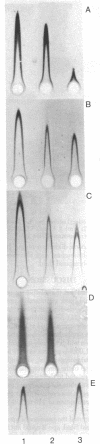
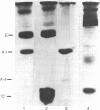
Abstract
The presence of apolipoproteins A-I, E, C-II, and C-III and the absence of apolipoprotein B was demonstrated in human cerebrospinal fluid. The concentration of apolipoproteins was measured by electroimmunoassay. Apolipoproteins E, C-II, and C-III were present in cerebrospinal fluid at 3--5% of their concentration in plasma; the cerebrospinal fluid level of apolipoprotein A-I was 0.4%. Most of the cerebrospinal fluid apolipoproteins were present in the rho less than 1.21 g/ml lipoprotein fraction. The major apolipoporteins of cerebrospinal fluid are E and A-I. The possible mechanism of transfer and the physiological and pathophysiological role of apolipoproteins in cerebrospinal fluid are postulated.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brown W. V., Levy R. I., Fredrickson D. S. Studies of the proteins in human plasma very low density lipoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1969 Oct 25;244(20):5687–5694. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chajek T., Fielding C. J. Isolation and characterization of a human serum cholesteryl ester transfer protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jul;75(7):3445–3449. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.7.3445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forte T., Nichols A. V. Application of electron microscopy to the study of plasma lipoprotein structure. Adv Lipid Res. 1972;10:1–41. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRABAR P., WILLIAMS C. A., Jr Méthode immuno-électrophorétique d'analyse de mélanges de substances antigéniques. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1955 May;17(1):67–74. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(55)90320-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S. The low-density lipoprotein pathway and its relation to atherosclerosis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1977;46:897–930. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.46.070177.004341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAVEL R. J., EDER H. A., BRAGDON J. H. The distribution and chemical composition of ultracentrifugally separated lipoproteins in human serum. J Clin Invest. 1955 Sep;34(9):1345–1353. doi: 10.1172/JCI103182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton R. L., Williams M. C., Fielding C. J., Havel R. J. Discoidal bilayer structure of nascent high density lipoproteins from perfused rat liver. J Clin Invest. 1976 Sep;58(3):667–680. doi: 10.1172/JCI108513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson R. L., Morrisett J. D., Gotto A. M., Jr Lipoprotein structure and metabolism. Physiol Rev. 1976 Apr;56(2):259–316. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1976.56.2.259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlin J. B., Juhn D. J., Starr J. I., Scanu A. M., Rubenstein A. H. Measurement of human high density lipoprotein apolipoprotein A-1 in serum by radioimmunoassay. J Lipid Res. 1976 Jan;17(1):30–37. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurell C. B. Electroimmuno assay. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1972;124:21–37. doi: 10.3109/00365517209102748. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahley R. W., Innerarity T. L., Pitas R. E., Weisgraber K. H., Brown J. H., Gross E. Inhibition of lipoprotein binding to cell surface receptors of fibroblasts following selective modification of arginyl residues in arginine-rich and B apoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1977 Oct 25;252(20):7279–7287. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nichols A. V., Gong E. L., Forte T. M., Blanche P. J. Interaction of plasma high density lipoprotein HDL2b (d 1.063-1.100 g/ml) with single-bilayer liposomes of dimyristoylphosphatidylcholine. Lipids. 1978 Dec;13(12):943–950. doi: 10.1007/BF02533854. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborne J. C., Jr, Brewer H. B., Jr The plasma lipoproteins. Adv Protein Chem. 1977;31:253–337. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60220-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen H. E. Cerebrospinal fluid cholesterol. Quantitative analysis of unesterified and esterified cholesterol and normal values in the cerebrospinal fluid. Acta Neurol Scand. 1973;49(5):626–638. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.1973.tb01335.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen H. E. Cerebrospinal fluid phospholipids. Quantitative determination of fractionated phospholipids and normal values in the cerebrospinal fluid. Acta Neurol Scand. 1973;49(5):639–648. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.1973.tb01336.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROHEIM P. S., MILLER L., EDER H. A. THE FORMATION OF PLASMA LIPOPROTEINS FROM APOPROTEIN IN PLASMA. J Biol Chem. 1965 Jul;240:2994–3001. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reichl D., Myant N. B., Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. Biologically active low density lipoprotein in human peripheral lymph. J Clin Invest. 1978 Jan;61(1):64–71. doi: 10.1172/JCI108926. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reichl D., Myant N. B., Pflug J. J. Concentration of lipoproteins containing apolipoprotein B in human peripheral lymph. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Oct 24;489(1):98–105. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(77)90236-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roheim P. S., Edelstein D., Pinter G. G. Apolipoproteins in rat serum and renal lymph. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 May;73(5):1757–1760. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.5.1757. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaefer E. J., Eisenberg S., Levy R. I. Lipoprotein apoprotein metabolism. J Lipid Res. 1978 Aug;19(6):667–687. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shah S. N., Johnson R. C. Cholesterol ester hydrolase activity in human cerebrospinal fluid. Exp Neurol. 1978 Jan 1;58(1):68–73. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(78)90121-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro A. L., Viñuela E., Maizel J. V., Jr Molecular weight estimation of polypeptide chains by electrophoresis in SDS-polyacrylamide gels. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1967 Sep 7;28(5):815–820. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(67)90391-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaitukaitis J., Robbins J. B., Nieschlag E., Ross G. T. A method for producing specific antisera with small doses of immunogen. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1971 Dec;33(6):988–991. doi: 10.1210/jcem-33-6-988. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volpe J. J., Hennessy S. W., Wong T. Regulation of cholesterol ester synthesis in cultured glial and neuronal cells. Relation to control of cholesterol synthesis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Mar 30;528(3):424–435. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(78)90032-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wender M., Filipek-Wender H., Stanislawska J. Cholesteryl esters of the brain in demyelinating diseases. Clin Chim Acta. 1974 Aug 20;54(3):269–275. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(74)90245-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]