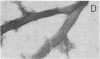
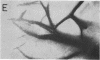
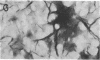
Abstract
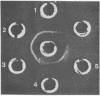
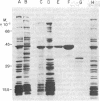
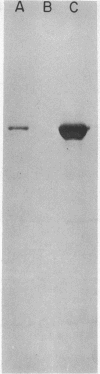
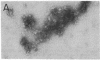
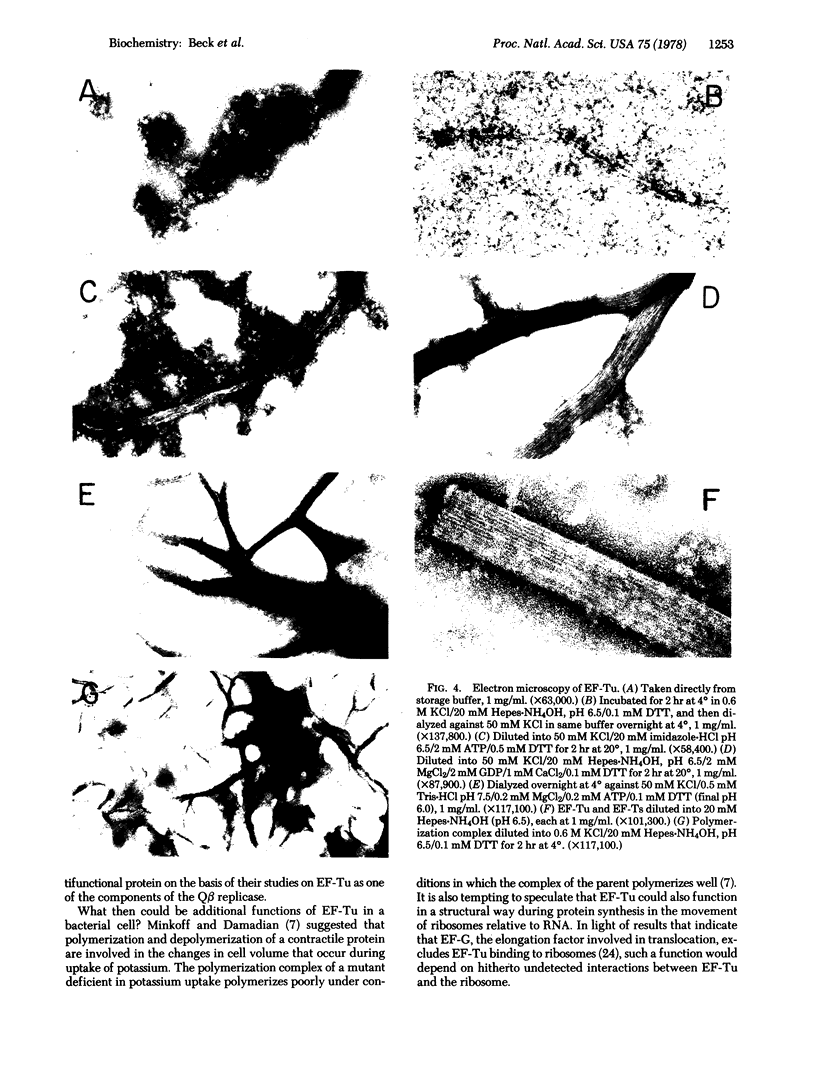
We have characterized novel properties of the bacterial protein synthesis elongation factor Tu which indicate that it may function as a structural protein. Under appropriate conditions, elongation factor Tu polymerizes to form filaments and, more often, bundles of filaments. It is also the predominant component of a complex of proteins from Escherichia coli that undergoes reversible polymerization in the presence of KCl and MgCl2. In addition, purified elongation factor Tu binds tightly to DNase I in the presence of 10 mM MgCl2. In crude extracts the factor shows no binding in the presence or absence of MgCl2. These properties suggest that elongation factor Tu may have certain actin-like properties and that it has cellular functions other than its role in protein synthesis.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beck B. D., Park J. T. Basis for the observed fluctuation of carboxypeptidase II activity during the cell cycle in BUG 6, a temperature-sensitive division mutant of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1977 Jun;130(3):1292–1302. doi: 10.1128/jb.130.3.1292-1302.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumenthal T., Landers T. A., Weber K. Bacteriophage Q replicase contains the protein biosynthesis elongation factors EF Tu and EF Ts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 May;69(5):1313–1317. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.5.1313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown S., Blumenthal T. Reconstitution of Qbeta RNA replicase from a covalently bonded elongation factor Tu-Ts complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Apr;73(4):1131–1135. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.4.1131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartree E. F. Determination of protein: a modification of the Lowry method that gives a linear photometric response. Anal Biochem. 1972 Aug;48(2):422–427. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(72)90094-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson G. R., Rosenbusch J. P. Abundance and membrane association of elongation factor Tu in E. coli. Nature. 1976 May 6;261(5555):23–26. doi: 10.1038/261023a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson G. R., Takacs B. J., Rosenbusch J. P. Properties of a major protein released from Escherichia coli by osmotic shock. Biochemistry. 1976 Jun 1;15(11):2297–2303. doi: 10.1021/bi00656a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LURIA S. E., ADAMS J. N., TING R. C. Transduction of lactose-utilizing ability among strains of E. coli and S. dysenteriae and the properties of the transducing phage particles. Virology. 1960 Nov;12:348–390. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(60)90161-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazarides E., Lindberg U. Actin is the naturally occurring inhibitor of deoxyribonuclease I. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Dec;71(12):4742–4746. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.12.4742. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller D. L. Elongation factors EF Tu and EF G interact at related sites on ribosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Mar;69(3):752–755. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.3.752. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller D. L., Hachmann J., Weissbach H. The reactions of the sulfhydryl groups on the elongation factors Tu and Ts. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1971 May;144(1):115–121. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(71)90460-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller D. L., Weissbach H. Studies on the purification and properties of factor Tu from E. coli. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1970 Nov;141(1):26–37. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(70)90102-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minkoff L., Damadian R. Actin-like properties from Escherichia coli: concept of cytotonus as the missing link between cell metabolism and the biological ion-exchange resin. J Bacteriol. 1976 Jan;125(1):353–365. doi: 10.1128/jb.125.1.353-365.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OUCHTERLONY O. Diffusion-in-gel methods for immunological analysis. Prog Allergy. 1958;5:1–78. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollard T. D., Weihing R. R. Actin and myosin and cell movement. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1974 Jan;2(1):1–65. doi: 10.3109/10409237409105443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenbusch J. P., Jacobson G. R., Jaton J. C. Does a bacterial elongation factor share a common evolutionary ancestor with actin? J Supramol Struct. 1976;5(3):391–396. doi: 10.1002/jss.400050311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossmann M. G., Argos P. The taxonomy of protein structure. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jan 5;109(1):99–129. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80048-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spudich J. A. Biochemical and structural studies of actomyosin-like proteins from non-muscle cells. II. Purification, properties, and membrane association of actin from amoebae of Dictyostelium discoideum. J Biol Chem. 1974 Sep 25;249(18):6013–6020. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Travers A. RNA polymerase specificity and the control of growth. Nature. 1976 Oct 21;263(5579):641–646. doi: 10.1038/263641a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weltman J. K., Dowben R. M. Relatedness among contractile and membrane proteins: evidence for evolution from common ancestral genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Nov;70(11):3230–3234. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.11.3230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson L., Bryan J., Ruby A., Mazia D. Precipitation of proteins by vinblastine and calcium ions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Jul;66(3):807–814. doi: 10.1073/pnas.66.3.807. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]