Abstract
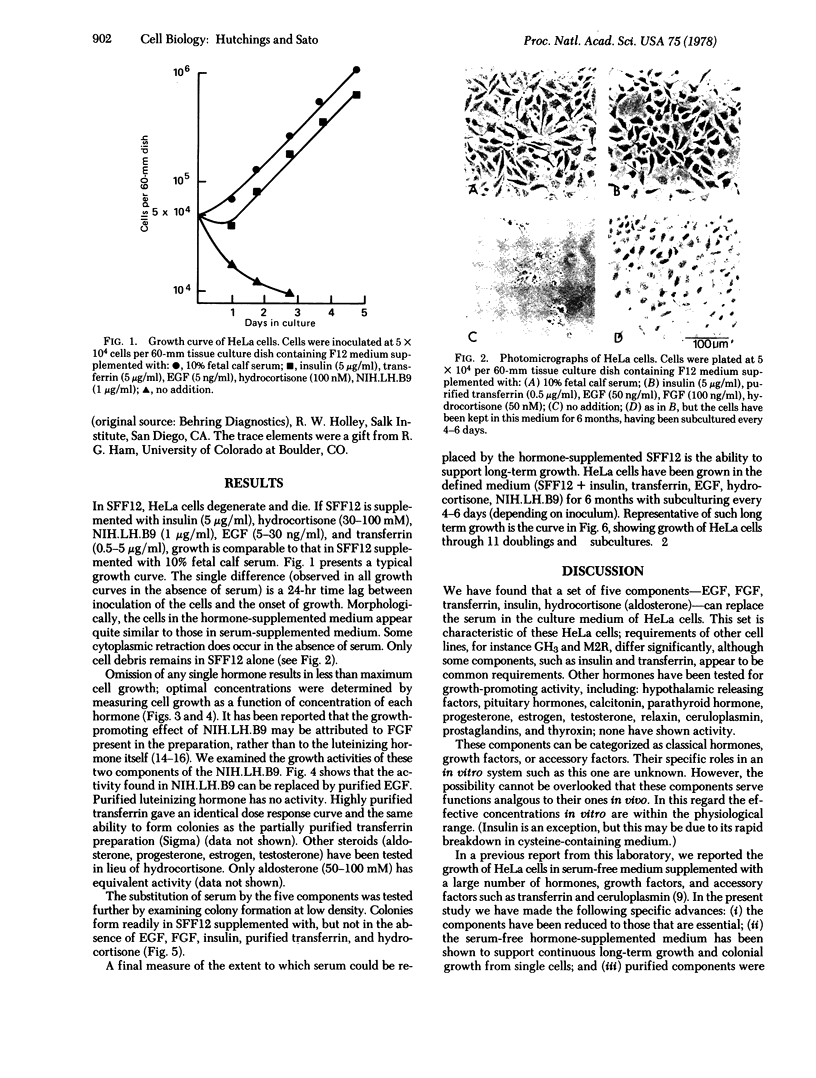
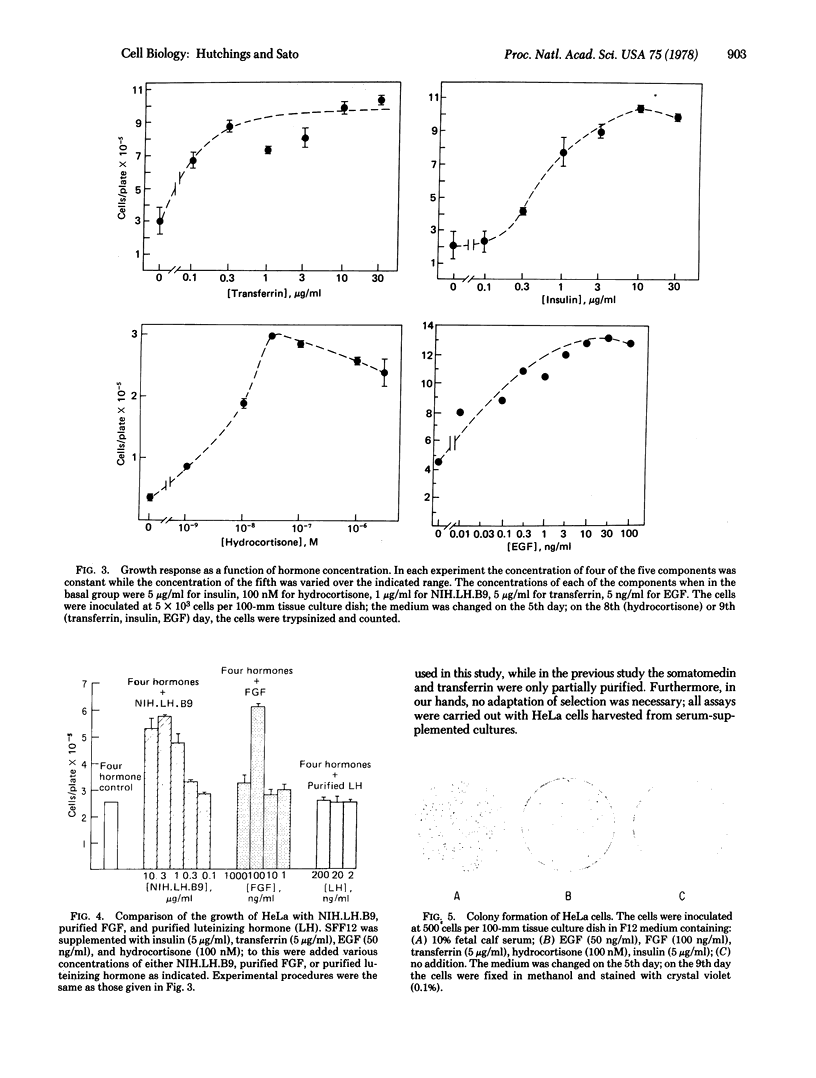
HeLa cells grow in a nutritionally complete synthetic medium (Ham's F12) supplemented with insulin, transferrin, hydrocortisone (aldosterone), fibroblast growth factor, and epidermal growth factor. This hormone-supplemented medium supports clonal growth, long-term cultivation, and a growth rate equal to that of serum-supplemented medium. The omission of any one of the five components results in less than maximal cell growth.
Full text
PDF
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armelin H. A. Pituitary extracts and steroid hormones in the control of 3T3 cell growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Sep;70(9):2702–2706. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.9.2702. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birch J. R., Pirt S. J. The choline and serum protein requirements of mouse fibroblast cells (strain LS) in culture. J Cell Sci. 1969 Jul;5(1):135–142. doi: 10.1242/jcs.5.1.135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark J. L., Jones K. I., Gospodarowicz D., Sato G. H. Growth response to hormones by a new rat ovary cell line. Nat New Biol. 1972 Apr 12;236(67):180–181. doi: 10.1038/newbio236180a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S., Taylor J. M. Epidermal growth factor: chemical and biological characterization. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1974;30(0):533–550. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-571130-2.50017-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EAGLE H. Nutrition needs of mammalian cells in tissue culture. Science. 1955 Sep 16;122(3168):501–514. doi: 10.1126/science.122.3168.501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EAGLE H. The specific amino acid requirements of a human carcinoma cell (Stain HeLa) in tissue culture. J Exp Med. 1955 Jul 1;102(1):37–48. doi: 10.1084/jem.102.1.37. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EVANS V. J., BRYANT J. C., KERR H. A., SCHILLING E. L. CHEMICALLY DEFINED MEDIA FOR CULTIVATION OF LONG-TERM CELL STRAINS FROM FOUR MAMMALIAN SPECIES. Exp Cell Res. 1964 Dec;36:439–474. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(64)90302-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gospodarowicz D. Purification of a fibroblast growth factor from bovine pituitary. J Biol Chem. 1975 Apr 10;250(7):2515–2520. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAM R. G. CLONAL GROWTH OF MAMMALIAN CELLS IN A CHEMICALLY DEFINED, SYNTHETIC MEDIUM. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Feb;53:288–293. doi: 10.1073/pnas.53.2.288. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi I., Sato G. H. Replacement of serum by hormones permits growth of cells in a defined medium. Nature. 1976 Jan 15;259(5539):132–134. doi: 10.1038/259132a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIEBERMAN I., OVE P. Growth factors for mammalian cells in culture. J Biol Chem. 1959 Oct;234:2754–2758. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKeehan W. L., Hamilton W. G., Ham R. G. Selenium is an essential trace nutrient for growth of WI-38 diploid human fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jun;73(6):2023–2027. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.6.2023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puck T. T., Marcus P. I. A RAPID METHOD FOR VIABLE CELL TITRATION AND CLONE PRODUCTION WITH HELA CELLS IN TISSUE CULTURE: THE USE OF X-IRRADIATED CELLS TO SUPPLY CONDITIONING FACTORS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1955 Jul 15;41(7):432–437. doi: 10.1073/pnas.41.7.432. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SALMON W. D., Jr, DAUGHADAY W. H. A hormonally controlled serum factor which stimulates sulfate incorporation by cartilage in vitro. J Lab Clin Med. 1957 Jun;49(6):825–836. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takaoka T., Katsuta H. Long-term cultivation of mammalian cell strains in protein- and lipid-free chemically defined synthetic media. Exp Cell Res. 1971 Aug;67(2):295–304. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(71)90412-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uthne K. Human somatomedians. Purification and some studies on their biological actions. Acta Endocrinol Suppl (Copenh) 1973;175:1–35. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]