Abstract
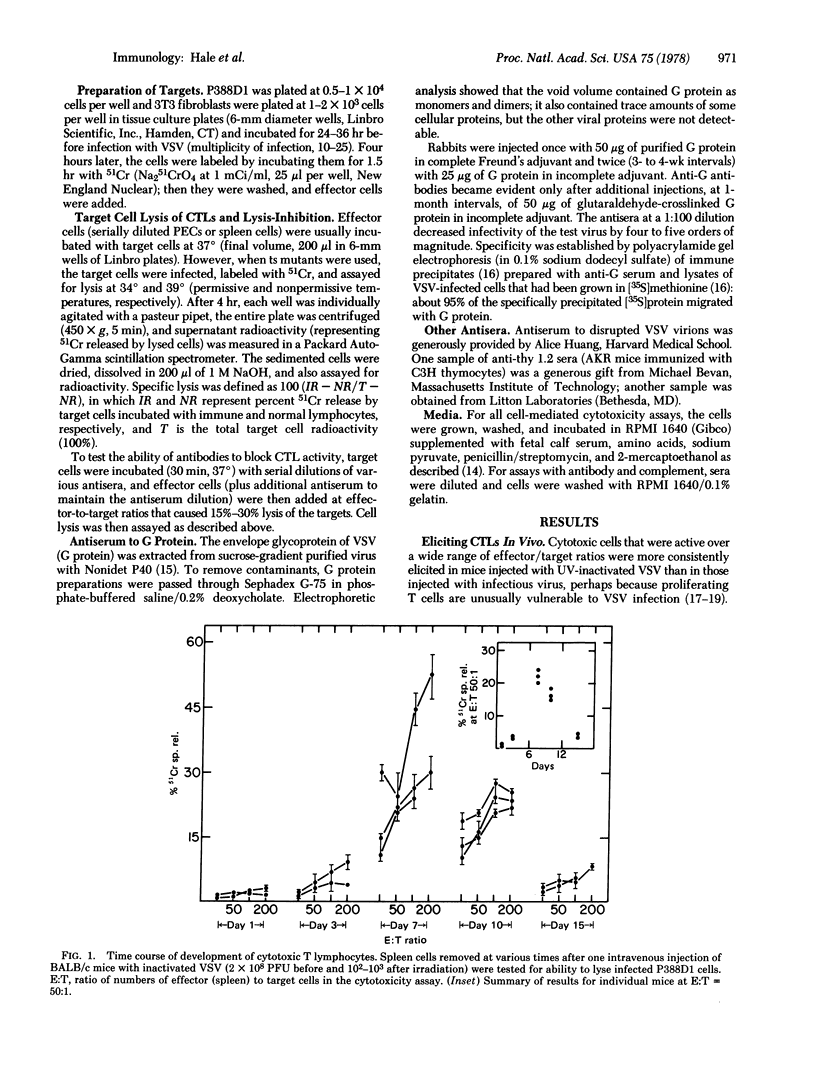
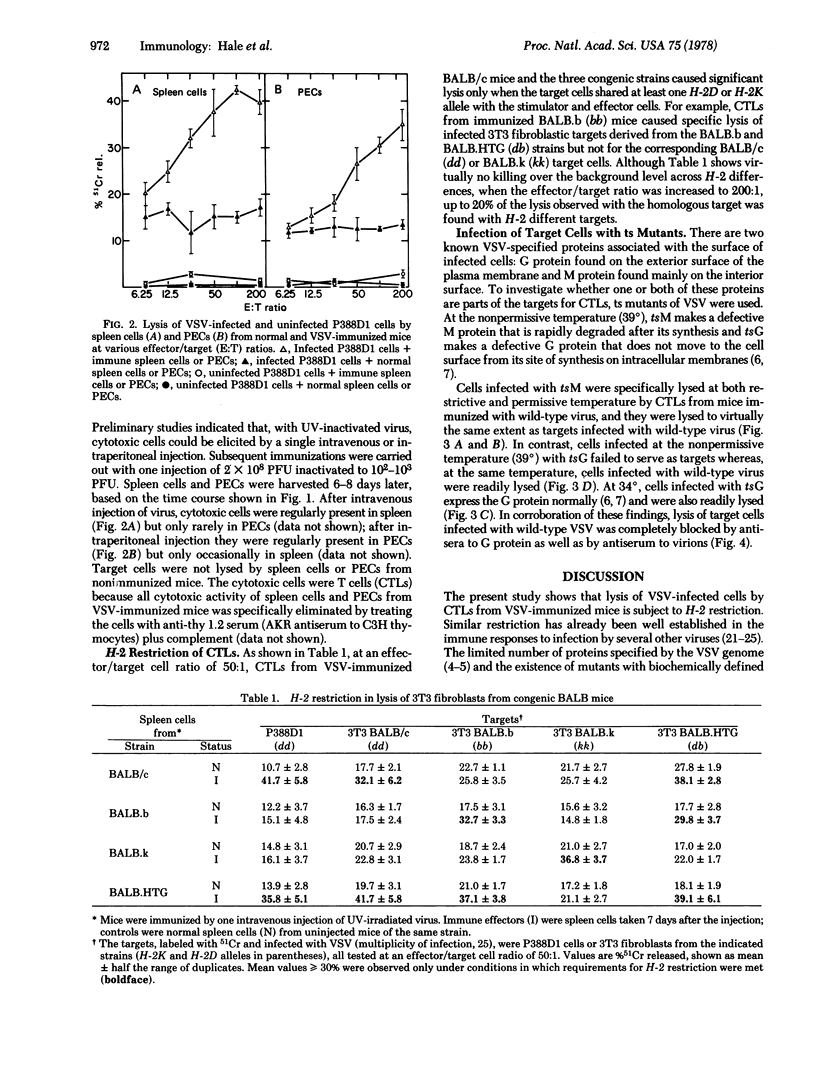
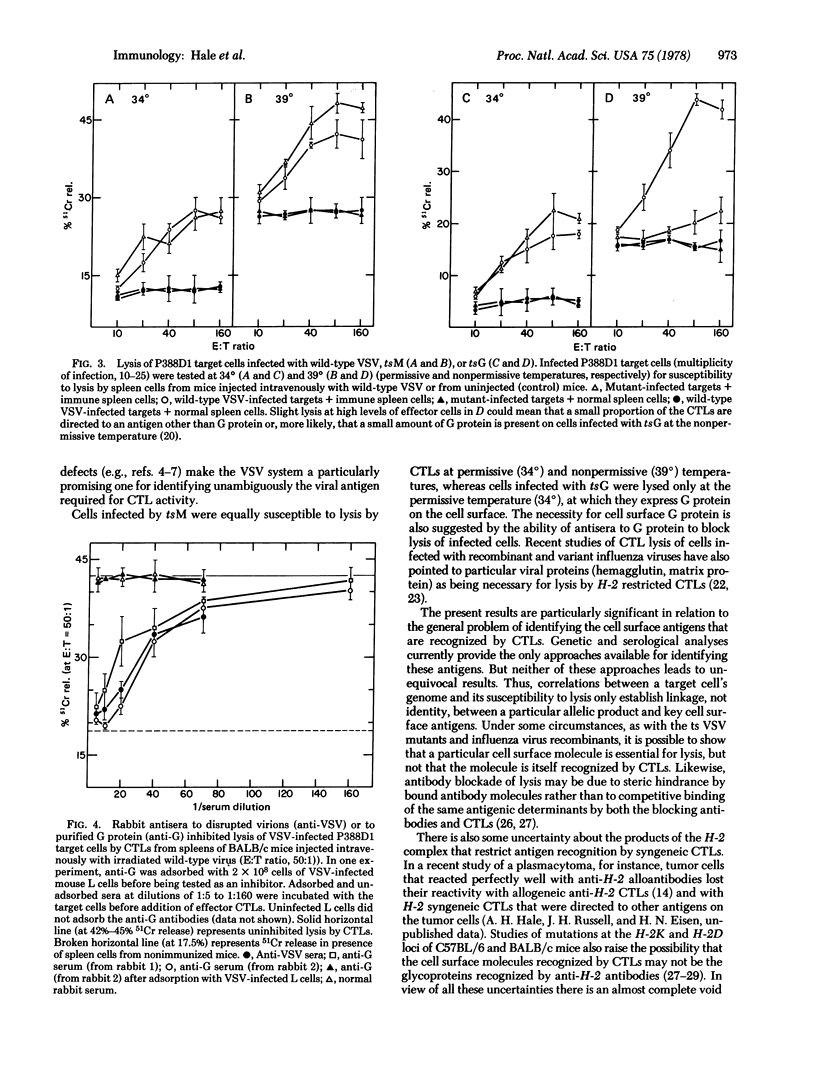
Vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV) elicited cytotoxic thymus-derived lymphocytes (CTLs) in mice of the BALB/c and three congenic strains (BALB.b, BALB.k, BALB.HTG). CTL lysis of VSV-infected fibroblasts from the four strains was restricted by the target cells' major histocompatibility complex (H-2). Target cells were also infected with two temperature-sensitive mutants of VSV, tsM and tsG in which, respectively, the viral matrix protein and glycoprotein are not expressed at 39 degrees (restrictive temperature) on the infected cell's surface membrane. At the restrictive temperature, cells infected with wild-type VSV or tsM were lysed by CTLs, but cells infected with tsG were not. The requirement for the glycoprotein on the target cell was also evident from the ability of antisera to the glycoprotein to block completely CTL lysis of VSV-infected cells.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blanden R. V., Doherty P. C., Dunlop M. B., Gardner I. D., Zinkernagel R. M., David C. S. Genes required for cytotoxicity against virus-infected target cells in K and D regions of H-2 complex. Nature. 1975 Mar 20;254(5497):269–270. doi: 10.1038/254269a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burakoff S. J., Germain R. N., Benacerraf B. Cross-reactive lysis of trinitrophenyl (TNP)-derivatized H-2 incompatible target cells by cytolytic T lymphocytes generated against syngeneic TNP spleen cells. J Exp Med. 1976 Dec 1;144(6):1609–1620. doi: 10.1084/jem.144.6.1609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doherty P. C., Blanden R. V., Zinkernagel R. M. Specificity of virus-immune effector T cells for H-2K or H-2D compatible interactions: implications for H-antigen diversity. Transplant Rev. 1976;29:89–124. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1976.tb00198.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doherty P. C., Effros R. B., Bennink J. Heterogeneity of the cytotoxic response of thymus-derived lymphocytes after immunization with influenza viruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Mar;74(3):1209–1213. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.3.1209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ennis F. A., Martin W. J., Verbonitz M. W., Butchko G. M. Specificity studies on cytotoxic thymus-derived lymphocytes reactive with influenza virus-infected cells: evidence for dual recognition of H-2 and viral hemagglutinin antigens. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jul;74(7):3006–3010. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.7.3006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen T. H., Cullen S. E., Melvold R., Kohn H., Flaherty L., Sachs D. H. Mutation in a new H-2-associated histocompatibility gene closely linked to H-2D. J Exp Med. 1977 Jun 1;145(6):1550–1558. doi: 10.1084/jem.145.6.1550. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen T. H., Cullen S. E., Sachs D. H. Immunochemical evidence for an additional H-2 region closely linked to H-2D. J Exp Med. 1977 Feb 1;145(2):438–442. doi: 10.1084/jem.145.2.438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kano S., Bloom B. R., Howe M. L. Enumeration of activated thymus-derived lymphocytes by the virus plaque assay. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Aug;70(8):2299–2303. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.8.2299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelley J. M., Emerson S. U., Wagner R. R. The glycoprotein of vesicular stomatitis virus is the antigen that gives rise to and reacts with neutralizing antibody. J Virol. 1972 Dec;10(6):1231–1235. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.6.1231-1235.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knipe D. M., Baltimore D., Lodish H. F. Maturation of viral proteins in cells infected with temperature-sensitive mutants of vesicular stomatitis virus. J Virol. 1977 Mar;21(3):1149–1158. doi: 10.1128/jvi.21.3.1149-1158.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knipe D., Lodish H. F., Baltimore D. Analysis of the defects of temperature-sensitive mutants of vesicular stomatitis virus: intracellular degradation of specific viral proteins. J Virol. 1977 Mar;21(3):1140–1148. doi: 10.1128/jvi.21.3.1140-1148.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koren H. S., Handwerger B. S., Wunderlich J. R. Identification of macrophage-like characteristics in a cultured murine tumor line. J Immunol. 1975 Feb;114(2 Pt 2):894–897. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koszinowski U., Thomssen R. Target cell-dependent T cell-mediated lysis of vaccinia virus-infected cells. Eur J Immunol. 1975 Apr;5(4):245–251. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830050405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little S. P., Huang A. S. Synthesis and distribution of vesicular stomatitis virus-specific polypeptides in the absence of progeny production. Virology. 1977 Aug;81(1):37–47. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90056-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romano T. J., Nowakowski M., Bloom B. R., Thorbecke G. J. Selective viral immunosuppression of the graft-versus-host reaction. J Exp Med. 1977 Mar 1;145(3):666–675. doi: 10.1084/jem.145.3.666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell J. H., Hale A. H., Ginns L. C., Eisen H. N. Periodic loss of reactivity of a myeloma tumor with cytotoxic thymus-derived lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jan;75(1):441–445. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.1.441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schrader J. W., Edelman G. M. Joint recognition by cytotoxic T cells of inactivated Sendai virus and products of the major histocompatibility complex. J Exp Med. 1977 Mar 1;145(3):523–539. doi: 10.1084/jem.145.3.523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stampfer M., Baltimore D., Huang A. S. Absence of interference during high-multiplicity infection by clonally purified vesicular stomatitis virus. J Virol. 1971 Mar;7(3):409–411. doi: 10.1128/jvi.7.3.409-411.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stampfer M., Baltimore D., Huang A. S. Ribonucleic acid synthesis of vesicular stomatitis virus. I. Species of ribonucleic acid found in Chinese hamster ovary cells infected with plaque-forming and defective particles. J Virol. 1969 Aug;4(2):154–161. doi: 10.1128/jvi.4.2.154-161.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TODARO G. J., GREEN H. Quantitative studies of the growth of mouse embryo cells in culture and their development into established lines. J Cell Biol. 1963 May;17:299–313. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.2.299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ting C. C., Rogers M. J. Inhibition by sera and soluble antigens of T-cell-mediated cytotoxicity against leukaemia-associated antigens. Nature. 1977 Apr 21;266(5604):727–729. doi: 10.1038/266727a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todd R. F., Stulting R. D., Amos D. B. Lymphocyte-mediated cytolysis of allogeneic tumor cells in vitro. I. Search for target antigens in subcellular fractions. Cell Immunol. 1975 Aug;18(2):304–323. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(75)90059-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witte O. N., Baltimore D. Mechanism of formation of pseudotypes between vesicular stomatitis virus and murine leukemia virus. Cell. 1977 Jul;11(3):505–511. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90068-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



