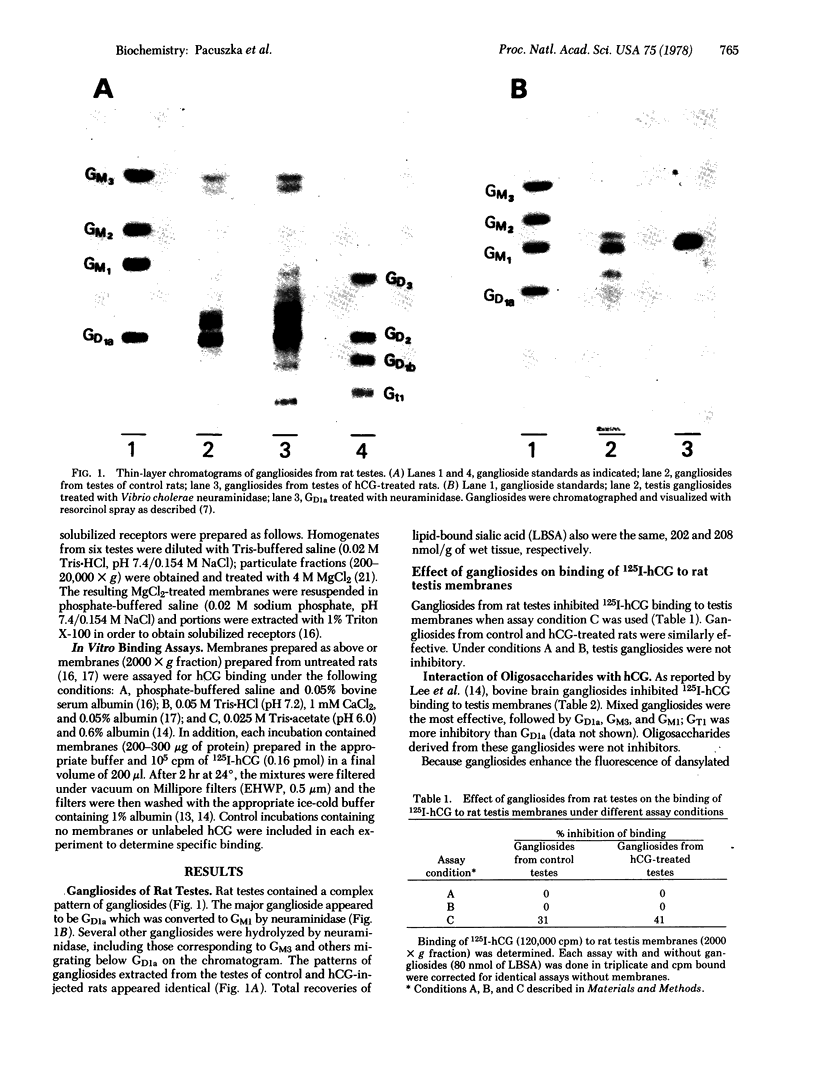
Abstract
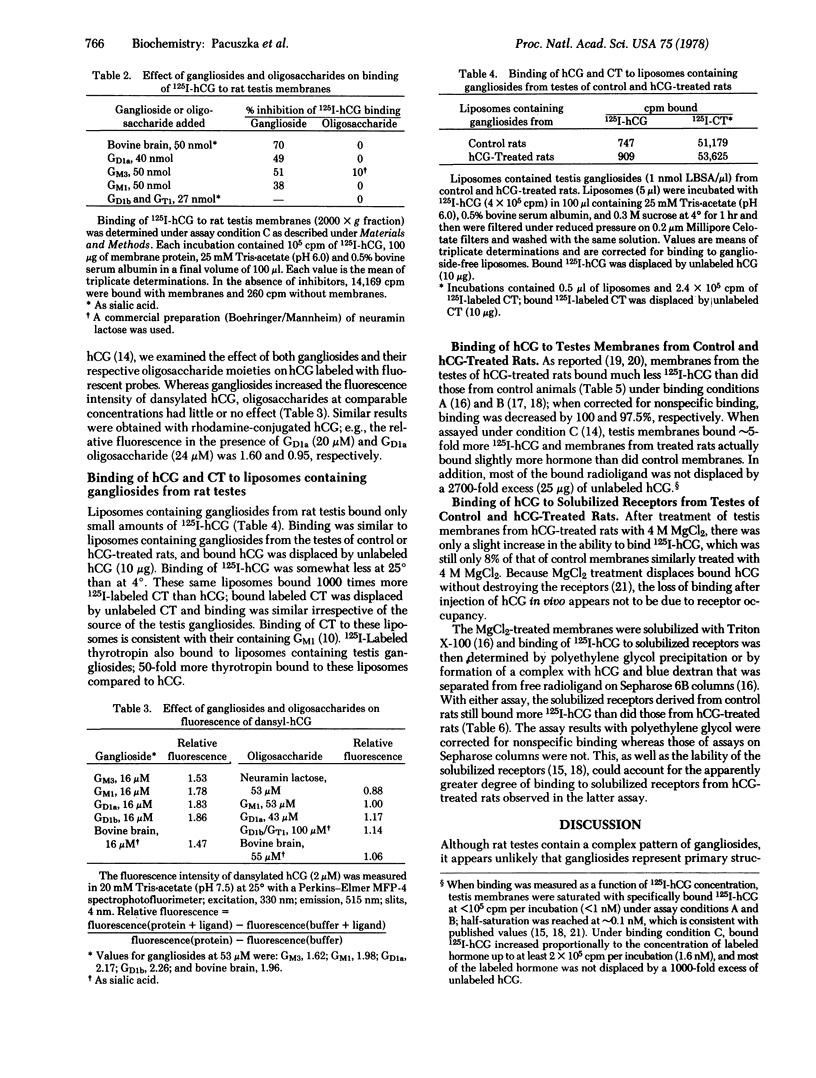
Previous studies demonstrating that gangliosides interacted with thyrotropin and human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) suggested that gangliosides participate in the transduction of the hormonal message across the target cell membrane. As a continuation of these investigations, we examined the effects of down-regulation of hCG receptors on the interaction of hCG with rat testis membrane components. Rat testes contained a complex ganglioside pattern that did not appear to change qualitatively or quantitatively after the injection of hCG into the animals, although testis membranes from hCG-treated rats lost their capacity to bind 125I-labeled hCG (125I-hCG). Gangliosides extracted from the testes of control and treated animals were equally effective inhibitors of 125I-hCG binding to testis membranes. However, inhibition of binding was observed only under conditions (pH 6.0, low ionic strength) such that unlabeled hCG (>2500-fold excess) did not block 125I-hCG binding, and 125I-hCG bound similarly to testis membranes from control and treated rats. Under conditions such that hCG binding was specific (blocked by 250-fold excess of unlabeled hCG), testis gangliosides were noninhibitory. Liposomes containing gangliosides from the testes of control or hCG-treated rats bound similar small amounts of 125I-hCG. These same liposomes bound 50 and 1000 times more thyrotropin and cholera toxin, respectively, than hCG. Oligosaccharides derived from gangliosides did not inhibit 125I-hCG binding to testis membranes nor did they alter the fluorescence of hCG conjugated with fluorescent probes, whereas the gangliosides themselves were inhibitory and enhanced the fluorescence intensity of the hCG derivatives. Exposure of testis membranes from hCG-treated rats to 4 M MgCl2, which displaces bound hCG [Chen, Y.-D. I. & Payne, A. H. (1977) Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 74, 1589-1596], did not restore their ability to bind 125I-hCG. When membranes were solubilized with Triton X-100, a solubilized receptor was detected from testis membranes of control but not hCG-treated rats.
These findings and the absence of demonstrable changes in the composition or quantity of rat testis gangliosides when hCG receptors are down-regulated suggest that gangliosides do not represent the primary binding determinants of hCG receptors.
Keywords: gangliosides, solubilized receptors, receptor regulation, cholera toxin
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bellisario R., Bahl O. P. Human chorionic gonadotropin. V. Tissue specificity of binding and partial characterization of soluble human chorionic gonadotropin-receptor complexes. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):3837–3844. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Y. D., Payne A. H. Regulation of testicular LH receptors by homologous hormone: in vitro studies on receptor occupancy and receptor loss. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Feb 21;74(4):1589–1596. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)90624-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuatrecasas P. Gangliosides and membrane receptors for cholera toxin. Biochemistry. 1973 Aug 28;12(18):3558–3566. doi: 10.1021/bi00742a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuatrecasas P. Interaction of Vibrio cholerae enterotoxin with cell membranes. Biochemistry. 1973 Aug 28;12(18):3547–3558. doi: 10.1021/bi00742a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cumar F. A., Fishman P. H., Brady R. O. Analogous reactions for the biosynthesis of monosialo- and disialo-gangliosides in brain. J Biol Chem. 1971 Aug 25;246(16):5075–5084. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dufau M. L., Ryan D. W., Baukal A. J., Catt K. J. Gonadotropin receptors. Solubilization and purification by affinity chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jun 25;250(12):4822–4824. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelhoch H., Osborne J. C., Jr The thermodynamic basis of the stability of proteins, nucleic acids, and membranes. Adv Protein Chem. 1976;30:183–250. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60480-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fishman P. H., Brady R. O. Biosynthesis and function of gangliosides. Science. 1976 Nov 26;194(4268):906–915. doi: 10.1126/science.185697. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmgren J., Lönnroth I., Svennerholm L. Tissue receptor for cholera exotoxin: postulated structure from studies with GM1 ganglioside and related glycolipids. Infect Immun. 1973 Aug;8(2):208–214. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.2.208-214.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsueh A. J., Dufau M. L., Catt K. J. Regulation of luteinizing hormone receptors in testicular interstitial cells by gonadotropin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Oct 4;72(3):1145–1152. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(76)80251-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King C. A., Van Heyningen W. E. Deactivation of cholera toxin by a sialidase-resistant monosialosylganglioside. J Infect Dis. 1973 Jun;127(6):639–647. doi: 10.1093/infdis/127.6.639. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee G., Aloj S. M., Brady R. O., Kohn L. D. The structure and function of glycoprotein hormone receptors: ganglioside interactions with human chorionic gonadotropin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Nov 22;73(2):370–377. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90717-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee G., Aloj S. M., Kohn L. D. The structure and function of glycoprotein hormone receptors: ganglioside interactions with luteinizing hormone. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Jul 11;77(1):434–441. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(77)80216-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss J., Fishman P. H., Manganiello V. C., Vaughan M., Brady R. O. Functional incorporation of ganglioside into intact cells: induction of choleragen responsiveness. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Apr;73(4):1034–1037. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.4.1034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss J., Fishman P. H., Richards R. L., Alving C. R., Vaughan M., Brady R. O. Choleragen-mediated release of trapped glucose from liposomes containing ganglioside GM1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Oct;73(10):3480–3483. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.10.3480. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss J., Manganiello V. C., Fishman P. H. Enzymatic and chemical oxidation of gangliosides in cultured cells: effects of choleragen. Biochemistry. 1977 May 3;16(9):1876–1881. doi: 10.1021/bi00628a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss J., Osborne J. C., Jr, Fishman P. H., Brewer H. B., Jr, Vaughan M., Brady R. O. Effect of gangliosides and substrate analogues on the hydrolysis of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide by choleragen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jan;74(1):74–78. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.1.74. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullin B. R., Aloj S. M., Fishman P. H., Lee G., Kohn L. D., Brady R. O. Cholera toxin interactions with thyrotropin receptors on thyroid plasma membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 May;73(5):1679–1683. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.5.1679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullin B. R., Fishman P. H., Lee G., Aloj S. M., Ledley F. D., Winand R. J., Kohn L. D., Brady R. O. Thyrotropin-ganglioside interactions and their relationship to the structure and function of thyrotropin receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Mar;73(3):842–846. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.3.842. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullin B. R., Pacuszka T., Lee G., Kohn L. D., Brady R. O., Fishman P. H. Thyroid gangliosides with high affinity for thyrotropin: potential role in thyroid regulation. Science. 1978 Jan 6;199(4324):77–79. doi: 10.1126/science.199.4324.77. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborne J. C., Steiner R. F. Interaction of the components of the lactose synthetase system. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1974 Dec;165(2):615–627. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(74)90289-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pandian M. R., Bahl O. P. Labeling of bovine corpus luteal plasma membrane human chorionic gonadotropin or luteinizing hormone (hCG/LH) receptor and its purification and properties. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1977 Aug;182(2):420–436. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(77)90523-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penick R. J., Meisler M. H., McCluer R. H. Thin-layer chromatographic studies of human brain gangliosides. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Apr 4;116(2):279–287. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(66)90010-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SVENNERHOLM L. CHROMATOGRAPHIC SEPARATION OF HUMAN BRAIN GANGLIOSIDES. J Neurochem. 1963 Sep;10:613–623. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1963.tb08933.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharpe R. M. hCG-induced decrease in availability of rat testis receptors. Nature. 1976 Dec 16;264(5587):644–646. doi: 10.1038/264644a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiegandt H., Bücking H. W. Carbohydrate components of extraneuronal gangliosides from bovine and human spleen, and bovine kidney. Eur J Biochem. 1970 Aug;15(2):287–292. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1970.tb01006.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]