Abstract
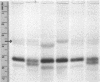
Two electrophoretic variants of murine complement component 3 (C3) were detected by using high-voltage electrophoresis of fresh mouse serum in agarose gels. Most of the inbred strains tested were homozygous for the S allele (for the slow-migrating variant); only four out of 46 strains had the alternative F allele (fast variant). Pen-bred Swiss-Webster animals belonged to one of three phenotypes--S, F, or SF--and the genes responsible for this variation segregated in a strictly Mendelian manner. In three such crosses, with 5* offspring, C3 segregated with H-2 in 46 instances, corresponding to a recombination frequency of approximately equal to 0.12.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen F. H., Jr Linkage of HL-A and GBG. Vox Sang. 1974;27(4):382–384. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1974.tb02433.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alper C. A. Genetics and the C3 molecule. Vox Sang. 1973;25(1):1–8. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1973.tb05205.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alper C. A. Inherited structural polymorphism in human C2: evidence for genetic linkage between C2 and Bf. J Exp Med. 1976 Oct 1;144(4):1111–1115. doi: 10.1084/jem.144.4.1111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alper C. A., Propp R. P. Genetic polymorphism of the third component of human complement (C'3). J Clin Invest. 1968 Sep;47(9):2181–2191. doi: 10.1172/JCI105904. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bitter-Suermann D., Krönke M., Brade V., Hadding U. Inherited polymorphism of guinea pig factor B and C4: evidence for genetic linkage between the C4 and Bf loci. J Immunol. 1977 May;118(5):1822–1826. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curman B., Ostberg L., Sandberg L., Malmheden-Eriksson I., Stålenheim G., Rask L., Peterson P. A. H-2 linked Ss protein is C4 component of complement. Nature. 1975 Nov 20;258(5532):243–245. doi: 10.1038/258243a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decary F., Rubinstein P. In reference to Kaliss. Transplantation. 1973 Jun;15(6):630–630. doi: 10.1097/00007890-197306000-00019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falk C. T., Walker M. E., Martin M. D., Allen F. H., Jr Autosomal linkage in humans (methodology and results of computer analysis). Ser Haematol. 1975;8(2):153–237. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira A., Nussenweig V. Control of C3 levels in mice during ontogeny by a gene in the central region of the H-2 complex. Nature. 1976 Apr 15;260(5552):613–615. doi: 10.1038/260613a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu S. M., Kunkel H. G., Brusman H. P., Allen F. H., Jr, Fotino M. Evidence for linkage between HL-A histocompatibility genes and those involved in the synthesis of the second component of complement. J Exp Med. 1974 Oct 1;140(4):1108–1111. doi: 10.1084/jem.140.4.1108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gedde-Dahl T., Jr, Teisberg P., Thorsby E. C3 polymorphism: genetic linkage relations. Clin Genet. 1974;6(1):66–72. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1974.tb00632.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinzová E., Démant P., Iványi P. Genetic control of haemolytic complement in mice: association with H-2. Folia Biol (Praha) 1972;18(4):237–243. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lachmann P. J., Grennan D., Martin A., Demant P. Identification of Ss protein as murine C4. Nature. 1975 Nov 20;258(5532):242–243. doi: 10.1038/258242a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meo T., Krasteff T., Shreffler D. C. Immunochemical characterization of murine H-2 controlled Ss (serum substance) protein through identification of its human homologue as the fourth component of complement. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Nov;72(11):4536–4540. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.11.4536. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ochs H. D., Rosenfeld S. I., Thomas E. D., Giblett E. R., Alper C. A., Dupont B., Schaller J. G., Gilliland B. C., Hansen J. A., Wedgwood R. J. Linkage between the gene (or genes) controlling synthesis of the fourth component of complement and the major histocompatibility complex. N Engl J Med. 1977 Mar 3;296(9):470–475. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197703032960902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RUBINSTEIN P., FERREBEE J. W. THE H-2 PHENOTYPES OF RANDOM-BRED SWISS-WEBSTER MICE. Transplantation. 1964 Nov;2:715–721. doi: 10.1097/00007890-196411000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubinstein P., Kaliss N. Letter: H-2 typing with the polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) method. Transplantation. 1974 Jan 1;17(1):121–121. doi: 10.1097/00007890-197401000-00018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shreffler D. C., David C. S. The H-2 major histocompatibility complex and the I immune response region: genetic variation, function, and organization. Adv Immunol. 1975;20:125–195. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60208-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stastny P. Mixed lymphocyte cultures in rheumatoid arthritis. J Clin Invest. 1976 May;57(5):1148–1157. doi: 10.1172/JCI108382. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieme R. J., Demeulenaere L. Genetically determined electrophoretic variant of the human complement component C'3. Nature. 1967 Jun 3;214(5092):1042–1043. doi: 10.1038/2141042a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziegler J. B., Alper C. A., Balner H. Properdin factor B and histocompatibility loci linked in the rhesus monkey. Nature. 1975 Apr 17;254(5501):609–611. doi: 10.1038/254609a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Vries R. R., Fat R. F., Nijenhuis L. E., van Rood J. J. HLA-linked genetic control of host response to Mycobacterium leprae. Lancet. 1976 Dec 18;2(7999):1328–1330. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)91975-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]