Abstract
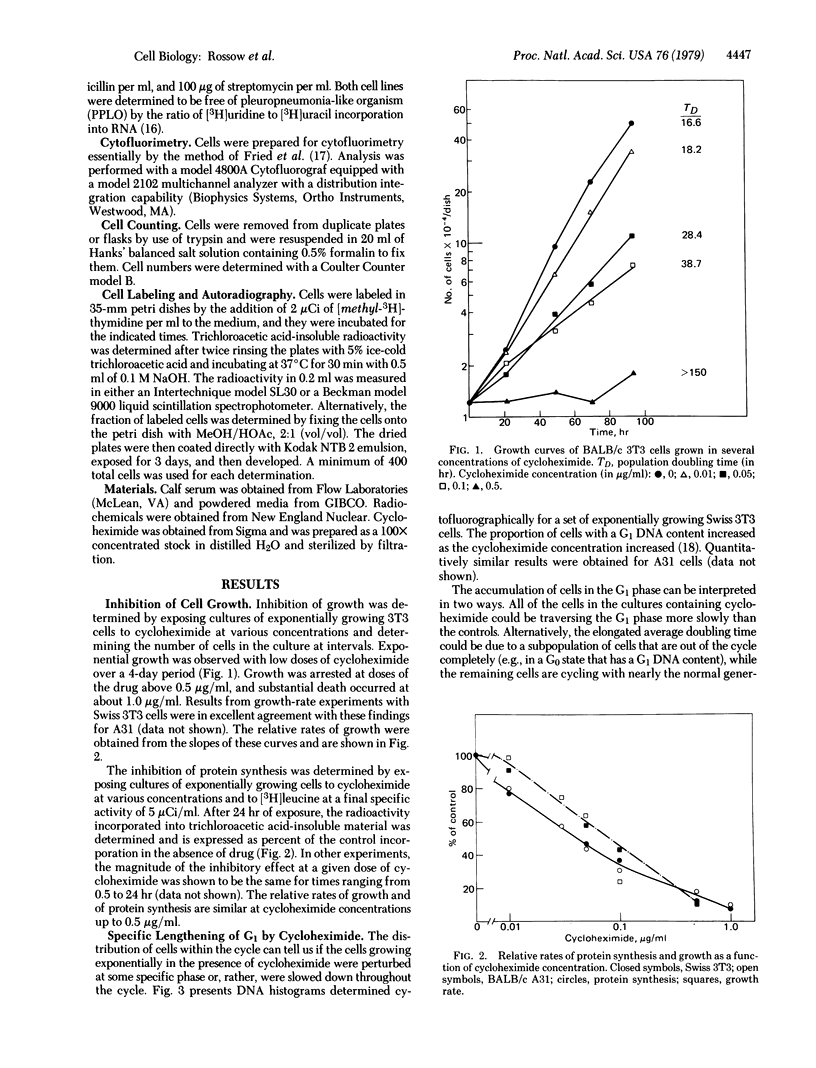
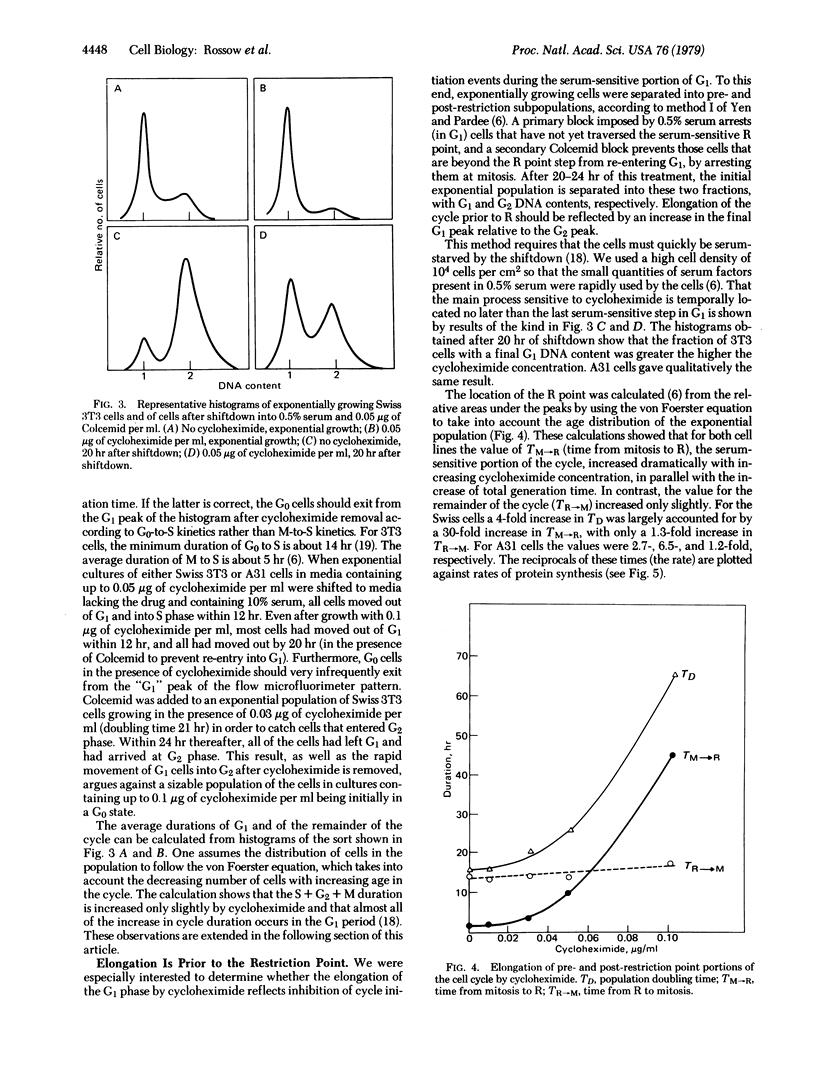
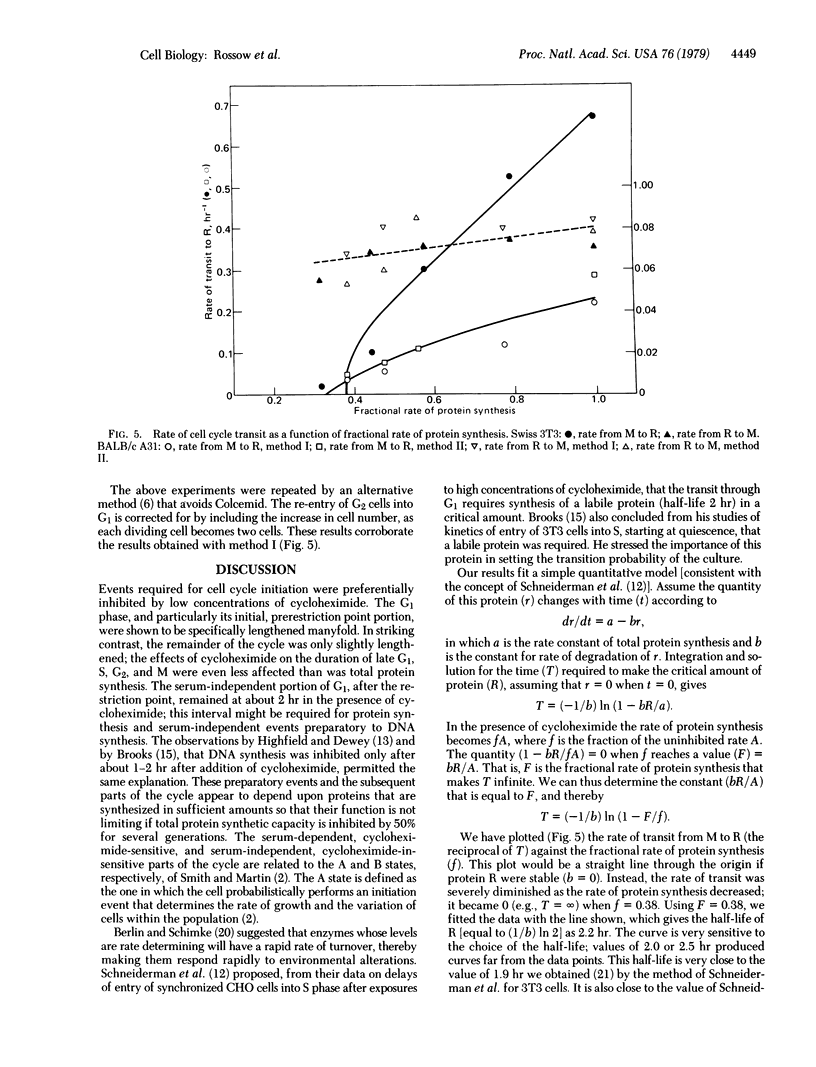
We present a model to account for several major observations on growth control of animal cells in culture. This model is tested by means of kinetic experiments which show that exponentially growing animal cells whose ability to synthesize total protein has been inhibited with cycloheximide (by up to 70%) grow at rates approximately proportional to their rates of protein synthesis. However, virtually the entire elongation of the cell cycle occurs in the part of the G1 phase that depends on a high concentration of serum in the medium. This part of the cycle has earlier been suggested to lie prior to the restriction point—i.e., the point beyond the main regulatory processes of G1. The remainder of the cycle, from restriction point to mitosis, is markedly insensitive to these concentrations of cycloheximide as well as to growth regulation. We quantitatively account for the specific lengthening of that part of the cycle involved in growth regulation by assuming that cells must accumulate a specific protein in a critical amount before they can proceed beyond the restriction point. The lability of this protein (half-life about 2 hr) makes its accumulation unusually sensitive to inhibition of total protein synthesis by cycloheximide. Its production appears to depend on growth factors provided by serum. The model can also account for greater variations of G1 durations as the growth of cell populations is made slower. It also predicts two sorts of quiescence: one of cells slowly traversing G1, in slightly suboptimal conditions; the other of cells that enter G0 under inadequate conditions. Transformation of different sorts could create cells with altered variables for initiation, synthesis, or inactivation of the regulatory protein or could altogether eliminate the need for the protein.
Keywords: 3T3 cells, restriction point, cycloheximide, cell cycle, protein synthesis
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bartholomew J. C., Yokota H., Ross P. Effect of serum on the growth of Balb oT3 A31 mouse fibroblasts and an SV40-transformed derivative. J Cell Physiol. 1976 Jul;88(3):277–286. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040880303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berlin C. M., Schimke R. T. Influence of turnover rates on the responses of enzymes to cortisone. Mol Pharmacol. 1965 Sep;1(2):149–156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks R. F. Continuous protein synthesis is required to maintain the probability of entry into S phase. Cell. 1977 Sep;12(1):311–317. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90209-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burstin S. J., Meiss H. K., Basilico C. A temperature-sensitive cell cycle mutant of the BHK cell line. J Cell Physiol. 1974 Dec;84(3):397–408. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040840308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherington P. V., Smith B. L., Pardee A. B. Loss of epidermal growth factor requirement and malignant transformation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3937–3941. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duesberg P. H., Vogt P. K. Avian acute leukemia viruses MC29 and MH2 share specific RNA sequences: evidence for a second class of transforming genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1633–1637. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried J., Perez A. G., Clarkson B. D. Flow cytofluorometric analysis of cell cycle distributions using propidium iodide. Properties of the method and mathematical analysis of the data. J Cell Biol. 1976 Oct;71(1):172–181. doi: 10.1083/jcb.71.1.172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi I., Sato G. H. Replacement of serum by hormones permits growth of cells in a defined medium. Nature. 1976 Jan 15;259(5539):132–134. doi: 10.1038/259132a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helmstetter C., Cooper S., Pierucci O., Revelas E. On the bacterial life sequence. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1968;33:809–822. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1968.033.01.093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Highfield D. P., Dewey W. C. Inhibition of DNA synthesis in synchronized Chinese hamster cells treated in G1 or early S phase with cycloheximide or puromycin. Exp Cell Res. 1972 Dec;75(2):314–320. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(72)90435-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holley R. W., Kiernan J. A. "Contact inhibition" of cell division in 3T3 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 May;60(1):300–304. doi: 10.1073/pnas.60.1.300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin R. G., Stein S. Resting state in normal and simian virus 40 transformed Chinese hamster lung cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 May;73(5):1655–1659. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.5.1655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppermann H., Levinson A. D., Varmus H. E., Levintow L., Bishop J. M. Uninfected vertebrate cells contain a protein that is closely related to the product of the avian sarcoma virus transforming gene (src). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1804–1808. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pardee A. B. A restriction point for control of normal animal cell proliferation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Apr;71(4):1286–1290. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.4.1286. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pardee A. B., James L. J. Selective killing of transformed baby hamster kidney (BHK) cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Dec;72(12):4994–4998. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.12.4994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul D. Quiescent SV40 virus transformed 3T3 cells in culture. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Aug 6;53(3):745–753. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)90156-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pledger W. J., Stiles C. D., Antoniades H. N., Scher C. D. An ordered sequence of events is required before BALB/c-3T3 cells become committed to DNA synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2839–2843. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riddle V. G., Dubrow R., Pardee A. B. Changes in the synthesis of actin and other cell proteins after stimulation of serum-arrested cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1298–1302. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider E. L., Stanbridge E. J., Epstein C. J. Incorporation of 3H-uridine and 3H-uracil into RNA: a simple technique for the detection of mycoplasma contamination of cultured cells. Exp Cell Res. 1974 Mar 15;84(1):311–318. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(74)90411-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneiderman M. H., Dewey W. C., Highfield D. P. Inhibition of DNA synthesis in synchronized Chinese hamster cells treated in G1 with cycloheximide. Exp Cell Res. 1971 Jul;67(1):147–155. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(71)90630-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shields R., Smith J. A. Cells regulate their proliferation through alterations in transition probability. J Cell Physiol. 1977 Jun;91(3):345–355. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040910304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. A., Martin L. Do cells cycle? Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Apr;70(4):1263–1267. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.4.1263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Temin H. M. Stimulation by serum of multiplication of stationary chicken cells. J Cell Physiol. 1971 Oct;78(2):161–170. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040780202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tenen D. G., Garewal H., Haines L. L., Hudson J., Woodard V., Light S., Livingston D. M. Purification of simian virus 40 tumor antigen from a line of simian virus 40-transformed human cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Sep;74(9):3745–3749. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.9.3745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tobey R. A., Ley K. D. Regulation of initiation of DNA synthesis in Chinese hamster cells. I. Production of stable, reversible G1-arrested populations in suspension culture. J Cell Biol. 1970 Jul;46(1):151–157. doi: 10.1083/jcb.46.1.151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yen A., Pardee A. B. Arrested states produced by isoleucine deprivation and their relationship to the low serum produced arrested state in Swiss 3T3 cells. Exp Cell Res. 1978 Jul;114(2):389–395. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(78)90497-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yen A., Pardee A. B. Exponential 3T3 cells escape in mid-G1 from their high serum requirement. Exp Cell Res. 1978 Oct 1;116(1):103–113. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(78)90068-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



