Abstract
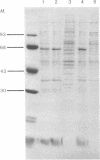
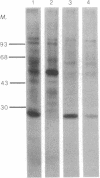
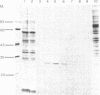
A 24,000-dalton polypeptide that binds strongly and can be specifically crosslinked to the 5'-terminal cap structure m7GpppN in eukaryotic mRNAs has been detected in protein synthesis initiation factor preparations [Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA (1978) 75, 4843--4847]. This polypeptide has been purified to apparent homogeneity by one chromatographic passage through an affinity resin prepared by coupling the levulinic acid O2',3'-acetal of m7GDP to AH-Sepharose 4B. Translation, in HeLa cell extracts, of capped mRNAs including Sindbis virus, reovirus, and rabbit globin mRNAs was stimulated by the cap-binding protein under conditions that did not increase translation of noncapped RNAs of encephalomyocarditis virus and satellite tobacco necrosis virus.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams B. L., Morgan M., Muthukrishnan S., Hecht S. M., Shatkin A. J. The effect of "cap" analogs on reovirus mRNA binding to wheat germ ribosomes. Evidence for enhancement of ribosomal binding via a preferred cap conformation. J Biol Chem. 1978 Apr 25;253(8):2589–2595. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergmann J. E., Trachsel H., Sonenberg N., Shatkin A. J., Lodish H. F. Characterization of rabbit reticulocyte factor(s) that stimulates the translation of mRNAs lacking 5'-terminal 7-methylguanosine. J Biol Chem. 1979 Mar 10;254(5):1440–1443. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolton A. E., Hunter W. M. The labelling of proteins to high specific radioactivities by conjugation to a 125I-containing acylating agent. Biochem J. 1973 Jul;133(3):529–539. doi: 10.1042/bj1330529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Both G. W., Furuichi Y., Muthukrishnan S., Shatkin A. J. Ribosome binding to reovirus mRNA in protein synthesis requires 5' terminal 7-methylguanosine. Cell. 1975 Oct;6(2):185–195. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90009-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cancedda R., Shatkin A. J. Ribosome-protected fragments from sindbis 42-S and 26-S RNAs. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Feb 15;94(1):41–50. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb12869.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eggen K. L., Shatkin A. J. In vitro translation of cardiovirus ribonucleic acid by mammalian cell-free extracts. J Virol. 1972 Apr;9(4):636–645. doi: 10.1128/jvi.9.4.636-645.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furuichi Y., LaFiandra A., Shatkin A. J. 5'-Terminal structure and mRNA stability. Nature. 1977 Mar 17;266(5599):235–239. doi: 10.1038/266235a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gedamu L., Dixon G. H. Effect of enzymatic "decapping" on protamine mRNA translation in wheat germ S-30. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Nov 14;85(1):114–124. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(78)80018-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golini F., Thach S. S., Birge C. H., Safer B., Merrick W. C., Thach R. E. Competition between cellular and viral mRNAs in vitro is regulated by a messenger discriminatory initiation factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Sep;73(9):3040–3044. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.9.3040. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kabat D., Chappell M. R. Competition between globin messenger ribonucleic acids for a discriminating initiation factor. J Biol Chem. 1977 Apr 25;252(8):2684–2690. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaempfer R., Rosen H., Israeli R. Translational control: recognition of the methylated 5' end and an internal sequence in eukaryotic mRNA by the initiation factor that binds methionyl-tRNAfMet. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Feb;75(2):650–654. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.2.650. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. How do eucaryotic ribosomes select initiation regions in messenger RNA? Cell. 1978 Dec;15(4):1109–1123. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90039-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M., Shatkin A. J. Migration of 40 S ribosomal subunits on messenger RNA in the presence of edeine. J Biol Chem. 1978 Sep 25;253(18):6568–6577. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ovchinnikov L. P., Spirin A. S., Erni B., Staehelin T. RNA-binding proteins of rabbit reticulocytes contain the two elongation factors and some of the initiation factors of translation. FEBS Lett. 1978 Apr 1;88(1):21–26. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80598-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry R. P., Kelley D. E. Kinetics of formation of 5' terminal caps in mRNA. Cell. 1976 Jul;8(3):433–442. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90156-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose J. K., Trachsel H., Leong K., Baltimore D. Inhibition of translation by poliovirus: inactivation of a specific initiation factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2732–2736. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2732. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreier M. H., Staehelin T. Initiation of mammalian protein synthesis: the importance of ribosome and initiation factor quality for the efficiency of in vitro systems. J Mol Biol. 1973 Feb 19;73(3):329–349. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90346-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seela F., Waldek S. Agarose linked adenosine and guanosine-5'-monophosphate; a new general method for the coupling of ribonucleotides to polymers through their cis-diols. Nucleic Acids Res. 1975 Dec;2(12):2343–2354. doi: 10.1093/nar/2.12.2343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shafritz D. A., Weinstein J. A., Safer B., Merrick W. C., Weber L. A., Hickey E. D., Baglioni C. Evidence for role of m7G5'-phosphate group in recognition of eukaryotic mRNA by initiation factor IF-M3. Nature. 1976 May 27;261(5558):291–294. doi: 10.1038/261291a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shatkin A. J. Capping of eucaryotic mRNAs. Cell. 1976 Dec;9(4 Pt 2):645–653. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90128-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimotohno K., Kodama Y., Hashimoto J., Miura K. I. Importance of 5'-terminal blocking structure to stabilize mRNA in eukaryotic protein synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jul;74(7):2734–2738. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.7.2734. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonenberg N., Morgan M. A., Merrick W. C., Shatkin A. J. A polypeptide in eukaryotic initiation factors that crosslinks specifically to the 5'-terminal cap in mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):4843–4847. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.4843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonenberg N., Shatkin A. J. Nonspecific effect of m7GMP on protein-RNA interactions. J Biol Chem. 1978 Oct 10;253(19):6630–6632. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonenberg N., Shatkin A. J. Reovirus mRNA can be covalently crosslinked via the 5' cap to proteins in initiation complexes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Oct;74(10):4288–4292. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.10.4288. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trachsel H., Erni B., Schreier M. H., Staehelin T. Initiation of mammalian protein synthesis. II. The assembly of the initiation complex with purified initiation factors. J Mol Biol. 1977 Nov;116(4):755–767. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90269-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]