Abstract
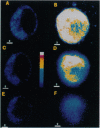
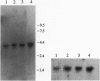
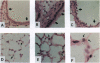
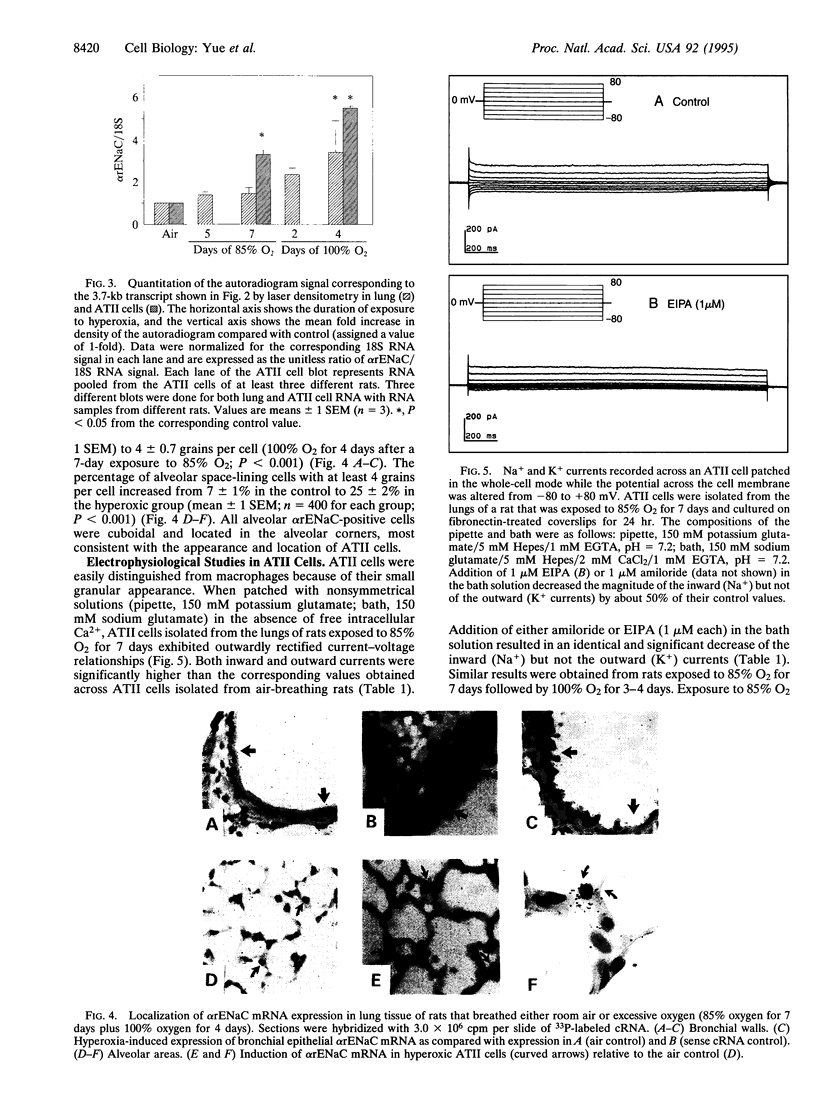
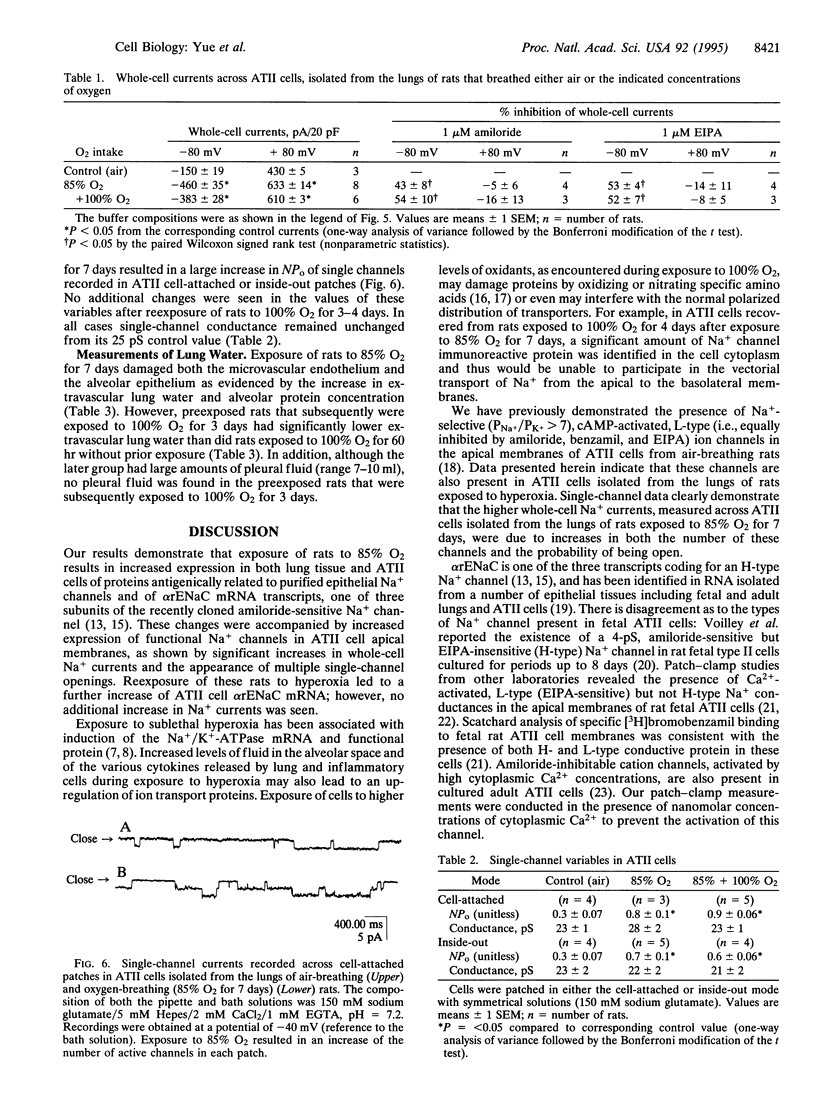
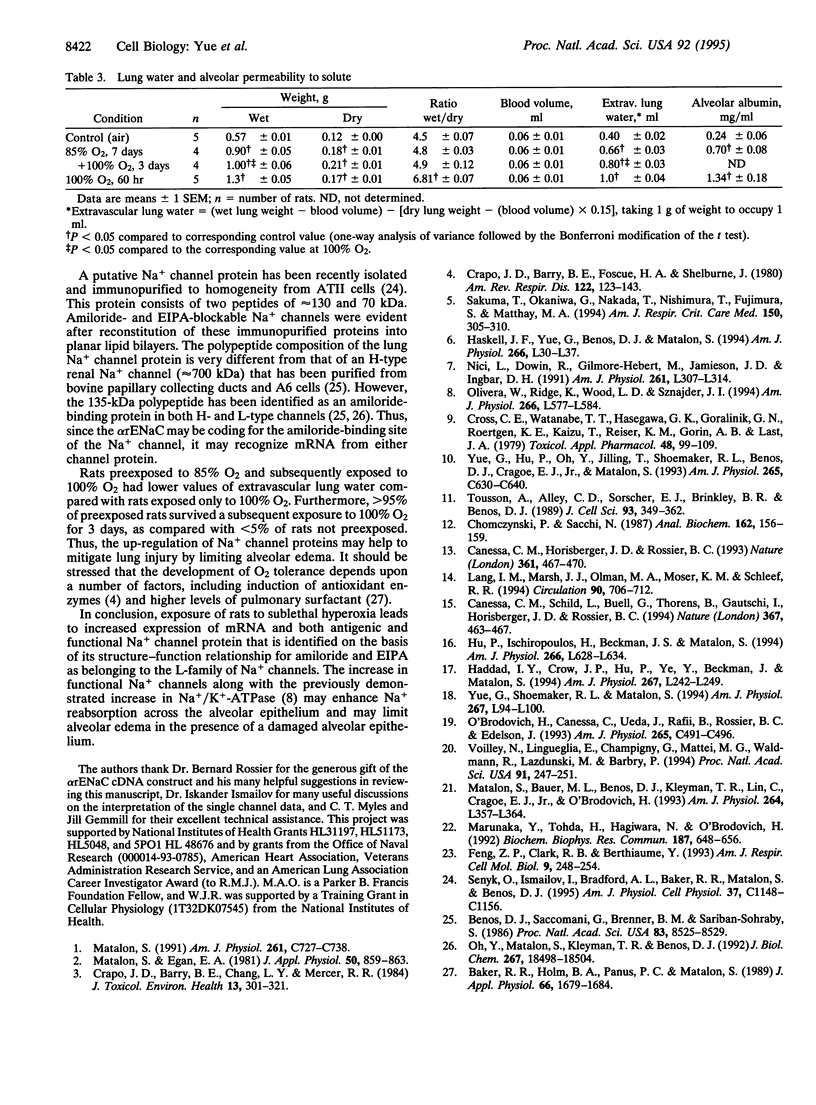
We investigated the cellular and molecular events associated with the increase in sodium transport across the alveolar epithelium of rats exposed to hyperoxia (85% O2 for 7 days followed by 100% O2 for 4 days). Alveolar type II (ATII) cell RNA was isolated and probed with a cDNA for one of the rat colonic epithelial sodium channel subunits (alpha rENaC). The alpha rENaC mRNA (3.7-kb transcript) increased 3-fold in ATII cell RNA isolated from rats exposed to 85% O2 for 7 days and 6-fold after 4 days of subsequent exposure to 100% O2. In situ hybridization revealed increased expression of alpha rENaC mRNA transcripts in both airway and alveolar epithelial cells of hyperoxic rats. When immunostained with a polyclonal antibody to kidney sodium channel protein, ATII cells from hyperoxic rats exhibited a significant increase in the amount of immunogenic protein present in both the plasma membrane and the cytoplasm. When patched in the whole-cell mode, ATII cells from hyperoxic rats exhibited amiloride and 5-(N-ethyl-N-isopropyl)-2',4'-amiloride (EIPA)-sensitive currents that were 100% higher compared with those obtained from air-breathing rats. Single-channel sodium currents (mean conductance of 25 pS) were seen in ATII cells patched in both the inside-out and cell-attached modes. The number and open probability of these channels increased significantly during exposure to hyperoxia. Exposure to sublethal hyperoxia up-regulated both alpha rENaC mRNA and the functional expression of sodium channels in ATII cells.
Full text
PDF
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker R. R., Holm B. A., Panus P. C., Matalon S. Development of O2 tolerance in rabbits with no increase in antioxidant enzymes. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1989 Apr;66(4):1679–1684. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1989.66.4.1679. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benos D. J., Saccomani G., Brenner B. M., Sariban-Sohraby S. Purification and characterization of the amiloride-sensitive sodium channel from A6 cultured cells and bovine renal papilla. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(22):8525–8529. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.22.8525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canessa C. M., Horisberger J. D., Rossier B. C. Epithelial sodium channel related to proteins involved in neurodegeneration. Nature. 1993 Feb 4;361(6411):467–470. doi: 10.1038/361467a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canessa C. M., Schild L., Buell G., Thorens B., Gautschi I., Horisberger J. D., Rossier B. C. Amiloride-sensitive epithelial Na+ channel is made of three homologous subunits. Nature. 1994 Feb 3;367(6462):463–467. doi: 10.1038/367463a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crapo J. D., Barry B. E., Chang L. Y., Mercer R. R. Alterations in lung structure caused by inhalation of oxidants. J Toxicol Environ Health. 1984;13(2-3):301–321. doi: 10.1080/15287398409530500. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crapo J. D., Barry B. E., Foscue H. A., Shelburne J. Structural and biochemical changes in rat lungs occurring during exposures to lethal and adaptive doses of oxygen. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1980 Jul;122(1):123–143. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1980.122.1.123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross C. E., Watanabe T. T., Hasegawa G. K., Goralnik G. N., Roertgen K. E., Kaizu T., Reiser K. M., Gorin A. B., Last J. A. Biochemical assays in lung homogenates: artifacts caused by trapped blood after perfusion. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1979 Mar 30;48(1 Pt 1):99–109. doi: 10.1016/s0041-008x(79)80012-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feng Z. P., Clark R. B., Berthiaume Y. Identification of nonselective cation channels in cultured adult rat alveolar type II cells. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1993 Sep;9(3):248–254. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb/9.3.248. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haddad I. Y., Crow J. P., Hu P., Ye Y., Beckman J., Matalon S. Concurrent generation of nitric oxide and superoxide damages surfactant protein A. Am J Physiol. 1994 Sep;267(3 Pt 1):L242–L249. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.1994.267.3.L242. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haskell J. F., Yue G., Benos D. J., Matalon S. Upregulation of sodium conductive pathways in alveolar type II cells in sublethal hyperoxia. Am J Physiol. 1994 Jan;266(1 Pt 1):L30–L37. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.1994.266.1.L30. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu P., Ischiropoulos H., Beckman J. S., Matalon S. Peroxynitrite inhibition of oxygen consumption and sodium transport in alveolar type II cells. Am J Physiol. 1994 Jun;266(6 Pt 1):L628–L634. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.1994.266.6.L628. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang I. M., Marsh J. J., Olman M. A., Moser K. M., Schleef R. R. Parallel analysis of tissue-type plasminogen activator and type 1 plasminogen activator inhibitor in plasma and endothelial cells derived from patients with chronic pulmonary thromboemboli. Circulation. 1994 Aug;90(2):706–712. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.90.2.706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marunaka Y., Tohda H., Hagiwara N., O'Brodovich H. Cytosolic Ca(2+)-induced modulation of ion selectivity and amiloride sensitivity of a cation channel and beta agonist action in fetal lung epithelium. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Sep 16;187(2):648–656. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)91244-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matalon S., Bauer M. L., Benos D. J., Kleyman T. R., Lin C., Cragoe E. J., Jr, O'Brodovich H. Fetal lung epithelial cells contain two populations of amiloride-sensitive Na+ channels. Am J Physiol. 1993 Apr;264(4 Pt 1):L357–L364. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.1993.264.4.L357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matalon S., Egan E. A. Effects of 100% O2 breathing on permeability of alveolar epithelium to solute. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1981 Apr;50(4):859–863. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1981.50.4.859. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matalon S. Mechanisms and regulation of ion transport in adult mammalian alveolar type II pneumocytes. Am J Physiol. 1991 Nov;261(5 Pt 1):C727–C738. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1991.261.5.C727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nici L., Dowin R., Gilmore-Hebert M., Jamieson J. D., Ingbar D. H. Upregulation of rat lung Na-K-ATPase during hyperoxic injury. Am J Physiol. 1991 Oct;261(4 Pt 1):L307–L314. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.1991.261.4.L307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brodovich H., Canessa C., Ueda J., Rafii B., Rossier B. C., Edelson J. Expression of the epithelial Na+ channel in the developing rat lung. Am J Physiol. 1993 Aug;265(2 Pt 1):C491–C496. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1993.265.2.C491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oh Y., Matalon S., Kleyman T. R., Benos D. J. Biochemical evidence for the presence of an amiloride binding protein in adult alveolar type II pneumocytes. J Biol Chem. 1992 Sep 15;267(26):18498–18504. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olivera W., Ridge K., Wood L. D., Sznajder J. I. Active sodium transport and alveolar epithelial Na-K-ATPase increase during subacute hyperoxia in rats. Am J Physiol. 1994 May;266(5 Pt 1):L577–L584. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.1994.266.5.L577. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakuma T., Okaniwa G., Nakada T., Nishimura T., Fujimura S., Matthay M. A. Alveolar fluid clearance in the resected human lung. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1994 Aug;150(2):305–310. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.150.2.8049807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senyk O., Ismailov I., Bradford A. L., Baker R. R., Matalon S., Benos D. J. Reconstitution of immunopurified alveolar type II cell Na+ channel protein into planar lipid bilayers. Am J Physiol. 1995 May;268(5 Pt 1):C1148–C1156. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1995.268.5.C1148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tousson A., Alley C. D., Sorscher E. J., Brinkley B. R., Benos D. J. Immunochemical localization of amiloride-sensitive sodium channels in sodium-transporting epithelia. J Cell Sci. 1989 Jun;93(Pt 2):349–362. doi: 10.1242/jcs.93.2.349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voilley N., Lingueglia E., Champigny G., Mattéi M. G., Waldmann R., Lazdunski M., Barbry P. The lung amiloride-sensitive Na+ channel: biophysical properties, pharmacology, ontogenesis, and molecular cloning. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jan 4;91(1):247–251. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.1.247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yue G., Hu P., Oh Y., Jilling T., Shoemaker R. L., Benos D. J., Cragoe E. J., Jr, Matalon S. Culture-induced alterations in alveolar type II cell Na+ conductance. Am J Physiol. 1993 Sep;265(3 Pt 1):C630–C640. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1993.265.3.C630. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]