Abstract
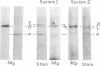
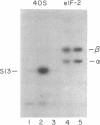
Initiation factor 2 (eIF-2) is phosphorylated in vitro by two different cyclic nucleotide-independent protein kinases. As previously shown, a protein kinase activity that comigrates with the major casein kinase activity from rabbit reticulocytes phosphorylates eIF-2beta. In addition, a second protein kinase that specifically phosphorylates eIF-2alpha has been identified. Both protein kinase activities demonstrate cyclic nucleotide-independent activity and are not inhibited by the inhibitor protein diagnostic for cyclic AMP-regulated protein kinase activities. Phosphorylation of eIF-2alpha is almost completely inhibited by 20--35 muM hemin, whereas phosphorylation of eIF-2beta is only partially inhibited. Hemin acts by decreasing the rate of incorporation of phosphate into eIF-2alpha. The protein kinase activity that modifies eIF-2alpha has been shown to have inhibitory activity in the cell-free protein-synthesizing system, whereas the protein kinase for eIF-2beta has no effect. The identity of the former enzyme with the hemin-controlled repressor and role of hemin in the control of initiation are discussed.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams S. L., Safer B., Anderson W. F., Merrick W. C. Eukaryotic initiation complex formation. Evidence for two distinct pathways. J Biol Chem. 1975 Dec 10;250(23):9083–9089. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adamson S. D., Herbert E., Godchaux W. Factors affecting the rate of protein synthesis in lysate systems from reticulocytes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1968 May;125(2):671–683. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(68)90625-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson C. W., Baum P. R., Gesteland R. F. Processing of adenovirus 2-induced proteins. J Virol. 1973 Aug;12(2):241–252. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.2.241-252.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashby C. D., Walsh D. A. Characterization of the interaction of a protein inhibitor with adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinases. I. Interaction with the catalytic subunit of the protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1972 Oct 25;247(20):6637–6642. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRUNS G. P., LONDON I. M. THE EFFECT OF HEMIN ON THE SYNTHESIS OF GLOBIN. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1965 Jan 18;18:236–242. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(65)90746-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balkow K., Hunt T., Jackson R. J. Control of protein synthesis in reticulocyte lysates: the effect of nucleotide triphosphates on formation of the translational repressor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Nov 3;67(1):366–375. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90325-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balkow K., Mizuno S., Fisher J. M., Rabinovitz M. Hemin control of globin synthesis: effect of a translational repressor on Met-tRNAf binding to the small ribosomal subunit and its relation to the activity and alailability of an initiation factor. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Oct 26;324(3):397–409. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(73)90284-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrieux A., Rosenfeld M. G. Characterization of GTP-dependent Met-tRNAf binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jun 10;252(11):3843–3847. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benne R., Wong C., Luedi M., Hershey J. W. Purification and characterization of initiation factor IF-E2 from rabbit reticulocytes. J Biol Chem. 1976 Dec 10;251(23):7675–7681. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clemens M. J., Henshaw E. C., Rahamimoff H., London I. M. Met-tRNAfMet binding to 40S ribosomal subunits: a site for the regulation of initiation of protein synthesis by hemin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Aug;71(8):2946–2950. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.8.2946. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clemens M. J., Safer B., Merrick W. C., Anderson W. F., London I. M. Inhibition of protein synthesis in rabbit reticulocyte lysates by double-stranded RNA and oxidized glutathione: indirect mode of action on polypeptide chain initiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Apr;72(4):1286–1290. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.4.1286. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darnbrough C., Legon S., Hunt T., Jackson R. J. Initiation of protein synthesis: evidence for messenger RNA-independent binding of methionyl-transfer RNA to the 40 S ribosomal subunit. J Mol Biol. 1973 May 25;76(3):379–403. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90511-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dettman G. L., Stanley W. M., Jr Recognition of eukaryotic initiator tRNA by an initiation factor and the transfer of the methionine moiety into peptide linkage. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Nov 16;287(1):124–133. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(72)90336-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ernst V., Levin D. H., Ranu R. S., London I. M. Control of protein synthesis in reticulocyte lysates: effects of 3':5'-cyclic AMP, ATP, and GTP on inhibitions induced by hemedeficiency, double-stranded RNA, and a reticulocyte translationa inhibitor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Apr;73(4):1112–1116. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.4.1112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrell P. J., Balkow K., Hunt T., Jackson R. J., Trachsel H. Phosphorylation of initiation factor elF-2 and the control of reticulocyte protein synthesis. Cell. 1977 May;11(1):187–200. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90330-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glynn I. M., Chappell J. B. A simple method for the preparation of 32-P-labelled adenosine triphosphate of high specific activity. Biochem J. 1964 Jan;90(1):147–149. doi: 10.1042/bj0900147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross M., Mendelewski J. Additional evidence that the hemin-controlled translational repressor from rabbit reticulocytes is a protein kinase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Jan 24;74(2):559–569. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)90340-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross M., Rabinovitz M. Control of globin synthesis by hemin: factors influencing formation of an inhibitor of globin chain initiation in reticulocyte lysates. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Dec 6;287(2):340–352. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(72)90383-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross M., Rabinovitz M. Control of globin synthesis in cell-free preparations of reticulocytes by formation of a translational repressor that is inactivated by hemin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1565–1568. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta N. K., Woodley C. L., Chen Y. C., Bose K. K. Protein synthesis in rabbit reticulocytes. Assays, purification, and properties of different ribosomal factors and their roles in peptide chain initiation. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jun 25;248(12):4500–4511. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt T., Vanderhoff G., London I. M. Control of globin synthesis: the role of heme. J Mol Biol. 1972 May 28;66(3):471–481. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90427-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Issinger O. G., Benne R., Hershey J. W., Traut R. R. Phosphorylation in vitro of eukaryotic initiation factors IF-E2 and IF-E3 by protein kinases. J Biol Chem. 1976 Oct 25;251(20):6471–6474. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer G., Cimadevilla J. M., Hardesty B. Specificity of the protein kinase activity associated with the hemin-controlled repressor of rabbit reticulocyte. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Sep;73(9):3078–3082. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.9.3078. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer G., Henderson A. B., Pinphanichakarn P., Wallis M. H., Hardesty B. Partial reaction of peptide initiation inhibited by phosphorylation of either initiation factor eIF-2 or 40S ribosomal proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Apr;74(4):1445–1449. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.4.1445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legon S., Brayley A., Hunt T., Jackson R. J. The effect of cyclic AMP and related compounds on the control of protein synthesis in reticulocyte lysates. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Feb 4;56(3):745–752. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)90668-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legon S., Jackson R. J., Hunt T. Control of protein synthesis in reticulocyte lysates by haemin. Nat New Biol. 1973 Jan 31;241(109):150–152. doi: 10.1038/newbio241150a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin D. H., Kyner D., Acs G. Protein synthesis initiation in eukaryotes. Characterization of ribosomal factors from mouse fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1973 Sep 25;248(18):6416–6425. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin D., Ranu R. S., Ernst V., London I. M. Regulation of protein synthesis in reticulocyte lysates: phosphorylation of methionyl-tRNAf binding factor by protein kinase activity of translational inhibitor isolated from hemedeficient lysates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Sep;73(9):3112–3116. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.9.3112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxwell C. R., Kamper C. S., Rabinovitz M. Hemin control of globin synthesis: an assay for the inhibitor formed in the absence of hemin and some characteristics of its formation. J Mol Biol. 1971 May 28;58(1):317–327. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90249-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuno S., Fisher J. M., Rabinovitz M. Hemin control of globin synthesis: action of an inhibitor formed in the absence of hemin on the reticulocyte cell-free system and its reversal by a ribosomal factor. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Jul 31;272(4):638–650. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinphanichakarn P., Kramer G., Hardesty B. Partial reaction of peptide initiation inhibited by the reticulocyte hemin-controlled repressor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Dec 6;73(3):625–631. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90856-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ranu R. S., London I. M. Regulation of protein synthesis in rabbit reticulocyte lysates: purification and initial characterization of the cyclic 3':5'-AMP independent protein kinase of the heme-regulated translational inhibitor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Dec;73(12):4349–4353. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.12.4349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ranu R. S., Wool I. G. Preparation and characterization of eukaryotic initiation factor EIF-3. Formation of binary (EIF-3-Met-tRNAf) and ternary (EIF-3-Met-tRNAf-GTP) complexes. J Biol Chem. 1976 Apr 10;251(7):1926–1935. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Safer B., Adams S. L., Kemper W. M., Berry K. W., Lloyd M., Merrick W. C. Purification and characterization of two initiation factors required for maximal activity of a highly fractionated globin mRNA translation system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Aug;73(8):2584–2588. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.8.2584. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Safer B., Anderson W. F., Merrick W. C. Purification and physical properties of homogeneous initiation factor MP from rabbit reticulocytes. J Biol Chem. 1975 Dec 10;250(23):9067–9075. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreier M. H., Staehelin T. Initiation of eukaryotic protein synthesis: (Met-tRNA f -40S ribosome) initiation complex catalysed by purified initiation factors in the absence of mRNA. Nat New Biol. 1973 Mar 14;242(115):35–38. doi: 10.1038/newbio242035a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith K. E., Henshaw E. C. Binding of Met-tRNA-f to native and derived 40S ribosomal subunits. Biochemistry. 1975 Mar 11;14(5):1060–1067. doi: 10.1021/bi00676a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traugh J. A., Tahara S. M., Sharp S. B., Safer B., Merrick W. C. Factors involved in initiation of haemoglobin synthesis can be phosphorylated in vitro. Nature. 1976 Sep 9;263(5573):163–165. doi: 10.1038/263163a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traugh J. A., Traut R. R. Characterization of protein kinases from rabbit reticulocytes. J Biol Chem. 1974 Feb 25;249(4):1207–1212. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zucker W. V., Schulman H. M. Stimulation of globin-chain initiation by hemin in the reticulocyte cell-free system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Feb;59(2):582–589. doi: 10.1073/pnas.59.2.582. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]