Abstract
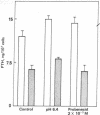
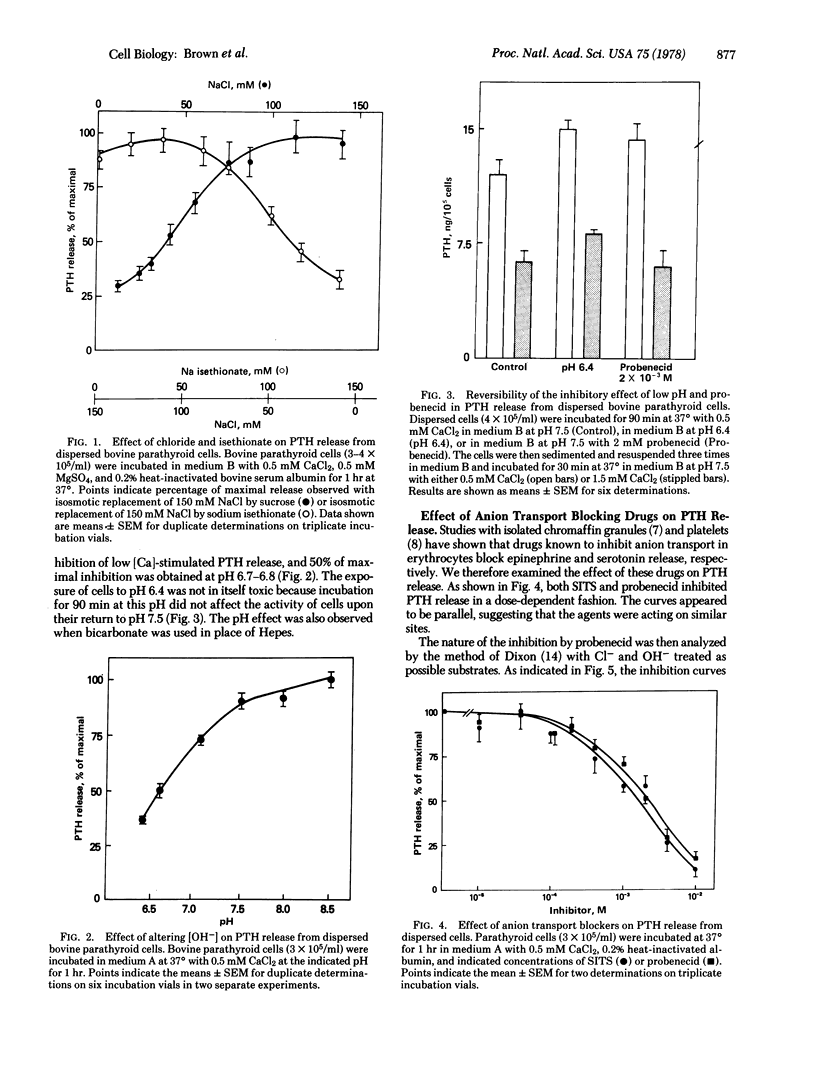
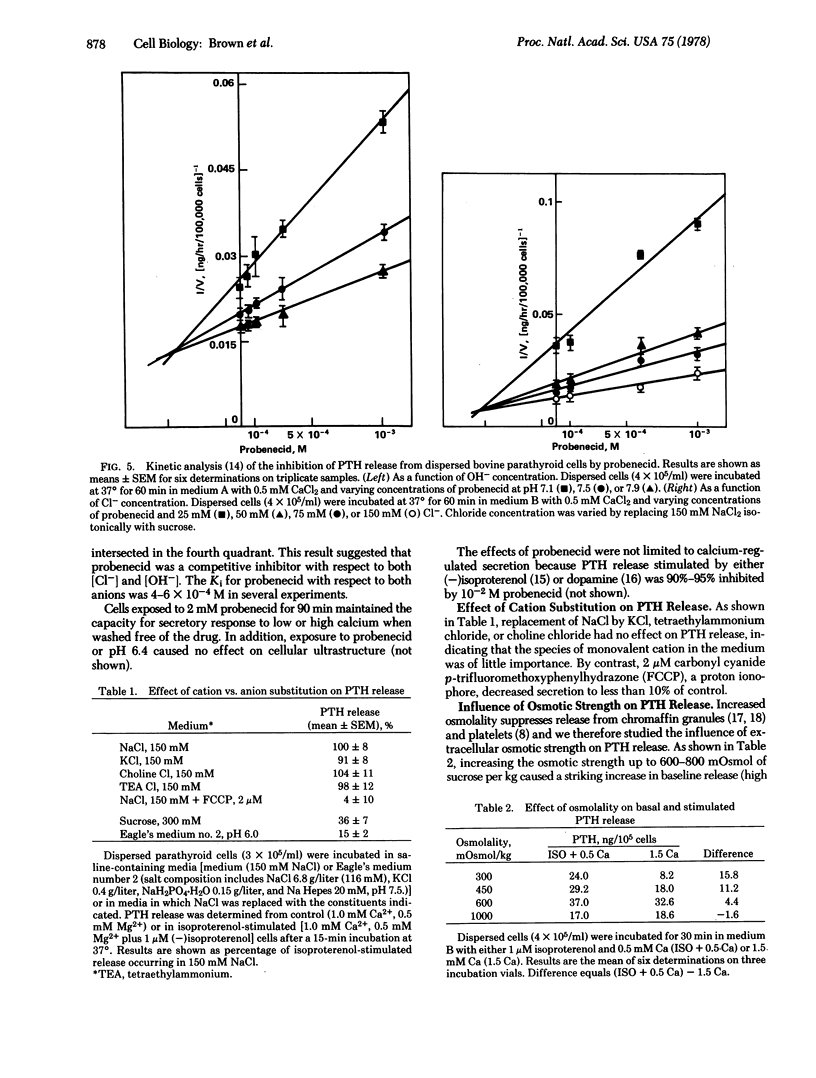
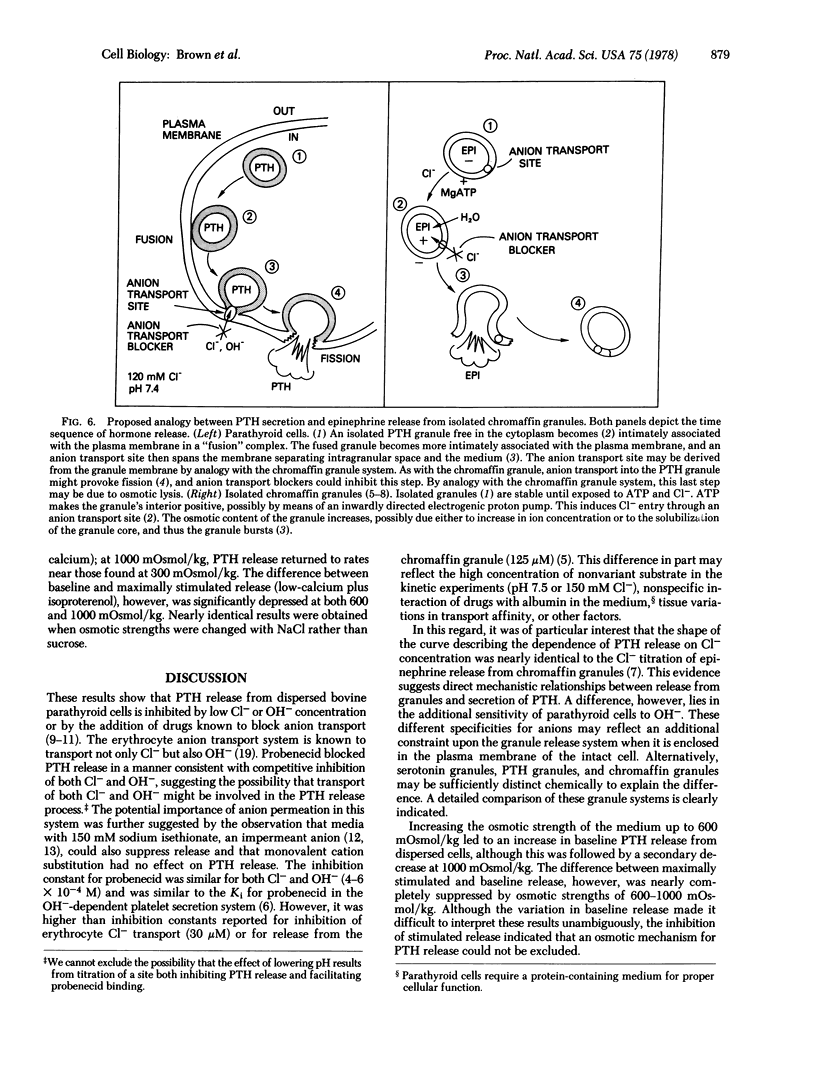
It is known that permeant anions are required for the release of epinephrine from isolated chromaffin granules and of serotonin from intact platelets. We have now investigated the role of anions in the release of a polypeptide hormone, parathyroid hormone, from dispersed bovine parathyroid cells. The release is inhibited 60%-80% by decreasing either [Cl-] or [OH-] and 60%-70% by replacement of NaCl with the impermeant anion isethionate. By contrast, substitution of various monovalent cations in the medium had no effect on the release. Disodium 4-acetamido-4'-isothiocyanostilbene-2,2'-disulfonate (SITS) and probenecid, which are known to block anion transport in the erythrocyte, also cause a dose-dependent 90%-100% inhibition of release. Moreover, kinetic analysis of inhibition by probenecid suggests that it is competitive with respect to either OH- or Cl-. These results suggest that anions and the anion transport system may play a role in exocytosis of a polypeptide hormone. The proton ionophore carbonyl cyanide p-trifluoromethoxyphenylhydrazone was was also found to block hormone release, and the possibility is discussed of a "chemosmotic" mechanism for exocytosis in this system similar to that previously postulated for chromaffin granules and platelets.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brown E. M., Carroll R. J., Aurbach G. D. Dopaminergic stimulation of cyclic AMP accumulation and parathyroid hormone release from dispersed bovine parathyroid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Oct;74(10):4210–4213. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.10.4210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown E. M., Hurwitz S., Aurbach G. D. Beta-adrenergic stimulation of cyclic AMP content and parathyroid hormone release from isolated bovine parathyroid cells. Endocrinology. 1977 Jun;100(6):1696–1702. doi: 10.1210/endo-100-6-1696. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown E. M., Hurwitz S., Aurbach G. D. Preparation of viable isolated bovine parathyroid cells. Endocrinology. 1976 Dec;99(6):1582–1588. doi: 10.1210/endo-99-6-1582. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capen C. C., Koestner A., Cole C. R. The ultrastructure and histochemistry of normal parathyroid glands of pregnant and nonpregnant cows. Lab Invest. 1965 Sep;14(9):1673–1690. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casey R. P., Njus D., Radda G. K., Sehr P. A. Adenosine triphosphate-evoked catecholamine release in chromatin granules. Osmotic lysis as a consequence of proton translocation. Biochem J. 1976 Sep 15;158(3):583–588. doi: 10.1042/bj1580583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DIXON M. The determination of enzyme inhibitor constants. Biochem J. 1953 Aug;55(1):170–171. doi: 10.1042/bj0550170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolais-Kitabgi J., Perlman R. L. The stimulation of cathecholamine release from chromaffin granules by valinomycin. Mol Pharmacol. 1975 Nov;11(6):745–750. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellsworth R., Nicholson W. M. FURTHER OBSERVATIONS UPON THE CHANGES IN THE ELECTROLYTES OF THE URINE FOLLOWING THE INJECTION OF PARATHYROID EXTRACT. J Clin Invest. 1935 Nov;14(6):823–827. doi: 10.1172/JCI100730. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellman D. E., Au W. Y., Bartter F. C. Evidence for a direct effect of parathyroid hormone on urinary acidification. Am J Physiol. 1965 Sep;209(3):643–650. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1965.209.3.643. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman P. G., Zinder O., Bonner W. M., Pollard H. B. Role of ATP and beta-gamma-iminoadenosinetriphosphate in the stimulation of epinephrine and protein release from isolated adrenal secretory vesicles. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1976 Sep;176(1):375–388. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(76)90177-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoskin F. C., Brande M. An improved sulphur assay applied to a problem of isethionate metabolism in squid axon and other nerves. J Neurochem. 1973 May;20(5):1317–1327. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1973.tb00243.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knauf P. A., Rothstein A. Chemical modification of membranes. I. Effects of sulfhydryl and amino reactive reagents on anion and cation permeability of the human red blood cell. J Gen Physiol. 1971 Aug;58(2):190–210. doi: 10.1085/jgp.58.2.190. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MADDY A. H. A FLUORESCENT LABEL FOR THE OUTER COMPONENTS OF THE PLASMA MEMBRANE. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Sep 25;88:390–399. doi: 10.1016/0926-6577(64)90194-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MUNGER B. L., ROTH S. I. The cytology of the normal parathyroid glands of man and Virginia deer; a light and electron microscopic study with morphologic evidence of secretory activity. J Cell Biol. 1963 Feb;16:379–400. doi: 10.1083/jcb.16.2.379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacGregor R. R., Chu L. L., Hamilton J. W., Cohn D. V. Studies on the subcellular localization of proparathyroid hormone and parathyroid hormone in the bovine parathyroid gland: separation of newly synthesized from mature forms. Endocrinology. 1973 Dec;93(6):1387–1397. doi: 10.1210/endo-93-6-1387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Motais R., Cousin J. L. The inhibitor effect of probencid and structural analogues on organic anions and chloride permeabilities in ox erythrocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Jan 21;419(2):309–313. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90356-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NORDIN B. E. The effect of intravenous parathyroid extract on urinary pH, bicarbonate and electrolyte excretion. Clin Sci. 1960 May;19:311–319. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palade G. Intracellular aspects of the process of protein synthesis. Science. 1975 Aug 1;189(4200):347–358. doi: 10.1126/science.1096303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollard H. B., Tack-Goldman K., Pazoles C. J., Creutz C. E., Shulman N. R. Evidence for control of serotonin secretion from human platelets by hydroxyl ion transport and osmotic lysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5295–5299. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollard H. B., Zinder O., Hoffman P. G., Nikodejevic O. Regulation of the transmembrane potential of isolated chromaffin granules by ATP, ATP analogs, and external pH. J Biol Chem. 1976 Aug 10;251(15):4544–4550. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]