD-5 will be essential before drawing any concrete connection between them. Nevertheless, we can conclude that PCM expansion is probably driven by the assembly of a few scaffolding proteins. Polo kinase and SPD-2, both of which are conserved proteins, regulate this process. In embryonic systems, the rates and final sizes of centrosomes are determined by limiting amounts of one or more of these proteins.
How PCM disassembles in a timely fashion at the end of mitosis is less clear. Dephosphorylation probably plays a major role in driving the PCM building blocks out of the assembly-competent state and thus dissolving the centromatrix. Additional pathways, including MT-mediated cortical forces could assist this process by rupturing the PCM, thus making the building blocks more accessible to protein phosphatases. We also cannot discount the possibility of protein degradation in controlling the levels of PCM protein, including polo kinase. This topic of research has only just begun, making it difficult to ascribe a specific mechanism to PCM disassembly or even speculate on the conservation of this process.
(b). Microtubule nucleation in the twenty-first century
The historical role of the PCM has been to nucleate MTs needed for spindle assembly, spindle positioning and intracellular transport. So how does our understanding of PCM structure and dynamics affect our view of MT-nucleation within the PCM? The traditional view proposes that the PCM serves as a binding platform for γ-tubulin-containing complexes that induce MT nucleation. Certainly, γ-tubulin associates with PCNT and SAS-4, and elimination of γ-tubulin reduces MT mass extending from the centrosome [31,32,82]. So far, however, γ-tubulin complexes are poor MT nucleators in vitro, and MT asters can still form in the absence of γ-tubulin in vivo, indicating that additional mechanisms exist to nucleate MTs (reviewed in [83]). Tumour overexpressed gene (TOG) proteins such as chTOG/ZYG-9 localize to the PCM, bind MTs directly and increase MT polymerization rates and nucleation in vitro, making them attractive candidates to regulate MT nucleation within the centrosome. Additionally, it has been shown that SAS-4/Cnn/Asterless/D-PLP-containing (S-CAP) complexes bind to α/β tubulin dimers [31]. Emerging evidence suggests that these S-CAP complexes form the underlying PCM lattice, meaning that the PCM has an abundance of α/β tubulin-binding sites. Diffusion of α/β tubulin dimers into the PCM and subsequent interaction with these binding sites could promote concentration of tubulin far above cytoplasmic background levels and thus favour spontaneous MT nucleation within the PCM. Indeed, in vivo fluorescence correlation spectroscopy and in silico models suggest that a similar mechanism regulates steady-state concentration of PLK-1 within the PCM [71]. It is possible, then, that the PCM network can concentrate tubulin to the point where MTs spontaneously nucleate. In this model, the role of γ-tubulin could be to cap MTs to provide stability and protect them from depolymerization at the minus ends, while additional MAPs stabilize MTs and drive polymerization of the plus ends.
(c). The pericentriolar material going forward
As seen for analysis of the PCM structure, novel techniques or approaches play a tremendous role in advancing a field. Emerging techniques such as selective chemical cross-linking (e.g. BioID and S-CROSS) [84,85] and cryo-electron tomography combined with focused-ion-beam milling [86] will certainly yield high-resolution information about the structure and hierarchy of PCM proteins in situ. But, the pressing mechanistic questions regarding PCM dynamics and function also require an experimental approach that permits precise control over the molecular machinery therein. In vitro reconstitution of a minimal PCM system would grant this kind of accessibility and control. The open questions addressable by such a system are numerous. What are the minimal requirements needed to initiate PCM assembly? How does phosphorylation affect the connectivity and activity of the major scaffold proteins? How does the PCM concentrate α/β tubulin and drive the nucleation of MTs in the absence of γ-tubulin? Furthermore, structural analysis of PCM assembled from minimal components in vitro could also yield atomic-scale resolution of the ‘centromatrix’ and its constituent proteins.
The study of PCM dynamics and structure will certainly clarify how centrosomes serve as MT-organizing centres, trafficking hubs and signalling platforms for the eukaryotic cell. Hopefully, the lessons learned from centrosomes will also shed light on the basic biophysical principles behind the formation of self-assembling macromolecular complexes, including other non-membrane-bound organelles.
References
- 1.Robbins E, Jentzsch G, Micali A. 1968. The centriole cycle in synchronized HeLa cells. J. Cell Biol. 36, 329–339. ( 10.1083/jcb.36.2.329) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Gould RR, Borisy GG. 1977. The pericentriolar material in Chinese hamster ovary cells nucleates microtubule formation. J. Cell Biol. 73, 601–615. ( 10.1083/jcb.73.3.601) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Moritz M, Braunfeld MB, Sedat JW, Alberts B, Agard DA. 1995. Microtubule nucleation by gamma-tubulin-containing rings in the centrosome. Nature 378, 638–640. ( 10.1038/378638a0) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Moritz M, Braunfeld MB, Guénebaut V, Heuser J, Agard DA. 2000. Structure of the gamma-tubulin ring complex: a template for microtubule nucleation. Nat. Cell Biol. 2, 365–370. ( 10.1038/35014058) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Schnackenberg BJ, Khodjakov A, Rieder CL, Palazzo RE. 1998. The disassembly and reassembly of functional centrosomes in vitro. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 95, 9295–9300. ( 10.1073/pnas.95.16.9295) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Mennella V, Keszthelyi B, McDonald KL, Chhun B, Kan F, Rogers GC, Huang B, Agard DA. 2012. Subdiffraction-resolution fluorescence microscopy reveals a domain of the centrosome critical for pericentriolar material organization. Nat. Cell Biol. 14, 1159–1168. ( 10.1038/ncb2597) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Lawo S, Hasegan M, Gupta GD, Pelletier L. 2012. Subdiffraction imaging of centrosomes reveals higher-order organizational features of pericentriolar material. Nat. Cell Biol. 14, 1148–1158. ( 10.1038/ncb2591) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Sonnen KF, Schermelleh L, Leonhardt H, Nigg EA. 2012. 3D-structured illumination microscopy provides novel insight into architecture of human centrosomes. Biol. Open 1, 965–976. ( 10.1242/bio.20122337) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Paintrand M, Moudjou M, Delacroix H, Bornens M. 1992. Centrosome organization and centriole architecture: their sensitivity to divalent cations. J. Struct. Biol. 108, 107–128. ( 10.1016/1047-8477(92)90011-X) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Tuffanelli DL. 1983. Anticentromere and anticentriole antibodies in the scleroderma spectrum. Arch. Dermatol. 119, 560 ( 10.1001/archderm.1983.01650310022004) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Gosti-Testu F, Marty MC, Berges J, Maunoury R, Bornens M. 1986. Identification of centrosomal proteins in a human lymphoblastic cell line. EMBO J. 5, 2545–2550. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Doxsey SJ, Stein P, Evans L, Calarco PD, Kirschner M. 1994. Pericentrin, a highly conserved centrosome protein involved in microtubule organization. Cell 76, 639–650. ( 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90504-5) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Pelletier L, Özlü N, Hannak E, Cowan C, Habermann B, Ruer M, Müller-Reichert T, Hyman AA. 2004. The Caenorhabditis elegans centrosomal protein SPD-2 is required for both pericentriolar material recruitment and centriole duplication. Curr. Biol. 14, 863–873. ( 10.1016/j.cub.2004.04.012) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Varmark H, Llamazares S, Rebollo E, Lange B, Reina J, Schwarz H, Gonzalez C. 2007. Asterless is a centriolar protein required for centrosome function and embryo development in Drosophila. Curr. Biol. 17, 1735–1745. ( 10.1016/j.cub.2007.09.031) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Vaizel-Ohayon D, Schejter ED. 1999. Mutations in centrosomin reveal requirements for centrosomal function during early Drosophila embryogenesis. Curr. Biol. 9, 889–898. ( 10.1016/S0960-9822(99)80393-5) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Hamill DR, Severson AF, Carter JC, Bowerman B. 2002. Centrosome maturation and mitotic spindle assembly in C. elegans require SPD-5, a protein with multiple coiled-coil domains. Dev. Cell 3, 673–684. ( 10.1016/S1534-5807(02)00327-1) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Andersen JS, Wilkinson CJ, Mayor T, Mortensen P, Nigg EA, Mann M. 2003. Proteomic characterization of the human centrosome by protein correlation profiling. Nature 426, 570–574. ( 10.1038/nature02166) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Bonaccorsi S, Giansanti MG, Gatti M. 1998. Spindle self-organization and cytokinesis during male meiosis in asterless mutants of Drosophila melanogaster. J. Cell Biol. 142, 751–761. ( 10.1083/jcb.142.3.751) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Lupas A, Van Dyke M, Stock J. 1991. Predicting coiled coils from protein sequences. Science 252, 1162–1164. ( 10.1126/science.252.5009.1162) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Salisbury JL. 2003. Centrosomes: coiled-coils organize the cell center. Curr. Biol. 13, R88–R90. ( 10.1016/S0960-9822(03)00033-2) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Sönnichsen B, et al. 2005. Full-genome RNAi profiling of early embryogenesis in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature 434, 462–469. ( 10.1038/nature03353) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Goshima G, Wollman R, Goodwin SS, Zhang N, Scholey JM, Vale RD, Stuurman N. 2007. Genes required for mitotic spindle assembly in Drosophila S2 cells. Science 316, 417–421. ( 10.1126/science.1141314) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Dobbelaere J, Josué F, Suijkerbuijk S, Baum B, Tapon N, Raff J. 2008. A genome-wide RNAi screen to dissect centriole duplication and centrosome maturation in Drosophila. PLoS Biol. 6, e224 ( 10.1371/journal.pbio.0060224) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Hutchins JRA, et al. 2010. Systematic analysis of human protein complexes identifies chromosome segregation proteins. Science 328, 593–599. ( 10.1126/science.1181348) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Neumann B, et al. 2010. Phenotypic profiling of the human genome by time-lapse microscopy reveals cell division genes. Nature 464, 721–727. ( 10.1038/nature08869) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Giansanti MG, Bucciarelli E, Bonaccorsi S, Gatti M. 2008. Drosophila SPD-2 is an essential centriole component required for PCM recruitment and astral-microtubule nucleation. Curr. Biol. 18, 303–309. ( 10.1016/j.cub.2008.01.058) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Gomez-Ferreria MA, Rath U, Buster DW, Chanda SK, Caldwell JS, Rines DR, Sharp DJ. 2007. Human Cep192 is required for mitotic centrosome and spindle assembly. Curr. Biol. 17, 1960–1966. ( 10.1016/j.cub.2007.10.019) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Kemp CA, Kopish KR, Zipperlen P, Ahringer J, O'Connell KF. 2004. Centrosome maturation and duplication in C. elegans require the coiled-coil protein SPD-2. Dev. Cell 6, 511–523. ( 10.1016/S1534-5807(04)00066-8) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Dzhindzhev NS, et al. 2010. Asterless is a scaffold for the onset of centriole assembly. Nature 467, 714–718. ( 10.1038/nature09445) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Kirkham M, Müller-Reichert T, Oegema K, Grill S, Hyman AA. 2003. SAS-4 is a C. elegans centriolar protein that controls centrosome size. Cell 112, 575–587. ( 10.1016/S0092-8674(03)00117-X) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Gopalakrishnan J, et al. 2011. Sas-4 provides a scaffold for cytoplasmic complexes and tethers them in a centrosome. Nat. Commun. 2, 359 ( 10.1038/ncomms1367) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Dictenberg JB, Zimmerman W, Sparks CA, Young A, Vidair C, Zheng Y, Carrington W, Fay FS, Doxsey SJ. 1998. Pericentrin and gamma-tubulin form a protein complex and are organized into a novel lattice at the centrosome. J. Cell Biol. 141, 163–174. ( 10.1083/jcb.141.1.163) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Zimmerman WC, Sillibourne J, Rosa J, Doxsey SJ. 2004. Mitosis-specific anchoring of tubulin complexes by pericentrin controls spindle organization and mitotic entry. Mol. Biol. Cell 15, 3642–3657. ( 10.1091/mbc.E03-11-0796) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Martinez-Campos M, Basto R, Baker J, Kernan M, Raff JW. 2004. The Drosophila pericentrin-like protein is essential for cilia/flagella function, but appears to be dispensable for mitosis. J. Cell Biol. 165, 673–683. ( 10.1083/jcb.200402130) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Conduit PT, Brunk K, Dobbelaere J, Dix CI, Lucas EP, Raff JW. 2010. Centrioles regulate centrosome size by controlling the rate of Cnn incorporation into the PCM. Curr. Biol. 20, 2178–2186. ( 10.1016/j.cub.2010.11.011) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Lucas EP, Raff JW. 2007. Maintaining the proper connection between the centrioles and the pericentriolar matrix requires Drosophila centrosomin. J. Cell Biol. 178, 725–732. ( 10.1083/jcb.200704081) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Megraw TL, Li K, Kao LR, Kaufman TC. 1999. The centrosomin protein is required for centrosome assembly and function during cleavage in Drosophila. Development 126, 2829–2839. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Takahashi M, Yamagiwa A, Nishimura T, Mukai H, Ono Y. 2002. Centrosomal proteins CG-NAP and kendrin provide microtubule nucleation sites by anchoring gamma-tubulin ring complex. Mol. Biol. Cell 13, 3235–3245. ( 10.1091/mbc.E02-02-0112) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Keryer G, Witczak O, Delouvée A, Kemmner WA, Rouillard D, Tasken K, Bornens M. 2003. Dissociating the centrosomal matrix protein AKAP450 from centrioles impairs centriole duplication and cell cycle progression. Mol. Biol. Cell 14, 2436–2446. ( 10.1091/mbc.E02-09-0614) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Sunkel CE, Glover DM. 1988. Polo, a mitotic mutant of Drosophila displaying abnormal spindle poles. J. Cell Sci. 89, 25–38. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Chase D, Golden A, Heidecker G, Ferris DK. 2000. Caenorhabditis elegans contains a third polo-like kinase gene. DNA Seq. 11, 327–334. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Haren L, Stearns T, Lüders J. 2009. Plk1-dependent recruitment of γ-tubulin complexes to mitotic centrosomes involves multiple PCM components. PLoS ONE 4, e5976 ( 10.1371/journal.pone.0005976) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Santamaria A, et al. 2010. The Plk1-dependent phosphoproteome of the early mitotic spindle. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 53, M110.004457 ( 10.1074/mcp.M110.004457) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Hannak E. 2001. Aurora-A kinase is required for centrosome maturation in Caenorhabditis elegans. J. Cell Biol. 155, 1109–1116. ( 10.1083/jcb.200108051) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Glover DM, Leibowitz MH, McLean DA, Parry H. 1995. Mutations in aurora prevent centrosome separation leading to the formation of monopolar spindles. Cell 81, 95–105. ( 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90374-7) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Giet R, McLean D, Descamps S, Lee MJ, Raff JW, Prigent C, Glover DM. 2002. Drosophila Aurora: a kinase is required to localize D-TACC to centrosomes and to regulate astral microtubules. J. Cell Biol. 156, 437–451. ( 10.1083/jcb.200108135) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Schlaitz A-L, et al. 2007. The C. elegans RSA complex localizes protein phosphatase 2A to centrosomes and regulates mitotic spindle assembly. Cell 128, 115–127. ( 10.1016/j.cell.2006.10.050) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Sontag E, Nunbhakdi-Craig V, Bloom GS, Mumby MC. 1995. A novel pool of protein phosphatase 2A is associated with microtubules and is regulated during the cell cycle. J. Cell Biol. 128, 1131–1144. ( 10.1083/jcb.128.6.1131) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Song MH, Liu Y, Anderson DE, Jahng WJ, O'Connell KF. 2011. Protein phosphatase 2A-SUR-6/B55 regulates centriole duplication in C. elegans by controlling the levels of centriole assembly factors. Dev. Cell 20, 563–571. ( 10.1016/j.devcel.2011.03.007) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Sumiyoshi E, Sugimoto A, Yamamoto M. 2002. Protein phosphatase 4 is required for centrosome maturation in mitosis and sperm meiosis in C. elegans. J. Cell Sci. 115, 1403–1410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Helps NR, Brewis ND, Lineruth K, Davis T, Kaiser K, Cohen PT. 1998. Protein phosphatase 4 is an essential enzyme required for organisation of microtubules at centrosomes in Drosophila embryos. J. Cell Sci. 111, 1331–1340. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Han X, Gomes J-E, Birmingham CL, Pintard L, Sugimoto A, Mains PE. 2009. The role of protein phosphatase 4 in regulating microtubule severing in the Caenorhabditis elegans embryo. Genetics 181, 933–943. ( 10.1534/genetics.108.096016) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Xie Y, Jüschke C, Esk C, Hirotsune S, Knoblich JA. 2013. The phosphatase PP4c controls spindle orientation to maintain proliferative symmetric divisions in the developing neocortex. Neuron 79, 254–265. ( 10.1016/j.neuron.2013.05.027) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Zheng Y, Jung MK, Oakley BR. 1991. Gamma-tubulin is present in Drosophila melanogaster and Homo sapiens and is associated with the centrosome. Cell 65, 817–823. ( 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90389-G) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Sunkel CE, Gomes R, Sampaio P, Perdigão J, González C. 1995. Gamma-tubulin is required for the structure and function of the microtubule organizing centre in Drosophila neuroblasts. EMBO J. 14, 28–36. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Barbosa V, Yamamoto RR, Henderson DS, Glover DM. 2000. Mutation of a Drosophila gamma tubulin ring complex subunit encoded by discs degenerate-4 differentially disrupts centrosomal protein localization. Genes Dev. 14, 3126–3139. ( 10.1101/gad.182800) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Hannak E, Oegema K, Kirkham M, Gönczy P, Habermann B, Hyman AA. 2002. The kinetically dominant assembly pathway for centrosomal asters in Caenorhabditis elegans is gamma-tubulin dependent. J. Cell Biol. 157, 591–602. ( 10.1083/jcb.200202047) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Gergely F, Kidd D, Jeffers K, Wakefield JG, Raff JW. 2000. D-TACC: a novel centrosomal protein required for normal spindle function in the early Drosophila embryo. EMBO J. 19, 241–252. ( 10.1093/emboj/19.2.241) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Gergely F, Karlsson C, Still I, Cowell J, Kilmartin J, Raff JW. 2000. The TACC domain identifies a family of centrosomal proteins that can interact with microtubules. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 97, 14 352–14 357. ( 10.1073/pnas.97.26.14352) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Srayko M, Quintin S, Schwager A, Hyman AA. 2003. Caenorhabditis elegans TAC-1 and ZYG-9 form a complex that is essential for long astral and spindle microtubules. Curr. Biol. 13, 1506–1511. ( 10.1016/S0960-9822(03)00597-9) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Bellanger J-M, Carter JC, Phillips JB, Canard C, Bowerman B, Gönczy P. 2007. ZYG-9, TAC-1 and ZYG-8 together ensure correct microtubule function throughout the cell cycle of C. elegans embryos. J. Cell Sci. 120, 2963–2973. ( 10.1242/jcs.004812) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Gergely F, Draviam VM, Raff JW. 2003. The ch-TOG/XMAP215 protein is essential for spindle pole organization in human somatic cells. Genes Dev. 17, 336–341. ( 10.1101/gad.245603) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Cassimeris L, Morabito J. 2004. TOGp, the human homolog of XMAP215/Dis1, is required for centrosome integrity, spindle pole organization, and bipolar spindle assembly. Mol. Biol. Cell 15, 1580–1590. ( 10.1091/mbc.E03-07-0544) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Spittle C, Charrasse S, Larroque C, Cassimeris L. 2000. The interaction of TOGp with microtubules and tubulin. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 20 748–20 753. ( 10.1074/jbc.M002597200) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Fu J, Glover DM. 2012. Structured illumination of the interface between centriole and peri-centriolar material. Open Biol. 2, 120104 ( 10.1016/j.ydbio.2010.10.021) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Decker M, Jaensch S, Pozniakovsky A, Zinke A, O'Connell KF, Zachariae W, Myers E, Hyman AA. 2011. Limiting amounts of centrosome material set centrosome size in C. elegans embryos. Curr. Biol. 21, 1259–1267. ( 10.1016/j.cub.2011.06.002) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Lee K, Rhee K. 2011. PLK1 phosphorylation of pericentrin initiates centrosome maturation at the onset of mitosis. J. Cell Biol. 195, 9 ( 10.1083/jcb.201106093) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Lane HA, Nigg EA. 1996. Antibody microinjection reveals an essential role for human polo-like kinase 1 (Plk1) in the functional maturation of mitotic centrosomes. J. Cell Biol. 135, 1701–1713. ( 10.1083/jcb.135.6.1701) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Lee K, Rhee K. 2011. PLK1 phosphorylation of pericentrin initiates centrosome maturation at the onset of mitosis. J. Cell Biol. 195, 1093–1101. ( 10.1083/jcb.201106093) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Loncarek J, Hergert P, Magidson V, Khodjakov A. 2008. Control of daughter centriole formation by the pericentriolar material. Nat. Cell Biol. 10, 322–328. ( 10.1038/ncb1694) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Mahen R, Jeyasekharan AD, Barry NP, Venkitaraman AR. 2011. Continuous polo-like kinase 1 activity regulates diffusion to maintain centrosome self-organization during mitosis. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 108, 9310–9315. ( 10.1073/pnas.1101112108) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Martin-Granados C, Philp A, Oxenham SK, Prescott AR, Cohen PTW. 2008. Depletion of protein phosphatase 4 in human cells reveals essential roles in centrosome maturation, cell migration and the regulation of Rho GTPases. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 40, 2315–2332. ( 10.1016/j.biocel.2008.03.021) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Krueger LE, Wu J-C, Tsou M-FB, Rose LS. 2010. LET-99 inhibits lateral posterior pulling forces during asymmetric spindle elongation in C. elegans embryos. J. Cell Biol. 189, 481–495. ( 10.1083/jcb.201001115) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Megraw TL, Kilaru S, Turner FR, Kaufman TC. 2002. The centrosome is a dynamic structure that ejects PCM flares. J. Cell Sci. 115, 4707–4718. ( 10.1242/jcs.00134) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Goehring NW, Hyman AA. 2012. Organelle growth control through limiting pools of cytoplasmic components. Curr. Biol. 22, R330–R339. ( 10.1016/j.cub.2012.03.046) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Kim S, Kim S, Rhee K. 2011. NEK7 is essential for centriole duplication and centrosomal accumulation of pericentriolar material proteins in interphase cells. J. Cell Sci. 124, 3760–3770. ( 10.1242/jcs.078089) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Terada Y. 2003. Interaction of Aurora-A and centrosomin at the microtubule-nucleating site in Drosophila and mammalian cells. J. Cell Biol. 162, 757–764. ( 10.1083/jcb.200305048) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Luksza M, Queguigner I, Verlhac M-H, Brunet S. 2013. Rebuilding MTOCs upon centriole loss during mouse oogenesis. Dev. Biol. 382, 48–56. ( 10.1016/j.ydbio.2013.07.029) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Gueth-Hallonet C, Antony C, Aghion J, Santa-Maria A, Lajoie-Mazenc I, Wright M, Maro B. 1993. gamma-tubulin is present in acentriolar MTOCs during early mouse development. J. Cell Sci. 105, 10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Good MC, Vahey MD, Skandarajah A, Fletcher DA, Heald R. 2013. Cytoplasmic volume modulates spindle size during embryogenesis. Science 342, 856–860. ( 10.1126/science.1243147) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Hazel J, Krutkramelis K, Mooney P, Tomschik M, Gerow K, Oakey J, Gatlin JC. 2013. Changes in cytoplasmic volume are sufficient to drive spindle scaling. Science 342, 853–856. ( 10.1126/science.1243110) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Kollman JM, Merdes A, Mourey L, Agard DA. 2011. Microtubule nucleation by γ-tubulin complexes. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 12, 709–721. ( 10.1038/nrm3209) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Wiese C, Zheng Y. 2006. Microtubule nucleation: gamma-tubulin and beyond. J. Cell Sci. 119, 4143–4153. ( 10.1242/jcs.03226) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Roux KJ, Kim DI, Raida M, Burke B. 2012. A promiscuous biotin ligase fusion protein identifies proximal and interacting proteins in mammalian cells. J. Cell Biol. 196, 801–810. ( 10.1083/jcb.201112098) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Lukinavičius G, Lavogina D, Orpinell M, Umezawa K, Reymond L, Garin N, Gönczy P, Johnsson K. 2013. Selective chemical crosslinking reveals a Cep57-Cep63-Cep152 centrosomal complex. Curr. Biol. 23, 265–270. ( 10.1016/j.cub.2012.12.030) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Villa E, Schaffer M, Plitzko JM, Baumeister W. 2013. Opening windows into the cell: focused-ion-beam milling for cryo-electron tomography. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 23, 771–777. ( 10.1016/j.sbi.2013.08.006) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]