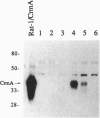
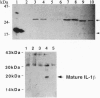
Abstract
We report here that the activation of the interleukin 1 beta (IL-1 beta)-converting enzyme (ICE) family is likely to be one of the crucial events of tumor necrosis factor (TNF) cytotoxicity. The cowpox virus CrmA protein, a member of the serpin superfamily, inhibits the enzymatic activity of ICE and ICE-mediated apoptosis. HeLa cells overexpressing crmA are resistant to apoptosis induced by Ice but not by Ich-1, another member of the Ice/ced-3 family of genes. We found that the CrmA-expressing HeLa cells are resistant to TNF-alpha/cycloheximide (CHX)-induced apoptosis. Induction of apoptosis in HeLa cells by TNF-alpha/CHX is associated with secretion of mature IL-1 beta, suggesting that an IL-1 beta-processing enzyme, most likely ICE itself, is activated by TNF-alpha/CHX stimulation. These results suggest that one or more members of the ICE family sensitive to CrmA inhibition are activated and play a critical role in apoptosis induced by TNF.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ayala J. M., Yamin T. T., Egger L. A., Chin J., Kostura M. J., Miller D. K. IL-1 beta-converting enzyme is present in monocytic cells as an inactive 45-kDa precursor. J Immunol. 1994 Sep 15;153(6):2592–2599. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beg A. A., Finco T. S., Nantermet P. V., Baldwin A. S., Jr Tumor necrosis factor and interleukin-1 lead to phosphorylation and loss of I kappa B alpha: a mechanism for NF-kappa B activation. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jun;13(6):3301–3310. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.6.3301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B., Cerami A. The biology of cachectin/TNF--a primary mediator of the host response. Annu Rev Immunol. 1989;7:625–655. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.07.040189.003205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B., Cerami A. Tumor necrosis, cachexia, shock, and inflammation: a common mediator. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:505–518. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.002445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black R. A., Kronheim S. R., Sleath P. R. Activation of interleukin-1 beta by a co-induced protease. FEBS Lett. 1989 Apr 24;247(2):386–390. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81376-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boudreau N., Sympson C. J., Werb Z., Bissell M. J. Suppression of ICE and apoptosis in mammary epithelial cells by extracellular matrix. Science. 1995 Feb 10;267(5199):891–893. doi: 10.1126/science.7531366. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiou S. K., Tseng C. C., Rao L., White E. Functional complementation of the adenovirus E1B 19-kilodalton protein with Bcl-2 in the inhibition of apoptosis in infected cells. J Virol. 1994 Oct;68(10):6553–6566. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.10.6553-6566.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis H. M., Horvitz H. R. Genetic control of programmed cell death in the nematode C. elegans. Cell. 1986 Mar 28;44(6):817–829. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90004-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelmann H., Holtmann H., Brakebusch C., Avni Y. S., Sarov I., Nophar Y., Hadas E., Leitner O., Wallach D. Antibodies to a soluble form of a tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptor have TNF-like activity. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 25;265(24):14497–14504. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fong Y., Tracey K. J., Moldawer L. L., Hesse D. G., Manogue K. B., Kenney J. S., Lee A. T., Kuo G. C., Allison A. C., Lowry S. F. Antibodies to cachectin/tumor necrosis factor reduce interleukin 1 beta and interleukin 6 appearance during lethal bacteremia. J Exp Med. 1989 Nov 1;170(5):1627–1633. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.5.1627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gagliardini V., Fernandez P. A., Lee R. K., Drexler H. C., Rotello R. J., Fishman M. C., Yuan J. Prevention of vertebrate neuronal death by the crmA gene. Science. 1994 Feb 11;263(5148):826–828. doi: 10.1126/science.8303301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hennet T., Richter C., Peterhans E. Tumour necrosis factor-alpha induces superoxide anion generation in mitochondria of L929 cells. Biochem J. 1993 Jan 15;289(Pt 2):587–592. doi: 10.1042/bj2890587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komiyama T., Ray C. A., Pickup D. J., Howard A. D., Thornberry N. A., Peterson E. P., Salvesen G. Inhibition of interleukin-1 beta converting enzyme by the cowpox virus serpin CrmA. An example of cross-class inhibition. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jul 29;269(30):19331–19337. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kostura M. J., Tocci M. J., Limjuco G., Chin J., Cameron P., Hillman A. G., Chartrain N. A., Schmidt J. A. Identification of a monocyte specific pre-interleukin 1 beta convertase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(14):5227–5231. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar S., Kinoshita M., Noda M., Copeland N. G., Jenkins N. A. Induction of apoptosis by the mouse Nedd2 gene, which encodes a protein similar to the product of the Caenorhabditis elegans cell death gene ced-3 and the mammalian IL-1 beta-converting enzyme. Genes Dev. 1994 Jul 15;8(14):1613–1626. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.14.1613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laster S. M., Wood J. G., Gooding L. R. Tumor necrosis factor can induce both apoptic and necrotic forms of cell lysis. J Immunol. 1988 Oct 15;141(8):2629–2634. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li P., Allen H., Banerjee S., Franklin S., Herzog L., Johnston C., McDowell J., Paskind M., Rodman L., Salfeld J. Mice deficient in IL-1 beta-converting enzyme are defective in production of mature IL-1 beta and resistant to endotoxic shock. Cell. 1995 Feb 10;80(3):401–411. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90490-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinou J. C., Dubois-Dauphin M., Staple J. K., Rodriguez I., Frankowski H., Missotten M., Albertini P., Talabot D., Catsicas S., Pietra C. Overexpression of BCL-2 in transgenic mice protects neurons from naturally occurring cell death and experimental ischemia. Neuron. 1994 Oct;13(4):1017–1030. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(94)90266-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miura M., Zhu H., Rotello R., Hartwieg E. A., Yuan J. Induction of apoptosis in fibroblasts by IL-1 beta-converting enzyme, a mammalian homolog of the C. elegans cell death gene ced-3. Cell. 1993 Nov 19;75(4):653–660. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90486-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul N. L., Ruddle N. H. Lymphotoxin. Annu Rev Immunol. 1988;6:407–438. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.06.040188.002203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeffer K., Matsuyama T., Kündig T. M., Wakeham A., Kishihara K., Shahinian A., Wiegmann K., Ohashi P. S., Krönke M., Mak T. W. Mice deficient for the 55 kd tumor necrosis factor receptor are resistant to endotoxic shock, yet succumb to L. monocytogenes infection. Cell. 1993 May 7;73(3):457–467. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90134-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray C. A., Black R. A., Kronheim S. R., Greenstreet T. A., Sleath P. R., Salvesen G. S., Pickup D. J. Viral inhibition of inflammation: cowpox virus encodes an inhibitor of the interleukin-1 beta converting enzyme. Cell. 1992 May 15;69(4):597–604. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90223-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid T. R., Torti F. M., Ringold G. M. Evidence for two mechanisms by which tumor necrosis factor kills cells. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 15;264(8):4583–4589. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid T., Ramesha C. S., Ringold G. M. Resistance to killing by tumor necrosis factor in an adipocyte cell line caused by a defect in arachidonic acid biosynthesis. J Biol Chem. 1991 Sep 5;266(25):16580–16586. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulze-Osthoff K., Bakker A. C., Vanhaesebroeck B., Beyaert R., Jacob W. A., Fiers W. Cytotoxic activity of tumor necrosis factor is mediated by early damage of mitochondrial functions. Evidence for the involvement of mitochondrial radical generation. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 15;267(8):5317–5323. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schütze S., Potthoff K., Machleidt T., Berkovic D., Wiegmann K., Krönke M. TNF activates NF-kappa B by phosphatidylcholine-specific phospholipase C-induced "acidic" sphingomyelin breakdown. Cell. 1992 Nov 27;71(5):765–776. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90553-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tewari M., Dixit V. M. Fas- and tumor necrosis factor-induced apoptosis is inhibited by the poxvirus crmA gene product. J Biol Chem. 1995 Feb 17;270(7):3255–3260. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.7.3255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thoma B., Grell M., Pfizenmaier K., Scheurich P. Identification of a 60-kD tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptor as the major signal transducing component in TNF responses. J Exp Med. 1990 Oct 1;172(4):1019–1023. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.4.1019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tracey K. J., Cerami A. Tumor necrosis factor, other cytokines and disease. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1993;9:317–343. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.09.110193.001533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vassalli P. The pathophysiology of tumor necrosis factors. Annu Rev Immunol. 1992;10:411–452. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.10.040192.002211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang L., Miura M., Bergeron L., Zhu H., Yuan J. Ich-1, an Ice/ced-3-related gene, encodes both positive and negative regulators of programmed cell death. Cell. 1994 Sep 9;78(5):739–750. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(94)90422-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White E., Sabbatini P., Debbas M., Wold W. S., Kusher D. I., Gooding L. R. The 19-kilodalton adenovirus E1B transforming protein inhibits programmed cell death and prevents cytolysis by tumor necrosis factor alpha. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jun;12(6):2570–2580. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.6.2570. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiegmann K., Schütze S., Kampen E., Himmler A., Machleidt T., Krönke M. Human 55-kDa receptor for tumor necrosis factor coupled to signal transduction cascades. J Biol Chem. 1992 Sep 5;267(25):17997–18001. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuan J., Shaham S., Ledoux S., Ellis H. M., Horvitz H. R. The C. elegans cell death gene ced-3 encodes a protein similar to mammalian interleukin-1 beta-converting enzyme. Cell. 1993 Nov 19;75(4):641–652. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90485-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]