Abstract
Peripheral blood leukocytes, obtained from volunteers after vaccination or natural illness with influenza, were assayed for cytotoxicity against influenza virus-infected cells. Approximately 7 days after vaccination or the onset of respiratory illness, peak cytotoxicity was demonstrated in a chromium-release assay. Secretion of specific antibody against hemagglutinin from the leukocytes during in vitro incubation was demonstrated in quantities that would mediate the cell cytotoxicity observed. Antibody secretion was inhibited by exposure to cycloheximide but not by exposure to trypsin. The secretion of antibody against hemagglutinin from peripheral blood leukocytes occurred only at the time of maximal cytotoxicity. We thus demonstrate secretion of specific antibody in vitro after recent viral antigen stimulation. Moreover, this antibody is capable of conveying cytotoxic capacity to peripheral blood leukocytes that may be important in the recovery process from acute viral infection.
Full text
PDF
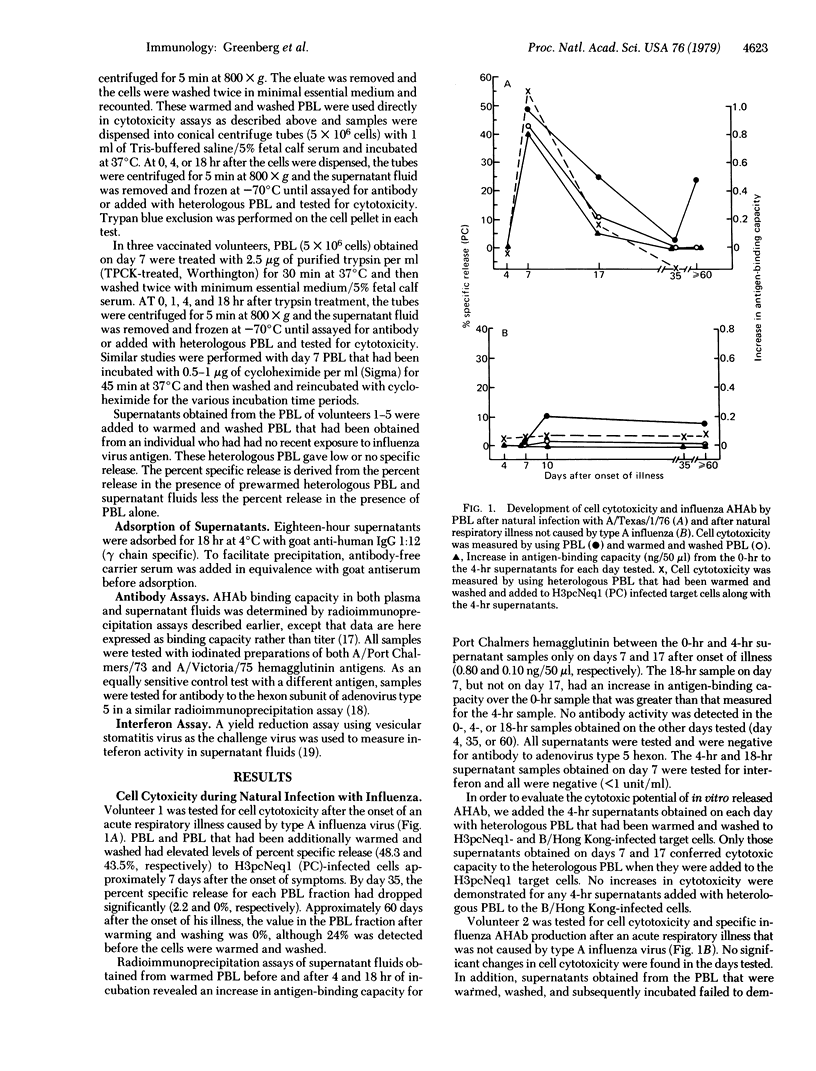
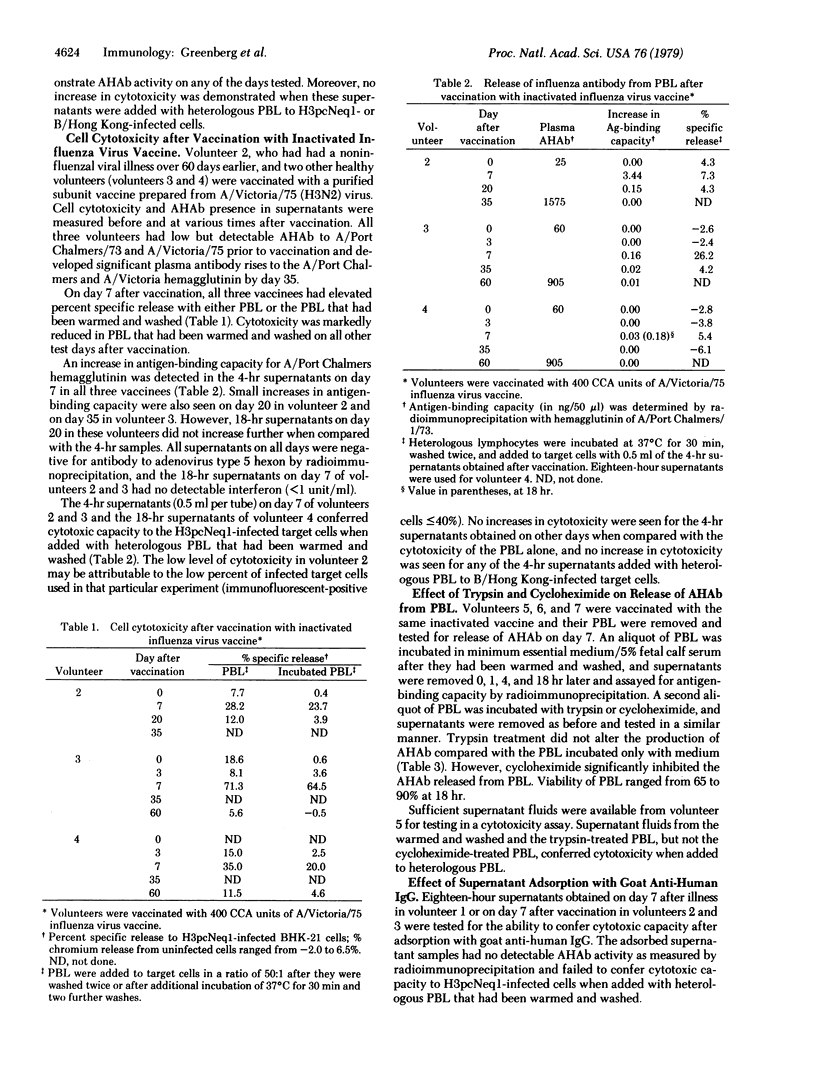


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blanden R. V., Gardner I. D. The cell-mediated immune response to ectromelia virus infection. I. Kinetics and characteristics of the primary effector T cell response in vivo. Cell Immunol. 1976 Mar 15;22(2):271–282. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(76)90029-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brier A. M., Wohlenberg C., Rosenthal J., Mage M., Notkins A. L. Inhibition or enhancement of immunological injury of virus-infected cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Dec;68(12):3073–3077. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.12.3073. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg A. H., Hudson L., Shen L., Roitt I. M. Antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity due to a "null" lymphoid cell. Nat New Biol. 1973 Mar 28;242(117):111–113. doi: 10.1038/newbio242111a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg S. B., Criswell B. S., Couch R. B. Lymohocyte-mediated cytotoxicity against influenza virus-infected cells: an in vitro method. J Immunol. 1975 Aug;115(2):601–603. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg S. B., Criswell B. S., Six H. R., Couch R. B. Lymphocyte cytotoxicity to influenza virus-infected cells. II. Requirement for antibody and non-T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1977 Dec;119(6):2100–2106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg S. B., Criswell B. S., Six H. R., Couch R. B. Lymphocyte cytotoxicity to influenza virus-infected cells: response to vaccination and virus infection. Infect Immun. 1978 Jun;20(3):640–645. doi: 10.1128/iai.20.3.640-645.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harmon M. W., Greenberg S. B., Johnson P. E., Couch R. B. Human nasal epithelial cell culture system: evaluation of response to human interferons. Infect Immun. 1977 May;16(2):480–485. doi: 10.1128/iai.16.2.480-485.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamon E. W., Whitten H. D., Skurzak H. M., Andersson B., Lidin B. IgM antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity in the Moloney sarcoma virus system: the involvement of T and B lymphocytes as effector cells. J Immunol. 1975 Nov;115(5):1288–1294. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamon E. W., Wigzel H., Klein E., Andersson B., Skurzak H. M. The lymphocyte response to primary Moloney sarcoma virus tumors in BALB-c mice. Definition of the active subpopulations at different times after infection. J Exp Med. 1973 Jun 1;137(6):1472–1493. doi: 10.1084/jem.137.6.1472. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leshem B., Naor D. Studies on the immune response to fixed antigens. III. Induction of helper function for antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity responses. J Immunol. 1978 Aug;121(2):401–408. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lodmell D. L., Niwa A., Hayashi K., Notkins A. L. Prevention of cell-to-cell spread of herpes simplex virus by leukocytes. J Exp Med. 1973 Mar 1;137(3):706–720. doi: 10.1084/jem.137.3.706. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Møller-Larsen A., Haahr S., Heron I. Lymphocyte-mediated cytotoxicity in humans during revaccination with vaccinia virus. Infect Immun. 1978 Sep;21(3):687–695. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.3.687-695.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perrin L. H., Tishon A., Oldstone M. B. Immunologic injury in measles virus infection. III. Presence and characterization of human cytotoxic lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1977 Jan;118(1):282–290. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perrin L. H., Zinkernagel R. M., Oldstone M. B. Immune response in humans after vaccination with vaccinia virus: generation of a virus-specific cytotoxic activity by human peripheral lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1977 Oct 1;146(4):949–969. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.4.949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santoli D., Trinchieri G., Lief F. S. Cell-mediated cytotoxicity against virus-infected target cells in humans. I. Characterization of the effector lymphocyte. J Immunol. 1978 Aug;121(2):526–531. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schirrmacher V., Rubin B., Pross H., Wigzell H. Cytotoxic immune cells with specificity for defined soluble antigens. IV. Antibody as mediator of specific cytotoxicity. J Exp Med. 1974 Jan 1;139(1):93–107. doi: 10.1084/jem.139.1.93. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott J. V., Dreesman G. R., Spira G., Kasel J. A. Radioimmunoassay of human serum antibody specific for adenovirus type 5-purified fiber. J Immunol. 1975 Jul;115(1):124–128. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shore S. L., Black C. M., Melewicz F. M., Wood P. A., Nahmias A. J. Antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity to target cells infected with type 1 and type 2 herpes simplex virus. J Immunol. 1976 Jan;116(1):194–201. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shore S. L., Nahmias A. J., Starr S. E., Wood P. A., McFarlin D. E. Detection of cell-dependent cytotoxic antibody to cells infected with herpes simplex virus. Nature. 1974 Sep 27;251(5473):350–352. doi: 10.1038/251350a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Six H. R., Kasel J. A. Radioimmunoprecipitation assay for quantitation of serum antibody to the hemagglutinin of type A influenza virus. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Feb;7(2):165–171. doi: 10.1128/jcm.7.2.165-171.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. W., Adam E., Melnick J. L., Rawls W. E. Use of the 51 Cr release test to demonstrate patterns of antibody response in humans to herpesvirus types 1 and 2. J Immunol. 1972 Sep;109(3):554–564. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ting C. C., Kirchner H., Rodrigues D., Park J. Y., Herberman R. B. Cell-mediated immunity to Friend virus-induced leukemia. III. Characteristics of secondary cell-mediated cytotoxic response. J Immunol. 1976 Jan;116(1):244–252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Boxel J. A., Stobo J. D., Paul W. E., Green I. Antibody-dependent lymphoid cell-mediated cytotoxicity: no requirement for thymus-derived lymphocytes. Science. 1972 Jan 14;175(4018):194–196. doi: 10.1126/science.175.4018.194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker W. S., Demus A. Antibody-dependent cytolysis of chicken erythrocytes by an in vitro-established line of mouse peritoneal macrophages. J Immunol. 1975 Feb;114(2 Pt 2):765–769. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wåhlin B., Perlmann H., Perlmann P. Analysis by a plaque assay of IgG- or IgM- dependent cytolytic lymphocytes in human blood. J Exp Med. 1976 Nov 2;144(5):1375–1380. doi: 10.1084/jem.144.5.1375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


