Abstract
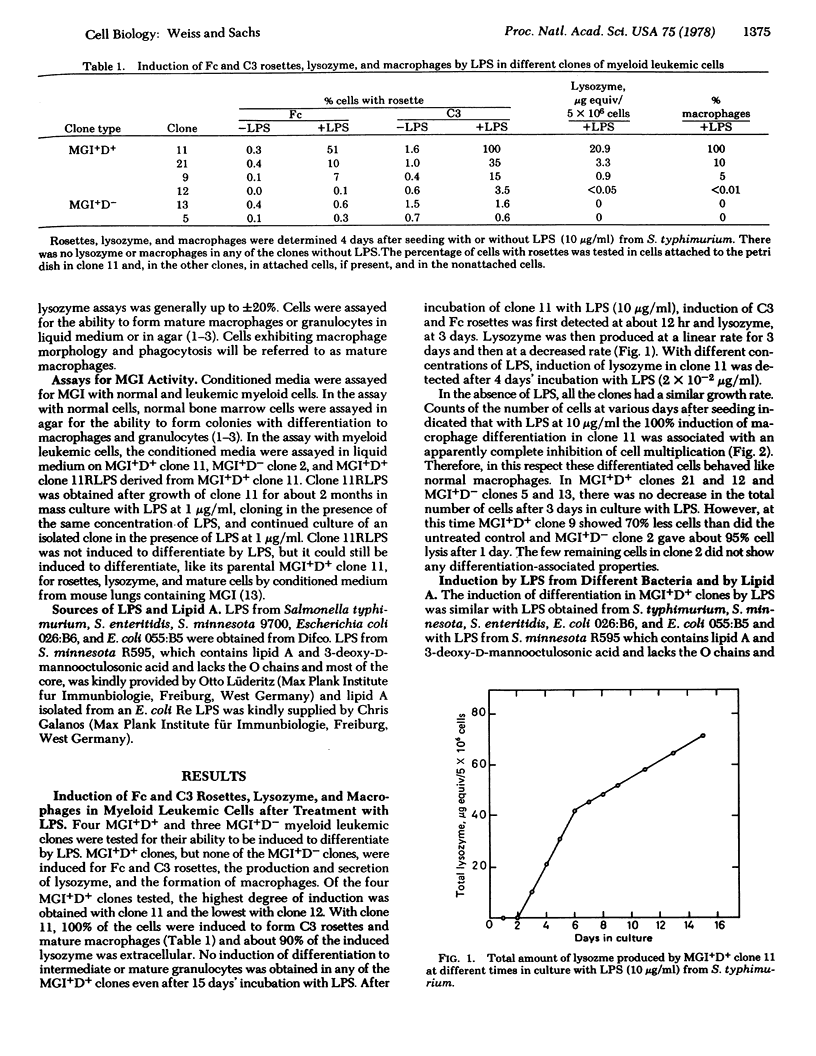
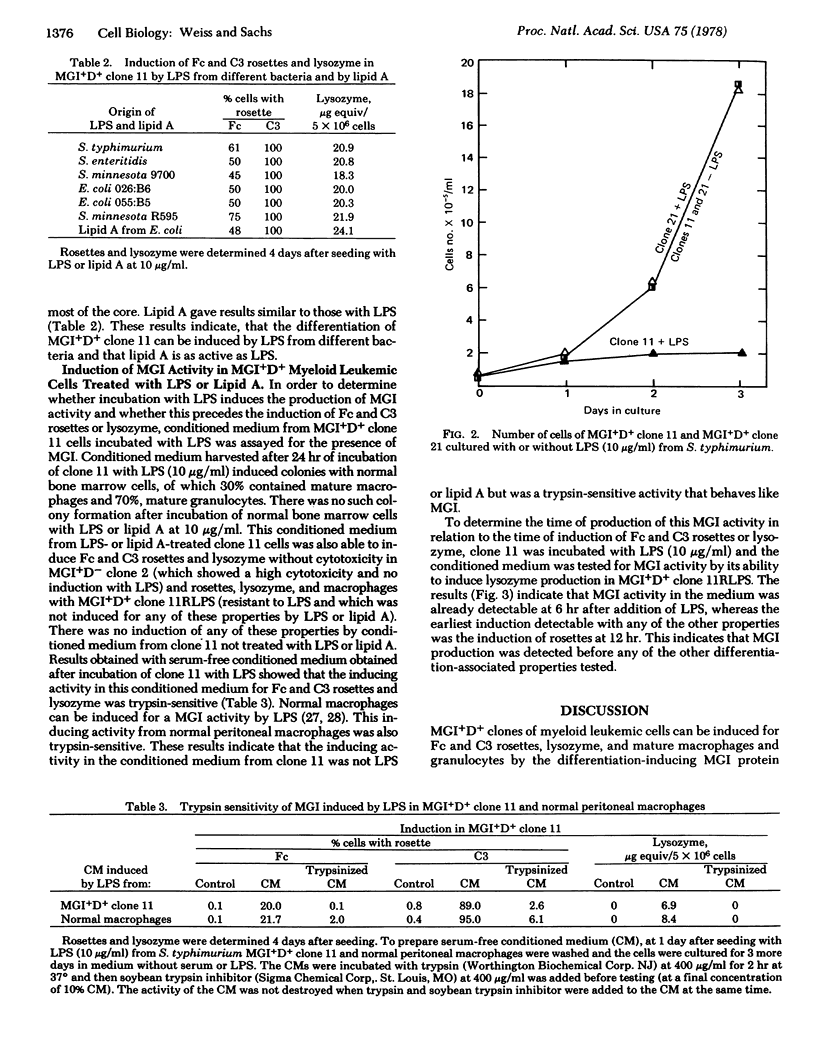
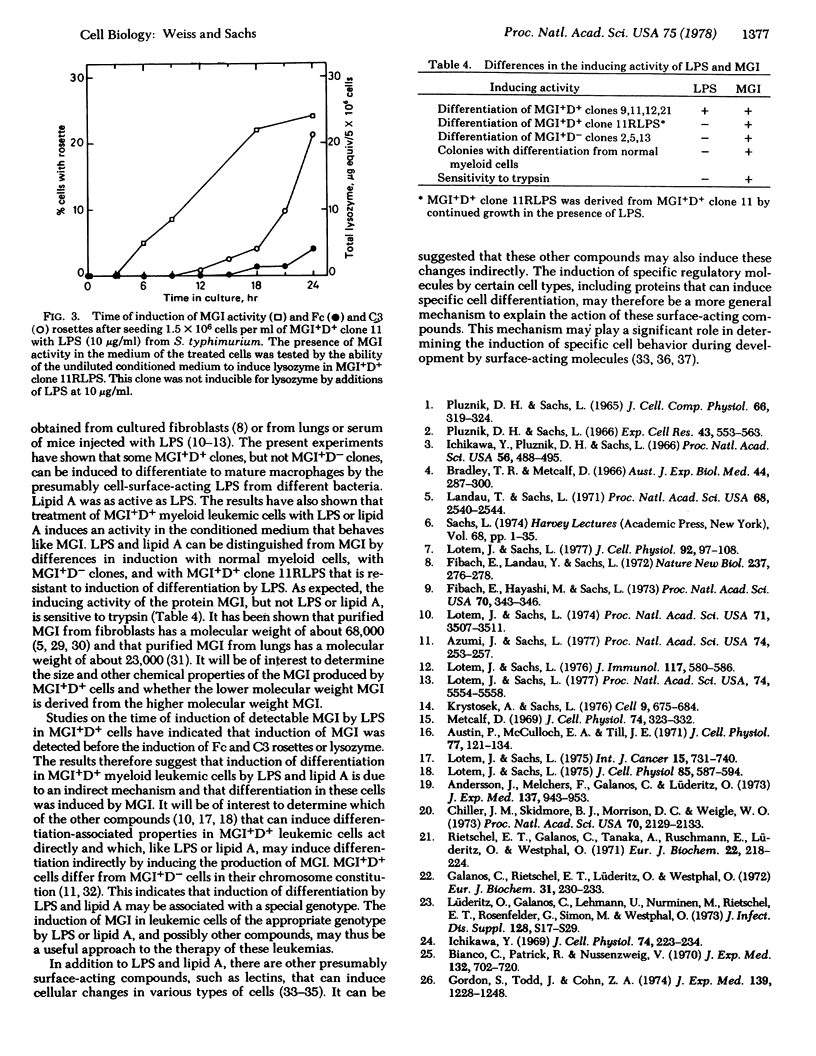
Normal myeloid and MGI+D+ clones of myeloid leukemic cells can be induced for Fc and complement component 3 rosettes, lysozme, and mature macrophages and granulocytes by a protein with macrophage- and granulocyte-inducing (MGI) activity, whereas MGI+D- clones can be induced by this protein for rosettes and lysozme but not mature cells. Lipopolysaccharides (LPS) from different bacteria induced the appearance of rosettes, lysozyme, and macrophages in some MGI+D+ clones but did not induce any of these changes in MGI+D- clones. Lipid A gave the same results as LPS. Incubation of MGI+D+ cells with LPS also induced an MGI activity detectable in the culture medium. This activity behaved like MGI in inducing (i) rosettes, lysozyme, and mature cells in MGI+D+ leukemic cells including a clone resistant to LPS, (ii) rosettes and lysozyme in MGI+D- leukemic cells, and (iii) differentiation of normal myeloid cells to mature macrophages and granulocytes. This activity was induced in MGI+D+ cells by LPS before the induction of rosettes or lysozyme. The results indicate that the lipid A portion of LPS indirectly induces differentiation of MGI+D+ myeloid leukemic cells by inducing MGI protein. It is suggested that induction of specific regulatory proteins may be a more general mechanism for the induction of differentiation by surface-acting compounds.
Keywords: lipopolysaccharide, genetic susceptibility, macrophages, MGI protein
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersson J., Melchers F., Galanos C., Lüderitz O. The mitogenic effect of lipopolysaccharide on bone marrow-derived mouse lymphocytes. Lipid A as the mitogenic part of the molecule. J Exp Med. 1973 Apr 1;137(4):943–953. doi: 10.1084/jem.137.4.943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Austin P. E., McCulloch E. A., Till J. E. Characterization of the factor in L-cell conditioned medium capable of stimulating colony formation by mouse marrow cells in culture. J Cell Physiol. 1971 Apr;77(2):121–134. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040770202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Azumi J. I., Sachs L. Chromosome mapping of the genes that control differentiation and malignancy in myeloid leukemic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jan;74(1):253–257. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.1.253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bianco C., Patrick R., Nussenzweig V. A population of lymphocytes bearing a membrane receptor for antigen-antibody-complement complexes. I. Separation and characterization. J Exp Med. 1970 Oct 1;132(4):702–720. doi: 10.1084/jem.132.4.702. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley T. R., Metcalf D. The growth of mouse bone marrow cells in vitro. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1966 Jun;44(3):287–299. doi: 10.1038/icb.1966.28. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess A. W., Camakaris J., Metcalf D. Purification and properties of colony-stimulating factor from mouse lung-conditioned medium. J Biol Chem. 1977 Mar 25;252(6):1998–2003. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiller J. M., Skidmore B. J., Morrison D. C., Weigle W. O. Relationship of the structure of bacterial lipopolysaccharides to its function in mitogenesis and adjuvanticity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jul;70(7):2129–2133. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.7.2129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cline M. J., Rothman B., Golde D. W. Effect of endotoxin on the production of colony-stimulating factor by human monocytes and macrophages. J Cell Physiol. 1974 Oct;84(2):193–196. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040840205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eaves A. C., Bruce W. R. In vitro production of colony-stimulating activity. I. Exposure of mouse peritoneal cells to endotoxin. Cell Tissue Kinet. 1974 Jan;7(1):19–30. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2184.1974.tb00395.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fibach E., Hayashi M., Sachs L. Control of normal differentiation of myeloid leukemic cells to macrophages and granulocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Feb;70(2):343–346. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.2.343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fibach E., Landau T., Sachs L. Normal differentiation of myeloid leukaemic cells induced by a differentiation-inducing protein. Nat New Biol. 1972 Jun 28;237(78):276–278. doi: 10.1038/newbio237276a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galanos C., Rietschel E. T., Lüderitz O., Westphal O., Kim Y. B., Watson D. W. Biological activities of lipid A complexed with bovine-serum albumin. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Dec 4;31(2):230–233. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb02524.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon S., Todd J., Cohn Z. A. In vitro synthesis and secretion of lysozyme by mononuclear phagocytes. J Exp Med. 1974 May 1;139(5):1228–1248. doi: 10.1084/jem.139.5.1228. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guez M., Sachs L. Purification of the protein that induces cell differentiation to macrophages and granulocytes. FEBS Lett. 1973 Dec 1;37(2):149–154. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80446-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hausman R. E., Moscona A. A. Isolation of retina-specific cell-aggregating factor from membranes of embryonic neural retina tissue. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Oct;73(10):3594–3598. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.10.3594. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi M., Fibach E., Sachs L. Control of normal differentiation of myeloid leukemic cells. V. Normal differentiation in aneuploid leukemic cells and the chromosome banding pattern of D+ and D minus clones. Int J Cancer. 1974 Jul 15;14(1):40–48. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910140106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ichikawa Y. Differentiation of a cell line of myeloid leukemia. J Cell Physiol. 1969 Dec;74(3):223–234. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040740303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ichikawa Y., Pluznik D. H., Sachs L. In vitro control of the development of macrophage and granulocyte colonies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Aug;56(2):488–495. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.2.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krystosek A., Sachs L. Control of lysozyme induction in the differentiation of myeloid leukemic cells. Cell. 1976 Dec;9(4 Pt 2):675–684. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90131-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landau T., Sachs L. Characterization of the inducer required for the development of macrophage and granulocyte colonies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Oct;68(10):2540–2544. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.10.2540. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lotem J., Sachs L. Control of Fc and C3 receptors on myeloid leukemic cells. J Immunol. 1976 Aug;117(2):580–586. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lotem J., Sachs L. Control of normal differentiation of myeloid leukemic cells. VI. Inhibition of cell multiplication and the formation of macrophages. J Cell Physiol. 1975 Jun;85(3):587–594. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040850310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lotem J., Sachs L. Control of normal differentiation of myeloid leukemic cells. XII. Isolation of normal myeloid colony-forming cells from bone marrow and the sequence of differentiation to mature granulocytes in normal and D+ myeloid leukemic cells. J Cell Physiol. 1977 Jul;92(1):97–108. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040920112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lotem J., Sachs L. Different blocks in the differentiation of myeloid leukemic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Sep;71(9):3507–3511. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.9.3507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lotem J., Sachs L. Genetic dissection of the control of normal differentiation in myeloid leukemic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5554–5558. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5554. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lotem J., Sachs L. Induction of specific changes in the surface membrane of myeloid leukemic cells by steroid hormones. Int J Cancer. 1975 May 15;15(5):731–740. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910150504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metcalf D. Studies on colony formation in vitro by mouse bone marrow cells. I. Continuous cluster formation and relation of clusters to colonies. J Cell Physiol. 1969 Dec;74(3):323–332. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040740313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pluznik D. H., Sachs L. The cloning of normal "mast" cells in tissue culture. J Cell Physiol. 1965 Dec;66(3):319–324. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1030660309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pluznik D. H., Sachs L. The induction of clones of normal mast cells by a substance from conditioned medium. Exp Cell Res. 1966 Oct;43(3):553–563. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(66)90026-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rietschel E. T., Galanos C., Tanaka A., Ruschmann E., Lüderitz O., Westphal O. Biological activities of chemically modified endotoxins. Eur J Biochem. 1971 Sep 24;22(2):218–224. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb01535.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sachs L. Regulation of membrane changes, differentiation, and malignancy in carcinogenesis. Harvey Lect. 1974;68:1–35. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley E. R., Heard P. M. Factors regulating macrophage production and growth. Purification and some properties of the colony stimulating factor from medium conditioned by mouse L cells. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jun 25;252(12):4305–4312. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


