Abstract
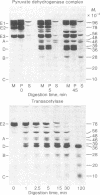
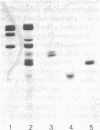
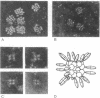
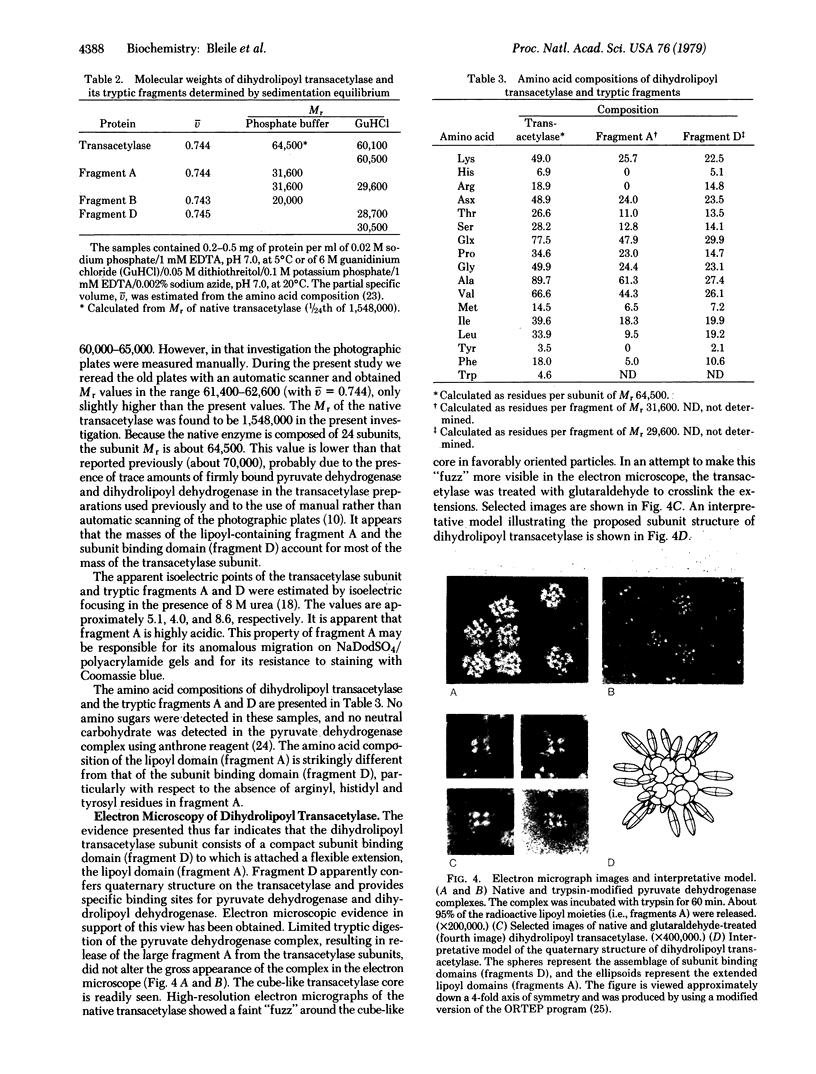
Limited tryptic digestion of the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex of Escherichia coli or its dihydrolipoyl transacetylase core cleaves the trypsin-sensitive transacetylase subunits into two large fragments, A (lipoyl domain) and D (subunit binding domain). Release of fragments A from the complex does not significantly affect its sedimentation coefficient or its appearance in the electron microscope. Fragment A contains the lipoyl moieties (3H-labeled), is acidic with an apparent isoelectric point of about 4.0, has a Mr of 31,600 as determined by sedimentation equilibrium analysis, and has a swollen or extended structure (f/fo = 1.78). Fragment A exhibits anomalous properties, probably due to its acidic nature. It is resistant to staining with Coomassie blue and it migrates on sodium dodecyl sulfate/polyacrylamide gels as if it had a Mr of 46,000-48,000. Further tryptic digestion converts fragment A into a lipoyl-containing fragment of Mr 20,000 (fragment B) and eventually into an apparently stable product of estimated Mr about 10,000 (fragment C). Fragment D has a compact structure of Mr about 29,600 as determined by sedimentation equilibrium analysis in 6 M guanidinium chloride, and it possesses the intersubunit binding sites of the transacetylase, the binding sites for pyruvate dehydrogenase and dihydrolipoyl dehydrogenase, and the catalytic site for transacetylation. The assemblage of fragments D is responsible for the cube-like appearance of the transacetylase in the electron microscope. High-resolution electron micrographs of the transacetylase show fiber-like extensions, apparently corresponding to tryptic fragment A, surrounding the cube-like core.
Keywords: multienzyme complex, binding domain, limited proteolysis
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Angelides K. J., Hammes G. G. Mechanism of action of the pyruvate dehydrogenase multienzyme complex from Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):4877–4880. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.4877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anker H. S. A solubilizable acrylamide gel for electrophoresis. FEBS Lett. 1970 Apr 16;7(3):293–293. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(70)80185-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butterworth P. J., Tsai C. S., Eley M. H., Roche T. E., Reed L. J. A kinetic study of dihydrolipoyl transacetylase from bovine kidney. J Biol Chem. 1975 Mar 10;250(5):1921–1925. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins J. H., Reed L. J. Acyl group and electron pair relay system: a network of interacting lipoyl moieties in the pyruvate and alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase complexes from Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Oct;74(10):4223–4227. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.10.4223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danson M. J., Fersht A. R., Perham R. N. Rapid intramolecular coupling of active sites in the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex of Escherichia coli: mechanism for rate enhancement in a multimeric structure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Nov;75(11):5386–5390. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.11.5386. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danson M. J., Perham R. N. Evidence for two lipoic acid residues per lipoate acetyltransferase chain in the pyruvate dehydrogenase multienzyme complex of Escherichia coli. Biochem J. 1976 Dec 1;159(3):677–682. doi: 10.1042/bj1590677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeRosier D. J., Munk P., Cox D. J. Automatic measurement of interference photographs from the ultracentrifuge. Anal Biochem. 1972 Nov;50(1):139–153. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(72)90493-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derosier D. J., Oliver R. M., Reed L. J. Crystallization and preliminary structural analysis of dihydrolipoyl transsuccinylase, the core of the 2-oxoglutarate dehydrogenase complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jun;68(6):1135–1137. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.6.1135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eley M. H., Namihira G., Hamilton L., Munk P., Reed L. J. -Keto acid dehydrogenase complexes. 18. Subunit composition of the Escherichia coli pyruvate dehydrogenase complex. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1972 Oct;152(2):655–669. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(72)90262-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frey P. A., Ikeda B. H., Gavino G. R., Speckhard D. C., Wong S. S. Escherichia coli pyruvate dehydrogenase complex. Site coupling in electron and acetyl group transfer pathways. J Biol Chem. 1978 Oct 25;253(20):7234–7241. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gebhardt C., Mecke D., Bisswanger H. Dihydrolipoamide transacetylase from Escherichia Coli: evidence for internal gene duplication. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Sep 29;84(2):508–514. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)90198-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hale G., Hooper E. A., Perham R. N. Amidination of pyruvate dehydrogenase complex of Escherichia coli under denaturing conditions. Biochem J. 1979 Jan 1;177(1):136–137. doi: 10.1042/bj1770136. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hale G., Perham R. N. Limited proteolysis of the pyruvate dehydrogenase multienzyme complex of Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Feb 15;94(1):119–126. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb12878.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOIKE M., REED L. J., CARROLL W. R. alpha-Keto acid dehydrogenation complexes. IV. Resolution and reconstitution of the Escherichia coli pyruvate dehydrogenation complex. J Biol Chem. 1963 Jan;238:30–39. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kung S. D., Sakano K., Wildman S. G. Multiple peptide composition of the large and small subunits of Nicotiana tabacum fraction I protein ascertained by fingerprinting and electrofocusing. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Sep 13;365(1):138–147. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(74)90258-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linn T. C., Pelley J. W., Pettit F. H., Hucho F., Randall D. D., Reed L. J. -Keto acid dehydrogenase complexes. XV. Purification and properties of the component enzymes of the pyruvate dehydrogenase complexes from bovine kidney and heart. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1972 Feb;148(2):327–342. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(72)90151-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu T. Y., Chang Y. H. Hydrolysis of proteins with p-toluenesulfonic acid. Determination of tryptophan. J Biol Chem. 1971 May 10;246(9):2842–2848. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris D. L. Quantitative Determination of Carbohydrates With Dreywood's Anthrone Reagent. Science. 1948 Mar 5;107(2775):254–255. doi: 10.1126/science.107.2775.254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver R. M. Negative stain electron microscopy of protein macromolecules. Methods Enzymol. 1973;27:616–672. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(73)27029-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed L. J., Oliver R. M. The multienzyme alpha-keto acid dehydrogenase complexes. Brookhaven Symp Biol. 1968 Jun;21(2):397–412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speckhard D. C., Ikeda B. H., Wong S. S., Frey P. A. Acetylation stoichiometry of Escherichia coli pyruvate dehydrogenase complex. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Jul 25;77(2):708–713. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(77)80036-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willms C. R., Oliver R. M., Henney H. R., Jr, Mukherjee B. B., Reed L. J. Alpha-keto acid dehydrogenase complexes. VI. Dissociation and reconstitution of the dihydrolipoyl transacetylase of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1967 Mar 10;242(5):889–897. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YPHANTIS D. A. EQUILIBRIUM ULTRACENTRIFUGATION OF DILUTE SOLUTIONS. Biochemistry. 1964 Mar;3:297–317. doi: 10.1021/bi00891a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]