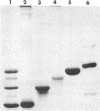
Abstract
Four polypeptide chains were purified from acetylcholine receptor of Torpedo californica electric organ. Their apparent molecular weights were 64,000, 57,000, 49,500, and 38,000. Rats immunized with any of the four chains produced antibodies that crossreacted with rat muscle receptors in vivo. Specificities of anti-chain sera were evaluated in vitro by reaction with native receptor solubilized from electric organs and muscles of several species and by inhibition of this reaction with the purified polypeptide chains. The chains are immunologically distinct from one another. Antigenic determinants comparable to each chain of torpedo receptor are found in receptor from both rat and human muscle. At least part of each of these determinants is exposed on the extracellular surface of the muscle membrane. The most immunogenic determinants on native receptor are lost on denaturation to polypeptide chains. Its component peptides are much less immunogenic than native receptor, and induce antibodies of different specificity. Anti-receptor antibodies of many specificities can cause experimental autoimmune myasthenia gravis.
Full text
PDF
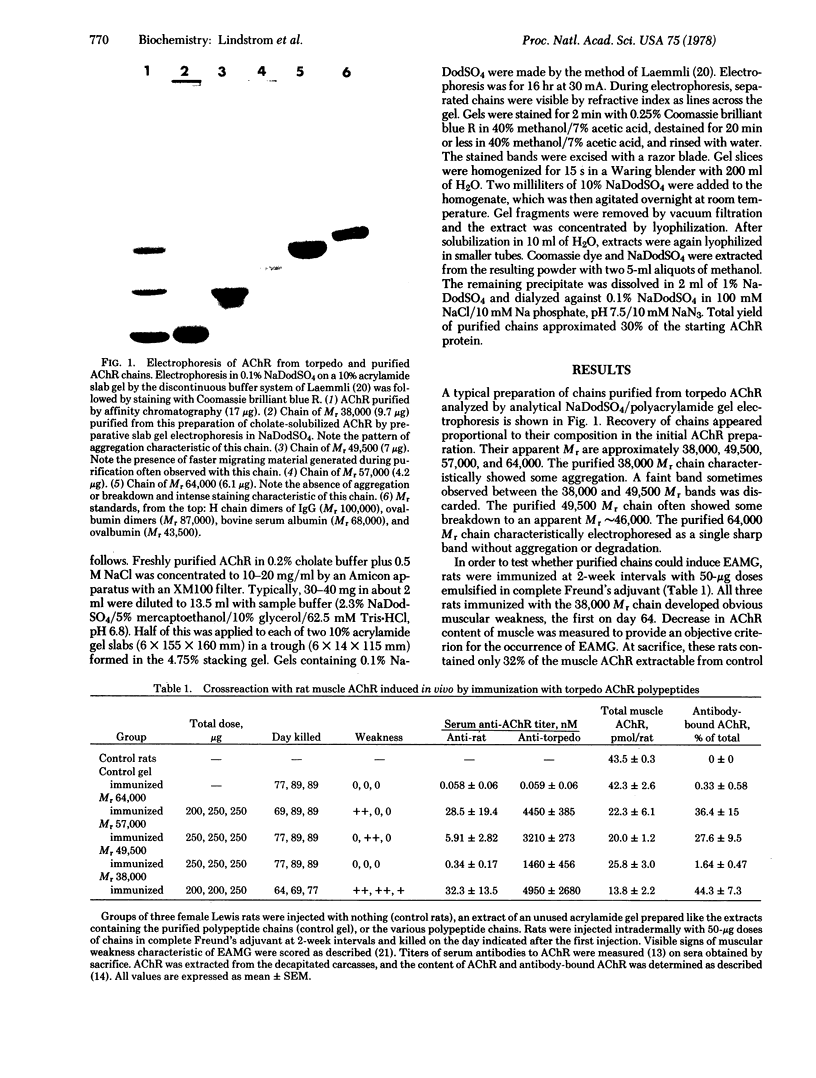
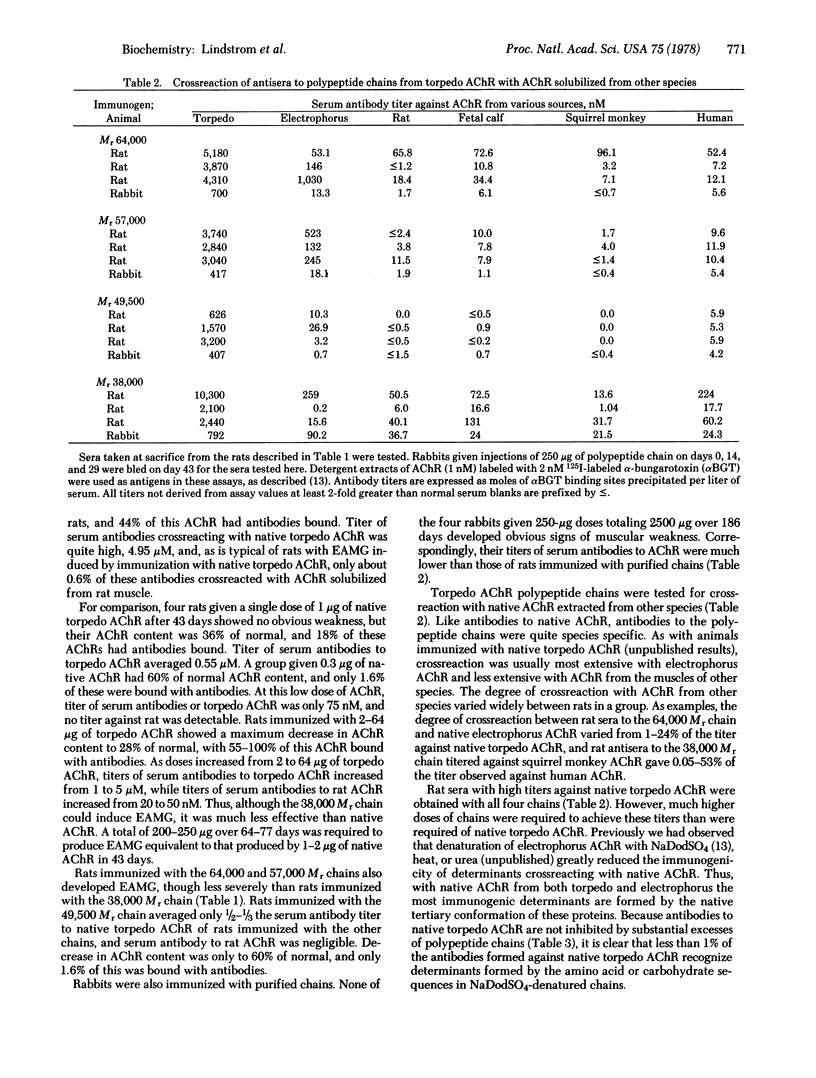


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Appel S. H., Anwyl R., McAdams M. W., Elias S. Accelerated degradation of acetylcholine receptor from cultured rat myotubes with myasthenia gravis sera and globulins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 May;74(5):2130–2134. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.5.2130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulter J., Patrick J. Purification of an acetylcholine receptor from a nonfusing muscle cell line. Biochemistry. 1977 Nov 1;16(22):4900–4908. doi: 10.1021/bi00641a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang H. W., Bock E. Molecular forms of acetylcholine receptor. Effects of calcium ions and a sulfhydryl reagent on the occurrence of oligomers. Biochemistry. 1977 Oct 4;16(20):4513–4520. doi: 10.1021/bi00639a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claudio T., Raftery M. A. Immunological comparison of acetylcholine receptors and their subunits from species of electric ray. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1977 Jun;181(2):484–489. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(77)90254-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engel A. G., Lambert E. H., Howard F. M. Immune complexes (IgG and C3) at the motor end-plate in myasthenia gravis: ultrastructural and light microscopic localization and electrophysiologic correlations. Mayo Clin Proc. 1977 May;52(5):267–280. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engel A. G., Tsujihata M., Lindstrom J. M., Lennon V. A. The motor end plate in myasthenia gravis and in experimental autoimmune myasthenia gravis. A quantitative ultrastructural study. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1976;274:60–79. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1976.tb47676.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Froehner S. C., Karlin A., Hall Z. W. Affinity alkylation labels two subunits of the reduced acetylcholine receptor from mammalian muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Oct;74(10):4685–4688. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.10.4685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Froehner S. C., Reiness C. G., Hall Z. W. Subunit structure of the acetylcholine receptor from denervated rat skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem. 1977 Dec 10;252(23):8589–8596. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinemann S., Bevan S., Kullberg R., Lindstrom J., Rice J. Modulation of acetylcholine receptor by antibody against the receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jul;74(7):3090–3094. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.7.3090. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kao I., Drachman D. B. Myasthenic immunoglobulin accelerates acetylcholine receptor degradation. Science. 1977 Apr 29;196(4289):527–529. doi: 10.1126/science.850793. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlin A., Weill C. L., McNamee M. G., Valderrama R. Facets of the structures of acetylcholine receptors from Electrophorus and Torpedo. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1976;40:203–210. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1976.040.01.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert E. H., Lindstrom J. M., Lennon V. A. End-plate potentials in experimental autoimmune myasthenia gravis in rats. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1976;274:300–318. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1976.tb47694.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lennon V. A., Lindstrom J. M., Seybold M. E. Experimental autoimmune myasthenia: A model of myasthenia gravis in rats and guinea pigs. J Exp Med. 1975 Jun 1;141(6):1365–1375. doi: 10.1084/jem.141.6.1365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindstrom J. M., Einarson B. L., Lennon V. A., Seybold M. E. Pathological mechanisms in experimental autoimmune myasthenia gravis. I. Immunogenicity of syngeneic muscle acetylcholine receptor and quantitative extraction of receptor and antibody-receptor complexes from muscles of rats with experimental automimmune myasthenia gravis. J Exp Med. 1976 Sep 1;144(3):726–738. doi: 10.1084/jem.144.3.726. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindstrom J. M., Engel A. G., Seybold M. E., Lennon V. A., Lambert E. H. Pathological mechanisms in experimental autoimmune myasthenia gravis. II. Passive transfer of experimental autoimmune myasthenia gravis in rats with anti-acetylcholine recepotr antibodies. J Exp Med. 1976 Sep 1;144(3):739–753. doi: 10.1084/jem.144.3.739. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindstrom J. M., Lennon V. A., Seybold M. E., Whittingham S. Experimental autoimmune myasthenia gravis and myasthenia gravis: biochemical and immunochemical aspects. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1976;274:254–274. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1976.tb47691.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patrick J., Lindstrom J. Autoimmune response to acetylcholine receptor. Science. 1973 May 25;180(4088):871–872. doi: 10.1126/science.180.4088.871. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patrick J., Lindstrom J., Culp B., McMillan J. Studies on purified eel acetylcholine receptor and anti-acetylcholine receptor antibody. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Dec;70(12):3334–3338. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.12.3334. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raftery M. A., Vandlen R. L., Reed K. L., Lee T. Characterization of Torpedo californica acetylcholine receptor: its subunit composition and ligand-binding properties. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1976;40:193–202. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1976.040.01.021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobel A., Changeux J. P. Purification and characterization of the cholinergic receptor protein in its membrane-bound and detergent-soluble forms from the electric organ of Torpedo marmorata. Biochem Soc Trans. 1977;5(2):511–514. doi: 10.1042/bst0050511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]