Abstract
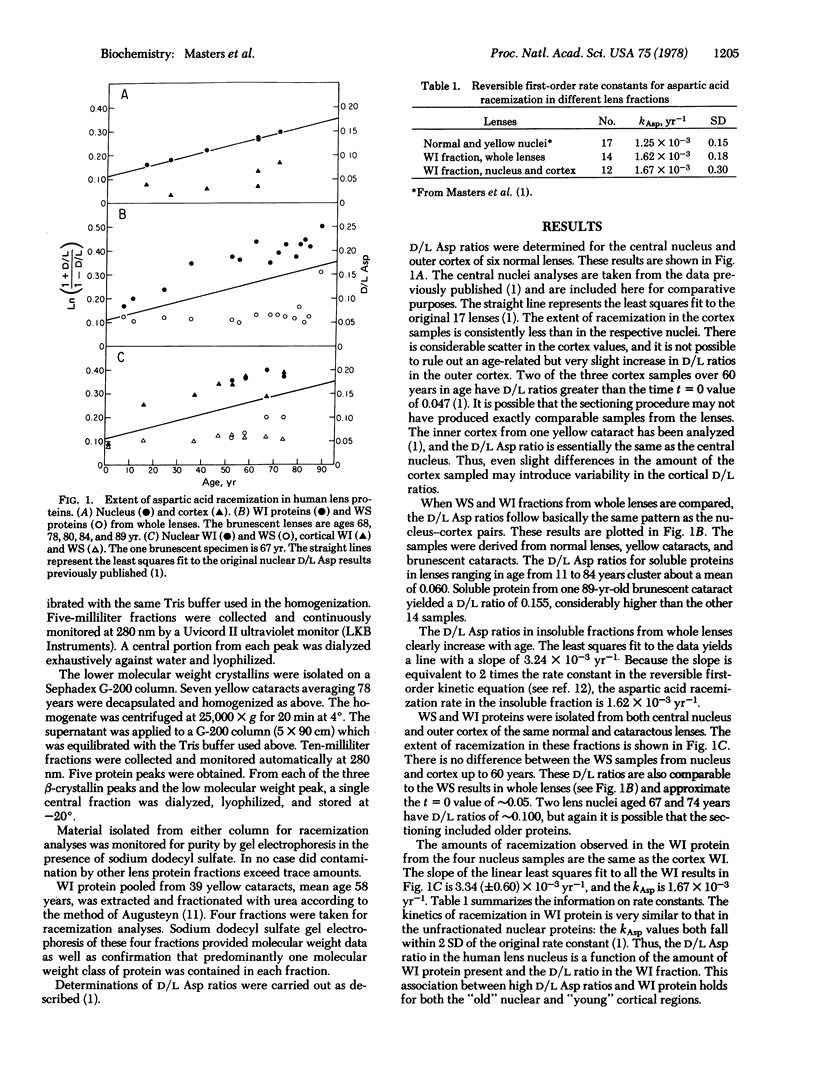
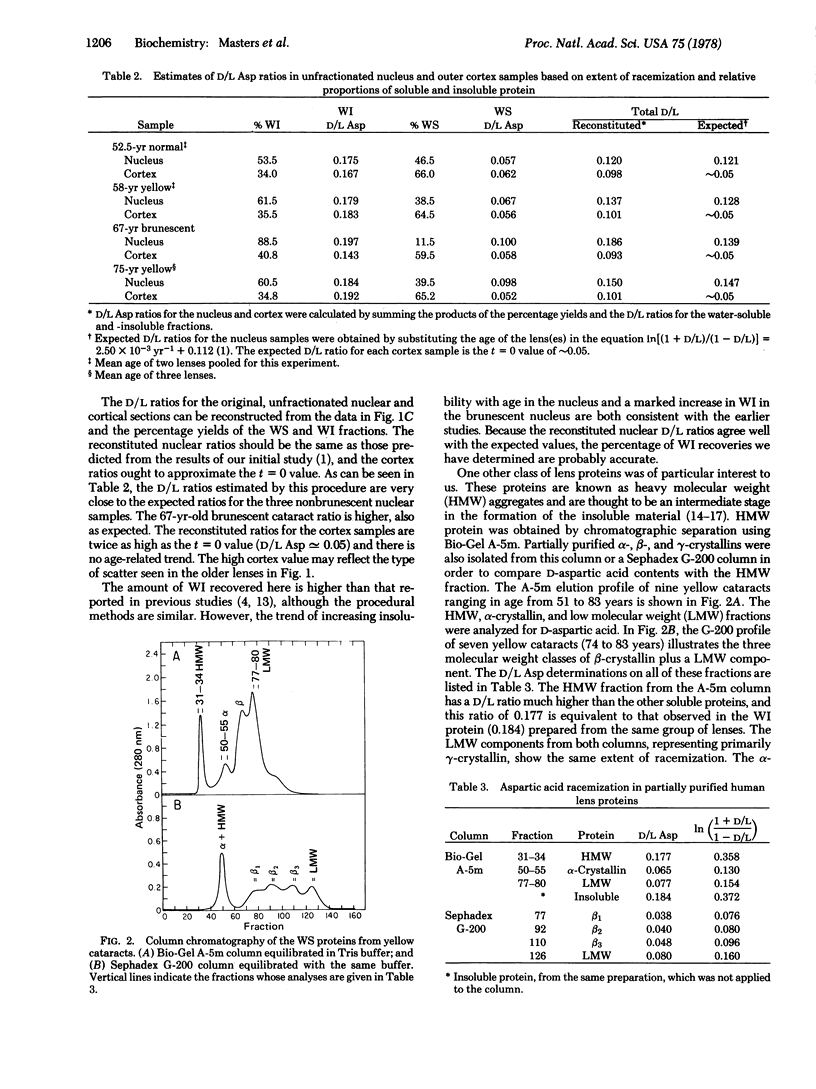
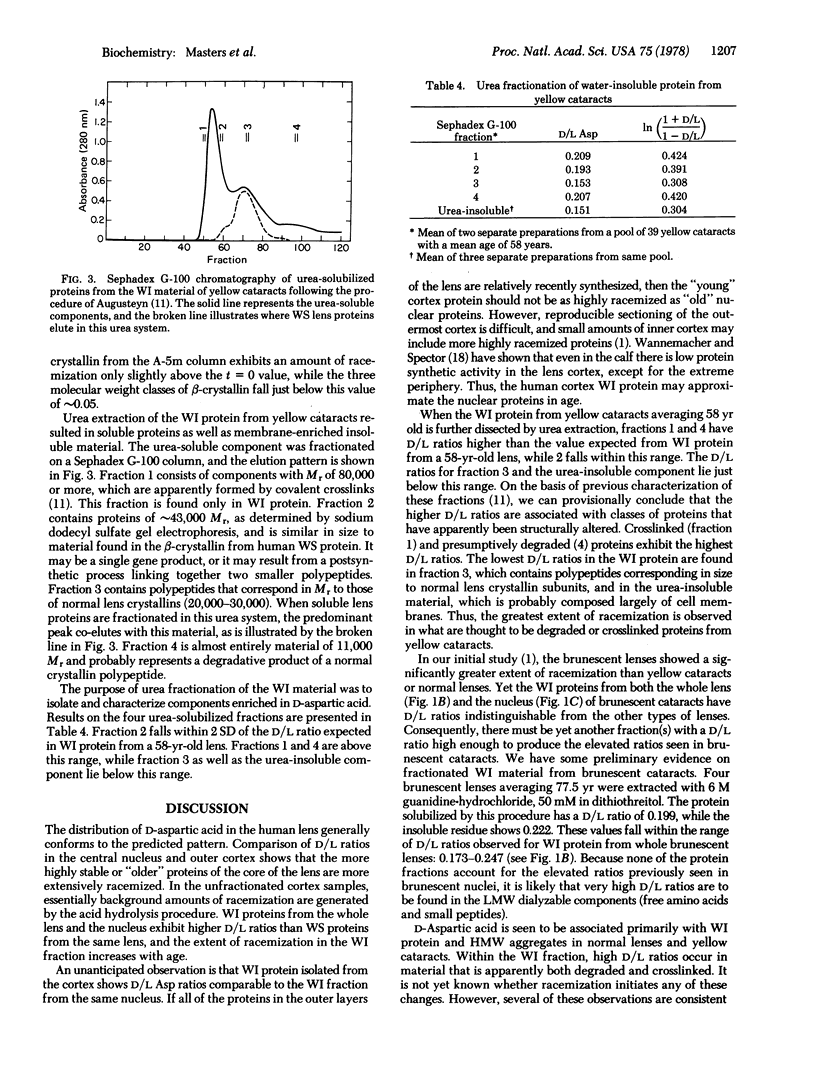
High D/L aspartic acid ratios are observed in heavy molecular weight aggregates and in water-insoluble protein extracted from whole lenses and nuclear and cortical regions. Purified alpha-, beta-, and gamma-crystallins have low D/L ratios. Fractionation of urea-solubilized material from the water-insoluble protein yields four molecular weight classes of proteins. Fractions representing crosslinked material or apparently degraded products have high D/L ratios. Racemization within lens proteins may contribute to formation of the water-insoluble fraction seen in aging lenses and cataracts.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Clark R., Zigman S., Lerman S. Studies on the structural proteins of the human lens. Exp Eye Res. 1969 Apr;8(2):172–182. doi: 10.1016/s0014-4835(69)80029-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dilley K. J., Pirie A. Changes to the proteins of the human lens nucleus in cataract. Exp Eye Res. 1974 Jul;19(1):59–72. doi: 10.1016/0014-4835(74)90073-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harding J. J. Conformational changes in human lens proteins in cataract. Biochem J. 1972 Aug;129(1):97–100. doi: 10.1042/bj1290097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helfman P. M., Bada J. L. Aspartic acid racemisation in dentine as a measure of ageing. Nature. 1976 Jul 22;262(5566):279–281. doi: 10.1038/262279b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helfman P. M., Bada J. L. Aspartic acid racemization in tooth enamel from living humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Aug;72(8):2891–2894. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.8.2891. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helfman P. M., Bada J. L., Shou M. Y. Considerations on the role of aspartic acid racemization in the aging process. Gerontology. 1977;23(6):419–425. doi: 10.1159/000212218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jedziniak J. A., Kinoshita J. H., Yates E. M., Hocker L. O., Benedek G. B. On the presence and mechanism of formation of heavy molecular weight aggregates in human normal and cataractous lenses. Exp Eye Res. 1973 Feb;15(2):185–192. doi: 10.1016/0014-4835(73)90118-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liem-The K. N., Hoenders H. J. HM-crystallin as an intermediate in the conversion of water-soluble into water-insoluble rabbit lens proteins. Exp Eye Res. 1974 Dec;19(6):549–557. doi: 10.1016/0014-4835(74)90092-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masters P. M., Bada J. L., Zigler J. S., Jr Aspartic acid racemisation in the human lens during ageing and in cataract formation. Nature. 1977 Jul 7;268(5615):71–73. doi: 10.1038/268071a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pirie A. Color and solubility of the proteins of human cataracts. Invest Ophthalmol. 1968 Dec;7(6):634–650. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satoh K. Age-related changes in the structural proteins of human lens. Exp Eye Res. 1972 Jul;14(1):53–57. doi: 10.1016/0014-4835(72)90142-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector A., Freund T., Li L. K., Augusteyn R. C. Age-dependent changes in the structure of alpha crystallin. Invest Ophthalmol. 1971 Sep;10(9):677–686. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector A., Roy D., Stauffer J. Isolation and characterization of an age-dependent polypeptide from human lens with non-tryptophan fluorescence. Exp Eye Res. 1975 Jul;21(1):9–24. doi: 10.1016/0014-4835(75)90053-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wannemacher C. F., Spector A. Protein synthesis in the core of calf lens. Exp Eye Res. 1968 Oct;7(4):623–625. doi: 10.1016/s0014-4835(68)80018-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zigman S., Groff J., Yulo T., Griess G. Light extinction and protein in lens. Exp Eye Res. 1976 Nov;23(5):555–567. doi: 10.1016/0014-4835(76)90163-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


