Abstract
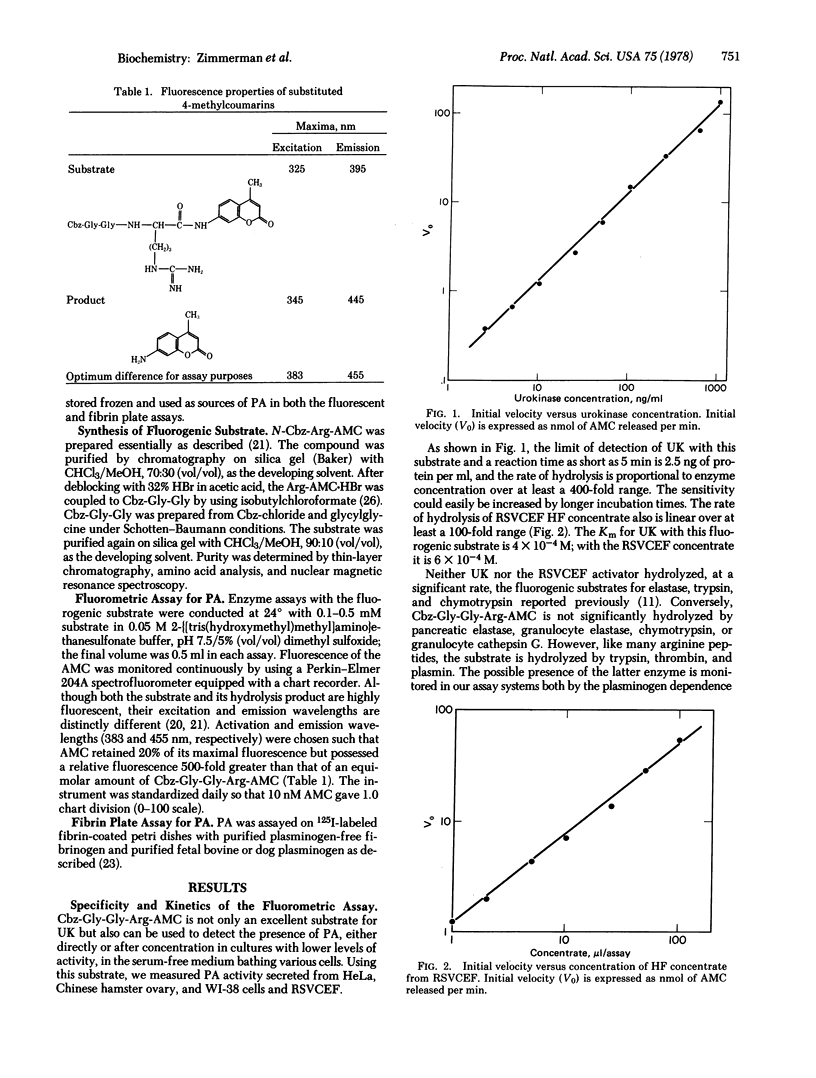
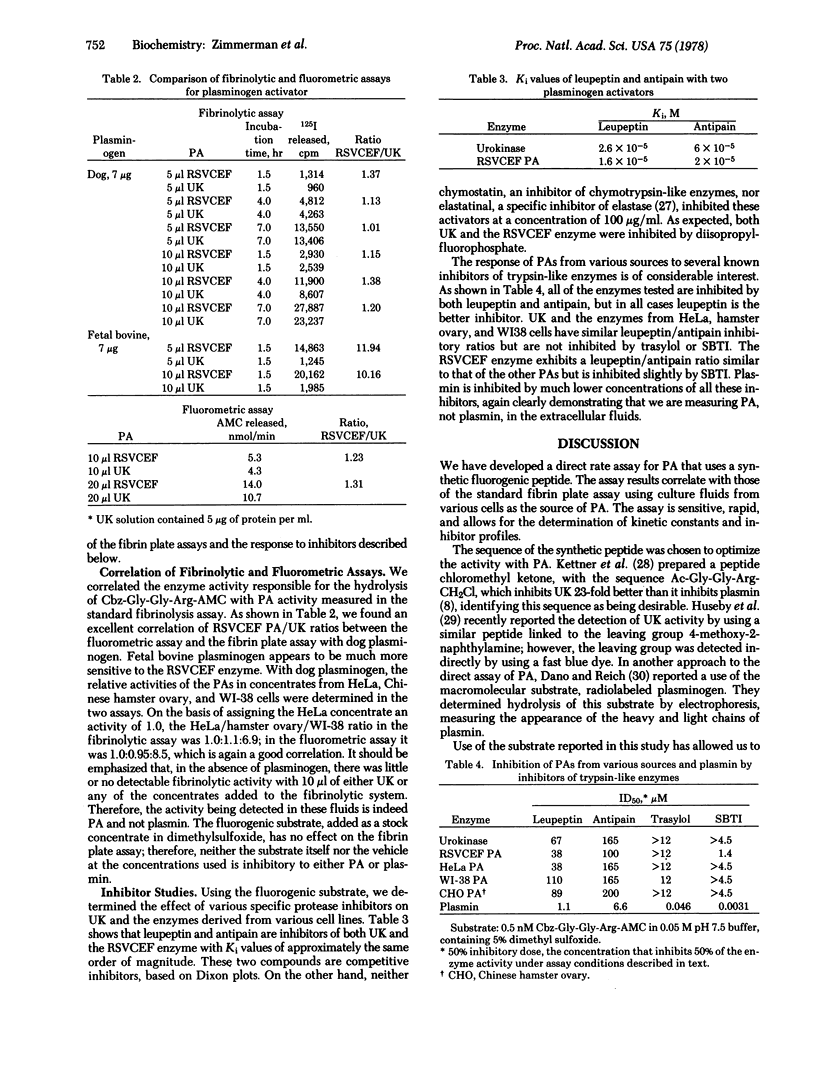
A direct rate assay for plasminogen activator has been developed using a synthetic fluorogenic peptide substrate, 7-(N-Cbz-glycylglycylargininamido)-4-methylcoumarin trifluoroacetate. The assay correlates well with the standard 125I-labeled fibrin plate assay using highly purified urokinase, culture fluids from WI-38, Chinese hamster vary or HeLa cells, or Rous sarcoma virus-transformed chick fibroblasts as the source of plasminogen activator. The assay is sensitive, rapid, and linear throughout a wide range of enzyme concentrations. With this substrate it is possible to determine inhibitor profiles for the various plasminogen activators, independently of the interfering potential of plasmin. All of the enzymes tested are inhibited by leupeptin and antipain but not by the related aldehydes, elastatinal and chymostatin. The macromolecular inhibitors soybean trypsin inhibitor and trasylol have little or no effect on the plasminogen activators tested. This substrate should be useful for the study of the effect of various agents on functional changes in cells secreting this enzyme and also should allow kinetic measurements of potential inhibitors.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ASTRUP T., MULLERTZ S. The fibrin plate method for estimating fibrinolytic activity. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1952 Oct;40(2):346–351. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(52)90121-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner B. M. Functional and structural determinants of glomerular filtration. A brief historical perspective. Fed Proc. 1977 Nov;36(12):2599–2601. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christman J. K., Silagi S., Newcomb E. W., Silverstein S. C., Acs G. Correlated suppression by 5-bromodeoxyuridine of tumorigenicity and plasminogen activator in mouse melanoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jan;72(1):47–50. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.1.47. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg A. R. Increased protease levels in transformed cells: a casein overlay assay for the detection of plasminogen activator production. Cell. 1974 Jun;2(2):95–102. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(74)90097-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higuchi K. An improved chemically defined culture medium for strain L mouse cells based on growth responses to graded levels of nutrients including iron and zinc ions. J Cell Physiol. 1970 Feb;75(1):65–72. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040750108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huseby R. M., Clavin S. A., Smith R. E., Hull R. N., Smithwick E. L., Jr Studies on tissue culture plasminogen activator. II. The detection and assay of urokinase and plasminogen activator from LLC-PK cultures (porcine) by the synthetic substrate Nalpha-benzyloxycarbonyl-glycyl-glycyl-arginyl-4-methoxy-2-napthylamide. Thromb Res. 1977 May;10(5):679–687. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(77)90050-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones P. A., Laug W. E., Benedict W. F. Fibrinolytic activity in a human fibrosarcoma cell line and evidence for the induction of plasminogen activator secretion during tumor formation. Cell. 1975 Oct;6(2):245–252. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90015-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz J., Troll W., Adler S. W., Levitz M. Antipain and leupeptin restrict uterine DNA synthesis and function in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Sep;74(9):3754–3757. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.9.3754. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessner A., Troll W. Fluorometric microassay of plasminogen activators. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1976 Oct;176(2):411–416. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(76)90183-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morita T., Kato H., Iwanaga S., Takada K., Kimura T. New fluorogenic substrates for alpha-thrombin, factor Xa, kallikreins, and urokinase. J Biochem. 1977 Nov;82(5):1495–1498. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a131840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mott D. M., Fabisch P. H., Sani B. P., Sorof S. Lack of correlation between fibrinolysis and the transformed state of cultured mammalian cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Nov 27;61(2):621–627. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)91002-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ossowski L., Unkeless J. C., Tobia A., Quigley J. P., Rifkin D. B., Reich E. An enzymatic function associated with transformation of fibroblasts by oncogenic viruses. II. Mammalian fibroblast cultures transformed by DNA and RNA tumor viruses. J Exp Med. 1973 Jan 1;137(1):112–126. doi: 10.1084/jem.137.1.112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollack R., Risser R., Conlon S., Rifkin D. Plasminogen activator production accompanies loss of anchorage regulation in transformation of primary rat embryo cells by simian virus 40. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Dec;71(12):4792–4796. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.12.4792. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quigley J. P. Association of a protease (plasminogen activator) with a specific membrane fraction isolated from transformed cells. J Cell Biol. 1976 Nov;71(2):472–486. doi: 10.1083/jcb.71.2.472. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quigley J. P., Ossowski L., Reich E. Plasminogen, the serum proenzyme activated by factors from cells transformed by oncogenic viruses. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jul 10;249(13):4306–4311. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rifkin D. B., Loeb J. N., Moore G., Reich E. Properties of plasminogen activators formed by neoplastic human cell cultures. J Exp Med. 1974 May 1;139(5):1317–1328. doi: 10.1084/jem.139.5.1317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rifkin D. B., Pollack R. Production of plasminogen activator by established cell lines of mouse origin. J Cell Biol. 1977 Apr;73(1):47–55. doi: 10.1083/jcb.73.1.47. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman M. I., Strickland S., Reich E. Differentiation of early mouse embryonic and teratocarcinoma cells in vitro: plasminogen activator production. Cancer Res. 1976 Nov;36(11 Pt 2):4208–4216. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strickland S., Beers W. H. Studies on the role of plasminogen activator in ovulation. In vitro response of granulosa cells to gonadotropins, cyclic nucleotides, and prostaglandins. J Biol Chem. 1976 Sep 25;251(18):5694–5702. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson R. C., Blout E. R. Dependence of the kinetic parameters for elastase-catalyzed amide hydrolysis on the length of peptide substrates. Biochemistry. 1973 Jan 2;12(1):57–65. doi: 10.1021/bi00725a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Topp W., Hall J. D., Marsden M., Teresky A. K., Rifkin D., Levine A. J., Pollack R. In vitro differentiation of teratomas and the distribution of creatine phosphokinase and plasminogen activator in teratocarcinoma-derived cells. Cancer Res. 1976 Nov;36(11 Pt 2):4217–4223. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unkeless J. C., Gordon S., Reich E. Secretion of plasminogen activator by stimulated macrophages. J Exp Med. 1974 Apr 1;139(4):834–850. doi: 10.1084/jem.139.4.834. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unkeless J. C., Tobia A., Ossowski L., Quigley J. P., Rifkin D. B., Reich E. An enzymatic function associated with transformation of fibroblasts by oncogenic viruses. I. Chick embryo fibroblast cultures transformed by avian RNA tumor viruses. J Exp Med. 1973 Jan 1;137(1):85–111. doi: 10.1084/jem.137.1.85. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unkeless J., Dano K., Kellerman G. M., Reich E. Fibrinolysis associated with oncogenic transformation. Partial purification and characterization of the cell factor, a plasminogen activator. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jul 10;249(13):4295–4305. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vassalli J. D., Hamilton J., Reich E. Macrophage plasminogen activator: modulation of enzyme production by anti-inflammatory steroids, mitotic inhibitors, and cyclic nucleotides. Cell. 1976 Jun;8(2):271–281. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90011-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigler M., Weinstein I. B. Tumour promotor induces plasminogen activator. Nature. 1976 Jan 22;259(5540):232–233. doi: 10.1038/259232a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman M., Ashe B. M. Sbustrate specificity of the elastase and the chymotrypsin-like enzyme of the human granulocyte. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Jan 11;480(1):241–245. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(77)90337-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman M., Ashe B., Yurewicz E. C., Patel G. Sensitive assays for trypsin, elastase, and chymotrypsin using new fluorogenic substrates. Anal Biochem. 1977 Mar;78(1):47–51. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90006-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman M., Yurewicz E., Patel G. A new fluorogenic substrate for chymotrypsin. Anal Biochem. 1976 Jan;70(1):258–262. doi: 10.1016/s0003-2697(76)80066-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



