Abstract
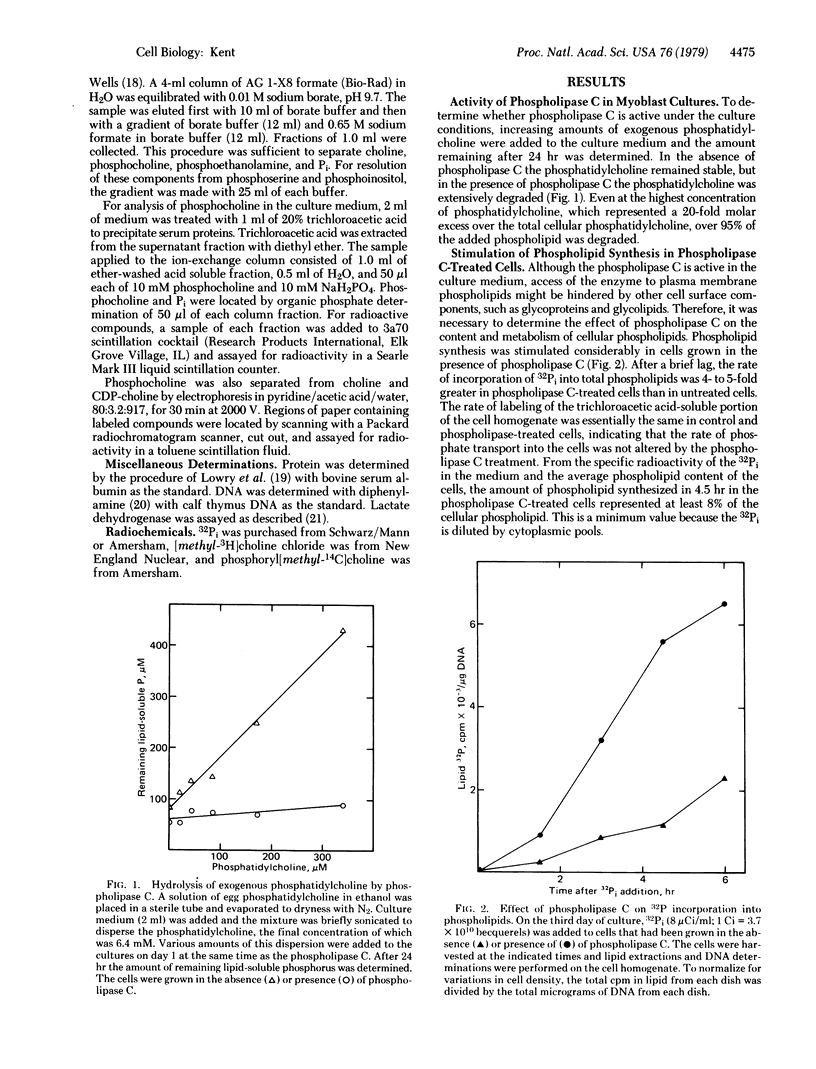
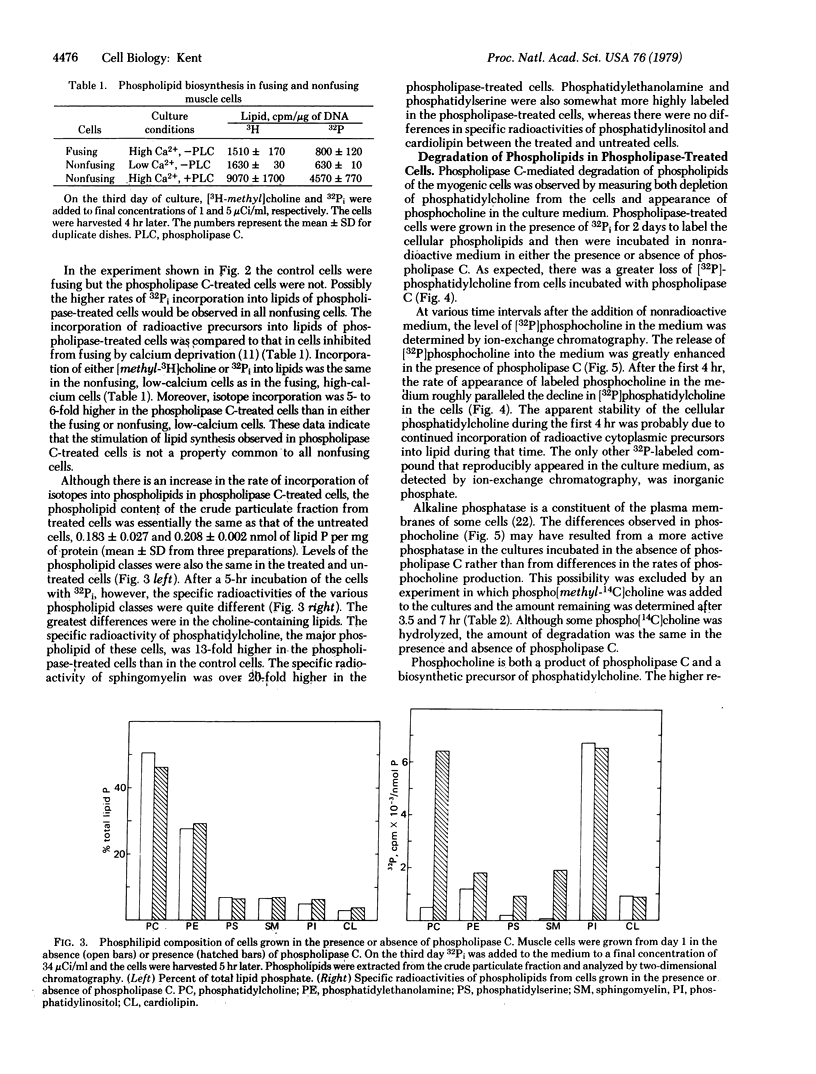
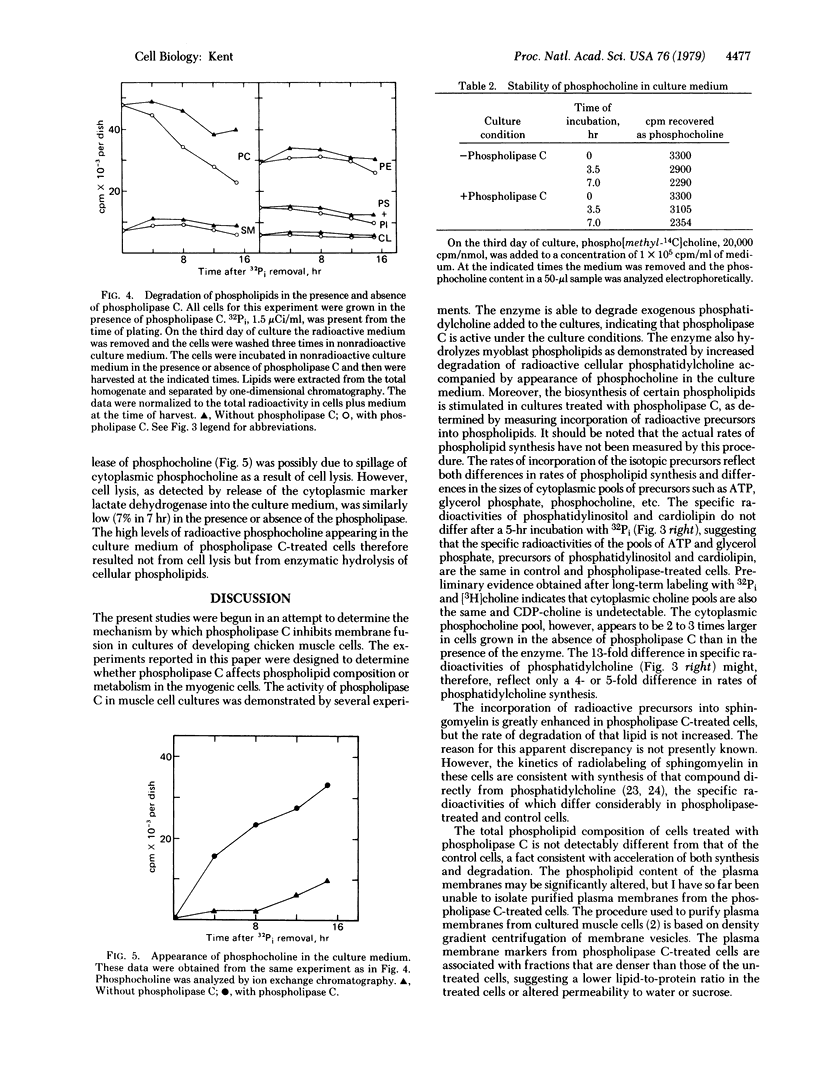
Phospholipid metabolism is dramatically stimulated in cultured myogenic cells in which cell fusion was inhibited with phospholipase C (phosphatidylcholine choline-phosphohydrolase; EC 3.1.4.3). Phospholipase C was active under the culture conditions as shown by the degradation of exogenous phosphatidylcholine. Rates of incorporation of 32Pi and [methyl-3H]choline into lipids were about 5-fold greater in phospholipase-treated cells than in either untreated fusing cells or untreated cells prevented from fusing by calcium deprivation. The greatest stimulation in the phospholipase C-treated cultures occurred with synthesis of phosphatidylcholine and sphingomyelin; synthesis of phosphatidylinositol and cardiolipin was not stimulated. Degradation of cellular [32P]phosphatidylcholine and appearance in the culture medium of the degradation product [32P]phosphocholine were both increased. Levels of total cellular phospholipids and of individual phospholipid classes were similar in control and phospholipase-treated cells. The results suggest that the membrane phospholipid composition in myogenic cells is controlled by a regulatory mechanism which increases the synthesis of phospholipids that are degraded in the presence of the phospholipase.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BLIGH E. G., DYER W. J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1959 Aug;37(8):911–917. doi: 10.1139/o59-099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breckenridge W. C., Gombos G., Morgan I. G. The lipid composition of adult rat brain synaptosomal plasma membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Jun 20;266(3):695–707. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(72)90012-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DePierre J. W., Karnovsky M. L. Plasma membranes of mammalian cells: a review of methods for their characterization and isolation. J Cell Biol. 1973 Feb;56(2):275–303. doi: 10.1083/jcb.56.2.275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischbach G. D. Synapse formation between dissociated nerve and muscle cells in low density cell cultures. Dev Biol. 1972 Jun;28(2):407–429. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(72)90023-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz A. F., Wight A., Ludwig P., Cornell R. Interrelated lipid alterations and their influence on the proliferation and fusion of cultured myogenic cells. J Cell Biol. 1978 May;77(2):334–357. doi: 10.1083/jcb.77.2.334. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kent C., Schimmel S. D., Vagelos P. R. Lipid composition of plasma membranes from developing chick muscle cells in culture. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Sep 19;360(3):312–321. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(74)90061-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leyva A., Jr, Kelley W. N. Measurement of DNA in cultured human cells. Anal Biochem. 1974 Nov;62(1):173–179. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90378-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marggraf W. D., Anderer F. A. Alternative pathways in the biosynthesis of sphingomyelin and the role of phosphatidylcholine, CDPcholine and phosphorylcholine as precursors. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1974 Jul;355(7):803–810. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1974.355.2.803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nameroff M., Munar E. Inhibition of cellular differentiation by phospholipase C. II. Separation of fusion and recognition among myogenic cells. Dev Biol. 1976 Mar;49(1):288–293. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(76)90275-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nameroff M., Trotter J. A., Keller J. M., Munar E. Inhibition of cellular differentiation by phospholipase C. I. Effects of the enzyme on myogenesis and chondrogenesis in vitro. J Cell Biol. 1973 Jul;58(1):107–118. doi: 10.1083/jcb.58.1.107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PANGBORN M. C. A simplified purification of lecithin. J Biol Chem. 1951 Feb;188(2):471–476. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouser G., Fkeischer S., Yamamoto A. Two dimensional then layer chromatographic separation of polar lipids and determination of phospholipids by phosphorus analysis of spots. Lipids. 1970 May;5(5):494–496. doi: 10.1007/BF02531316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schimmel S. D., Kent C., Bischoff R., Vagelos P. R. Plasma membranes from cultured muscle cells: isolation procedure and separation of putative plasma-membrane marker enzymes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Nov;70(11):3195–3199. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.11.3195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shainberg A., Yagil G., Yaffe D. Alterations of enzymatic activities during muscle differentiation in vitro. Dev Biol. 1971 May;25(1):1–29. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(71)90017-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skipski V. P., Peterson R. F., Barclay M. Quantitative analysis of phospholipids by thin-layer chromatography. Biochem J. 1964 Feb;90(2):374–378. doi: 10.1042/bj0900374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullman M. D., Radin N. S. The enzymatic formation of sphingomyelin from ceramide and lecithin in mouse liver. J Biol Chem. 1974 Mar 10;249(5):1506–1512. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaffe D. Retention of differentiation potentialities during prolonged cultivation of myogenic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Oct;61(2):477–483. doi: 10.1073/pnas.61.2.477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Bosch H. Phosphoglyceride metabolism. Annu Rev Biochem. 1974;43(0):243–277. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.43.070174.001331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



