Abstract
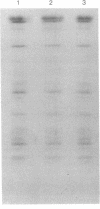
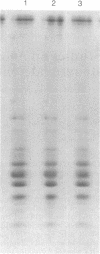
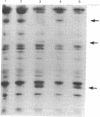
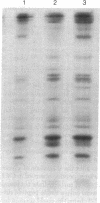
Although genes controlling the expression of certain complement components have been shown to be linked to the major histocompatibility complex of several species, the structural genes that encode these molecules have been more difficult to map. In this study, the three constitutive polypeptide chains of the fourth component of murine complement (C4) (alpha, beta, and gamma) were isolated from 14 different inbred strains and compared by peptide mapping on analytical sodium dodecyl sulfate gels. The peptide patterns of the alpha and gamma subunits appeared to be nearly identical, but two distinctly different patterns were observed for the C4 beta chain. This structural variant was mapped to the S or G region and, as such, provides direct evidence that a structural gene for a complement component is encoded within a major histocompatibility complex.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alper C. A. Inherited structural polymorphism in human C2: evidence for genetic linkage between C2 and Bf. J Exp Med. 1976 Oct 1;144(4):1111–1115. doi: 10.1084/jem.144.4.1111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bitter-Suermann D., Krönke M., Brade V., Hadding U. Inherited polymorphism of guinea pig factor B and C4: evidence for genetic linkage between the C4 and Bf loci. J Immunol. 1977 May;118(5):1822–1826. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolotin C., Morris S., Tack B., Prahl J. Purification and structural analysis of the fourth component of human complement. Biochemistry. 1977 May 3;16(9):2008–2015. doi: 10.1021/bi00628a039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capra J. D., Vitetta E. S., Klein J. Studies on the murine Ss protein. I. Purification, molecular weight, and subunit structure. J Exp Med. 1975 Sep 1;142(3):664–672. doi: 10.1084/jem.142.3.664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll M. C., Capra J. D. Studies on the murine Ss protein: demonstration that the Ss protein is functionally the fourth component of complement. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 May;75(5):2424–2428. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.5.2424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Fischer S. G., Kirschner M. W., Laemmli U. K. Peptide mapping by limited proteolysis in sodium dodecyl sulfate and analysis by gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 10;252(3):1102–1106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook R., Carroll M. C., Uhr J. W., Vitetta E. S., Capra J. D. Studies on the protein products of murine chromosome 17:a status report. Transplant Proc. 1978 Dec;10(4):695–699. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curman B., Ostberg L., Sandberg L., Malmheden-Eriksson I., Stålenheim G., Rask L., Peterson P. A. H-2 linked Ss protein is C4 component of complement. Nature. 1975 Nov 20;258(5532):243–245. doi: 10.1038/258243a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Da Silva F. P., Hoecker G. F., Day N. K., Vienne K., Rubinstein P. Murine complement component 3: genetic variation and linkage to H-2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Feb;75(2):963–965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.2.963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Day N. K., L'Esperance R., Good R. A., Michael A. F., Hansen J. A., Dupont B., Jersild C. Hereditary C2 deficiency: Genetic studies and association with the HL-A system. J Exp Med. 1975 Jun 1;141(6):1464–1469. doi: 10.1084/jem.141.6.1464. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Démant P., Capková J., Hinzová E., Vorácová B. The role of the histocompatibility-2-linked Ss-Slp region in the control of mouse complement. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Mar;70(3):863–864. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.3.863. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira A., Nussenzweig V. Genetic linkage between serum levels of the third component of complement and the H-2 complex. J Exp Med. 1975 Feb 1;141(2):513–517. doi: 10.1084/jem.141.2.513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira A., Nussenzweig V., Gigli I. Structural and functional differences between the H-2 controlled Ss and Slp proteins. J Exp Med. 1978 Nov 1;148(5):1186–1197. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.5.1186. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu S. M., Kunkel H. G., Brusman H. P., Allen F. H., Jr, Fotino M. Evidence for linkage between HL-A histocompatibility genes and those involved in the synthesis of the second component of complement. J Exp Med. 1974 Oct 1;140(4):1108–1111. doi: 10.1084/jem.140.4.1108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gigli I., von Zabern I., Porter R. R. The isolation and structure of C4, the fourth component of human complement. Biochem J. 1977 Sep 1;165(3):439–446. doi: 10.1042/bj1650439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall R. E., Colten H. R. Cell-free synthesis of the fourth component of guinea pig complement (C4): identification of a precursor of serum C4 (pro-C4). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Apr;74(4):1707–1710. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.4.1707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall R. E., Colten H. R. Genetic defect in biosynthesis of the precursor form of the fourth component of complement. Science. 1978 Jan 6;199(4324):69–70. doi: 10.1126/science.199.4324.69. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen T. H., Shin H. S., Shreffler D. C. Evidence for the involvement of the Ss protein of the mouse in the hemolytic complement system. J Exp Med. 1975 May 1;141(5):1216–1220. doi: 10.1084/jem.141.5.1216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houmard J., Drapeau G. R. Staphylococcal protease: a proteolytic enzyme specific for glutamoyl bonds. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Dec;69(12):3506–3509. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.12.3506. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnstone A. P., Thunberg A. L., Kindt T. J. Homogeneous rabbit immunoglobulin lacking group a allotypes: amino acid sequence analysis of the heavy chain. Biochemistry. 1978 Apr 4;17(7):1337–1344. doi: 10.1021/bi00600a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lachmann P. J., Grennan D., Martin A., Demant P. Identification of Ss protein as murine C4. Nature. 1975 Nov 20;258(5532):242–243. doi: 10.1038/258242a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meo T., Krasteff T., Shreffler D. C. Immunochemical characterization of murine H-2 controlled Ss (serum substance) protein through identification of its human homologue as the fourth component of complement. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Nov;72(11):4536–4540. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.11.4536. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Natsuume-Sakai S., Hayakawa J. I., Takahashi M. Genetic polymorphism of murine C3 controlled by a single co-dominant locus on chromosome 17. J Immunol. 1978 Aug;121(2):491–498. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Neill G. J., Yang S. Y., Dupont B. Two HLA-linked loci controlling the fourth component of human complement. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):5165–5169. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.5165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pangburn M. K., Schreiber R. D., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Human complement C3b inactivator: isolation, characterization, and demonstration of an absolute requirement for the serum protein beta1H for cleavage of C3b and C4b in solution. J Exp Med. 1977 Jul 1;146(1):257–270. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.1.257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Passmore H. C., Shreffler D. C. A sex-limited serum protein variant in the mouse: hormonal control of phenotypic expression. Biochem Genet. 1971 Apr;5(2):201–209. doi: 10.1007/BF00485645. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Passmore H. C., Shreffler D. C. A sex-limited serum protein variant in the mouse: inheritance and association with the H-2 region. Biochem Genet. 1970 Jun;4(3):351–365. doi: 10.1007/BF00485752. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roos M. H., Atkinson J. P., Shreffler D. C. Molecular characterization of the Ss and Slp (C4) proteins of the mouse H-2 complex: subunit composition, chain size polymorphism, and an intracellular (PRO-Ss) precursor. J Immunol. 1978 Sep;121(3):1106–1115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenfeld S. I., Ruddy S., Austen K. F. Structural polymorphism of the fourth component of human complement. J Clin Invest. 1969 Dec;48(12):2283–2292. doi: 10.1172/JCI106194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber R. D., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Fourth component of human complement: description of a three polypeptide chain structure. J Exp Med. 1974 Nov 1;140(5):1324–1335. doi: 10.1084/jem.140.5.1324. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shreffler D C, Owen R D. A Serologically Detected Variant in Mouse Serum: Inheritance and Association with the Histocompatibility-2 Locus. Genetics. 1963 Jan;48(1):9–25. doi: 10.1093/genetics/48.1.9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shreffler D. C., David C. S. The H-2 major histocompatibility complex and the I immune response region: genetic variation, function, and organization. Adv Immunol. 1975;20:125–195. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60208-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teisberg P., Olaisen B., Jonassen R., Gedde-Dahl T., Jr, Thorsby E. The genetic polymorphism of the fourth component of human complement: methodological aspects and a presentation of linkage and association data relevant to its localization in the HLA region. J Exp Med. 1977 Nov 1;146(5):1380–1389. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.5.1380. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vitetta E. S., Capra J. D. The protein products of the murine 17th chromosome: genetics and structure. Adv Immunol. 1978;26:147–193. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60230-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziegler J. B., Alper C. A., Balner H. Properdin factor B and histocompatibility loci linked in the rhesus monkey. Nature. 1975 Apr 17;254(5501):609–611. doi: 10.1038/254609a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]