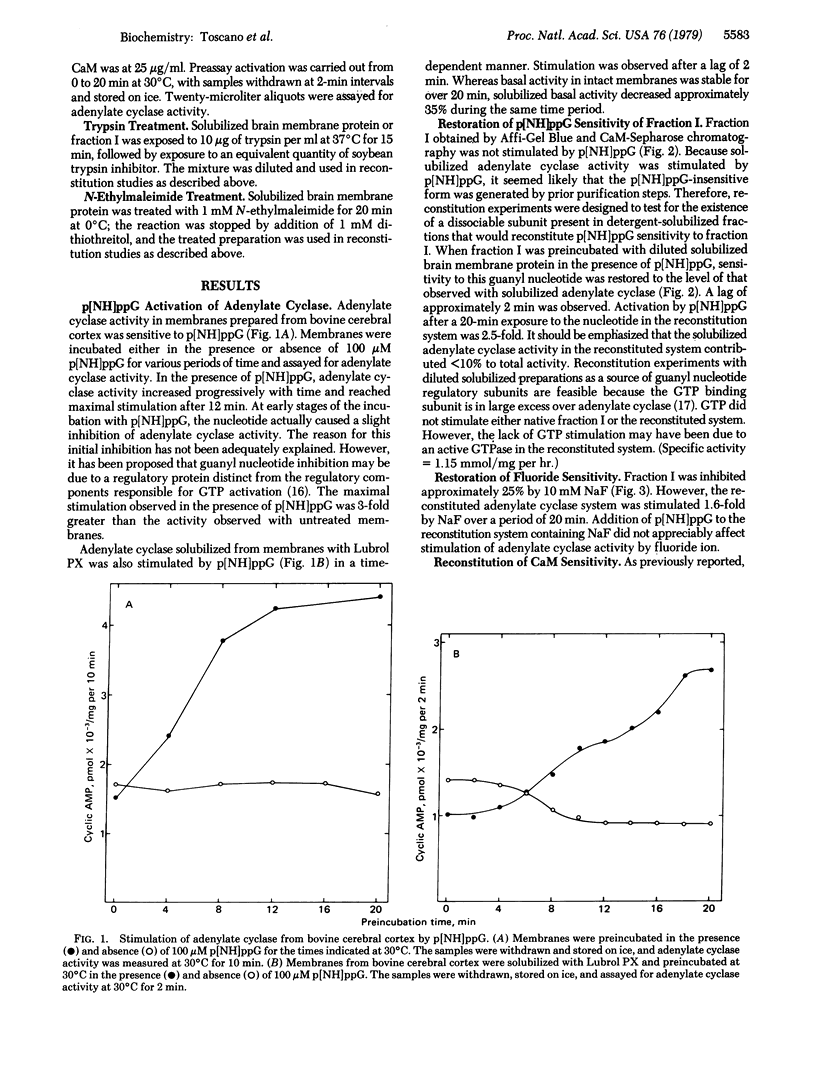
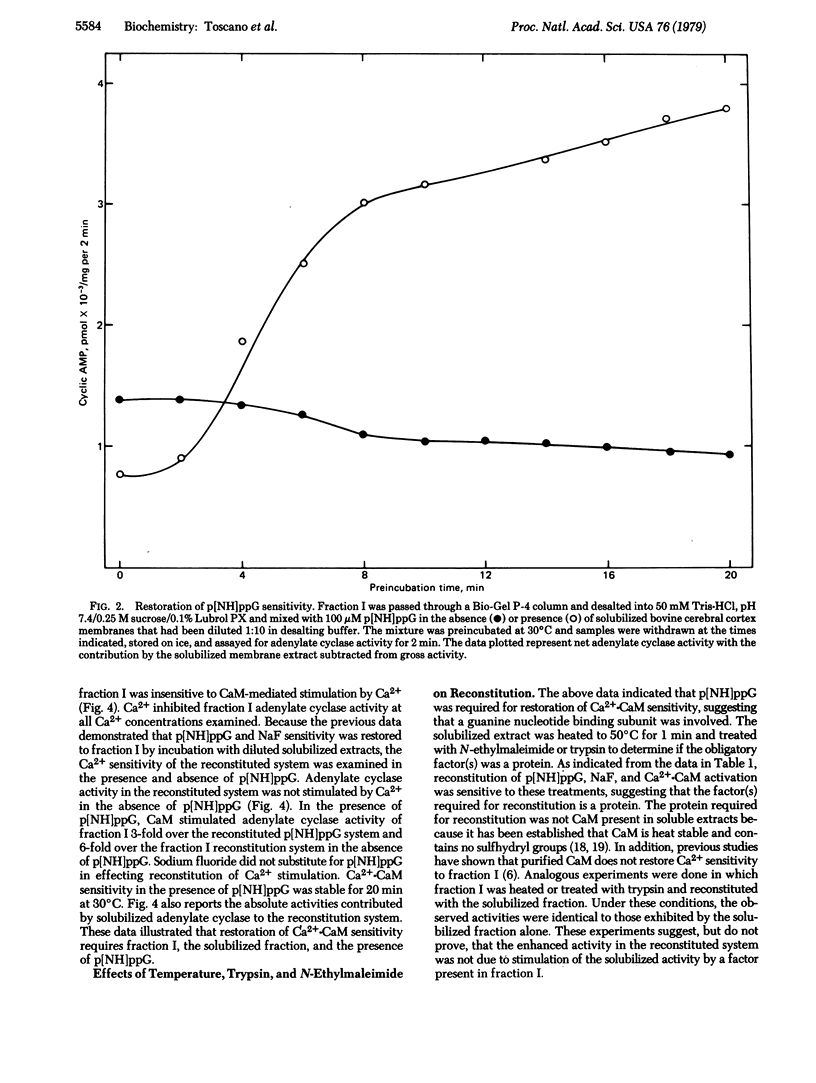
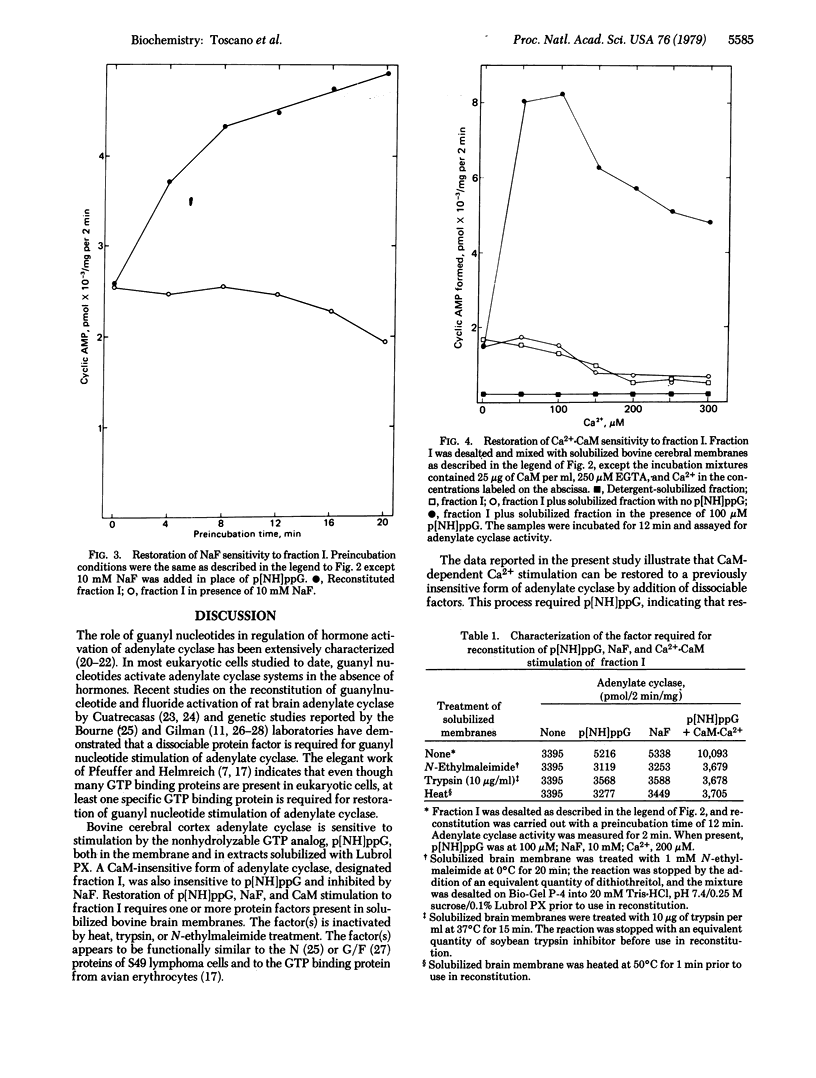
Abstract
An adenylate cyclase [ATP pyrophosphatelyase (cyclizing), EC 4.6.1.1] preparation that is not stimulated by NaF,5'-guanylyl imidodiphosphate, or Ca2+.calmodulin has been isolated from bovine cerebral cortex by Affi-Gel Blue chromatography and calmodulin-Sepharose chromatography. Sensitivity to these effectors was restored by incubation of the adenylate cyclase preparation with detergent-solubilized protein from bovine cerebral cortex. Reconstitution of of Ca2+.calmodulin activation required the presence of 5'-guanylyl imidodiphosphate. The factor required for restoration of Ca2+.calmodulin stimulation was sensitive to heat, trypsin digestion, and N-ethylmaleimide. These observations suggest that this adenylate cyclase activity requires the presence of one or more guanyl nucleotide binding subunits for calmodulin sensitivity.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brostrom C. O., Brostrom M. A., Wolff D. J. Calcium-dependent adenylate cyclase from rat cerebral cortex. Reversible activation by sodium fluoride. J Biol Chem. 1977 Aug 25;252(16):5677–5685. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brostrom C. O., Huang Y. C., Breckenridge B. M., Wolff D. J. Identification of a calcium-binding protein as a calcium-dependent regulator of brain adenylate cyclase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jan;72(1):64–68. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.1.64. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brostrom M. A., Brostrom C. O., Breckenridge B. M., Wolff D. J. Regulation of adenylate cyclase from glial tumor cells by calcium and a calcium-binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1976 Aug 10;251(15):4744–4750. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung W. Y., Bradham L. S., Lynch T. J., Lin Y. M., Tallant E. A. Protein activator of cyclic 3':5'-nucleotide phosphodiesterase of bovine or rat brain also activates its adenylate cyclase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Oct 6;66(3):1055–1062. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90747-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung W. Y. Cyclic 3',5'-nucleotide phosphodiesterase. Evidence for and properties of a protein activator. J Biol Chem. 1971 May 10;246(9):2859–2869. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harwood J. P., Löw H., Rodbell M. Stimulatory and inhibitory effects of guanyl nucleotides on fat cell adenylate cyclase. J Biol Chem. 1973 Sep 10;248(17):6239–6245. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hebdon M., Le Vine H., 3rd, Sahyoun N., Schmitges C. J., Cuatrecasas P. Properties of the interaction of fluoride- and guanylyl-5'-imidodiphosphate-regulatory proteins with adenylate cyclase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Aug;75(8):3693–3697. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.8.3693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howlett A. C., Sternweis P. C., Macik B. A., Van Arsdale P. M., Gilman A. G. Reconstitution of catecholamine-sensitive adenylate cyclase. Association of a regulatory component of the enzyme with membranes containing the catalytic protein and beta-adrenergic receptors. J Biol Chem. 1979 Apr 10;254(7):2287–2295. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson G. L., Kaslow H. R., Bourne H. R. Reconstitution of cholera toxin-activated adenylate cyclase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jul;75(7):3113–3117. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.7.3113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaPorte D. C., Toscano W. A., Jr, Storm D. R. Cross-linking of iodine-125-labeled, calcium-dependent regulatory protein to the Ca2+-sensitive phosphodiesterase purified from bovine heart. Biochemistry. 1979 Jun 26;18(13):2820–2825. doi: 10.1021/bi00580a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitzki A. The role of GTP in the activation of adenylate cyclase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Feb 7;74(3):1154–1159. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)91639-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Limbird L. E., Lefkowitz R. J. Resolution of beta-adrenergic receptor binding and adenylate cyclase activity by gel exclusion chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jan 25;252(2):799–802. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynch T. J., Tallant E. A., Cheung W. Y. Ca++-dependent formation of brain adenylate cyclase-protein activator complex. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Jan 26;68(2):616–625. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)91190-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naya-Vigne J., Johnson G. L., Bourne H. R., Coffino P. Complementation analysis of hormone-sensitive adenylate cyclase. Nature. 1978 Apr 20;272(5655):720–722. doi: 10.1038/272720a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orly J., Schramm M. Coupling of catecholamine receptor from one cell with adenylate cyclase from another cell by cell fusion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Dec;73(12):4410–4414. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.12.4410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson G. L. A simplification of the protein assay method of Lowry et al. which is more generally applicable. Anal Biochem. 1977 Dec;83(2):346–356. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90043-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeuffer T. GTP-binding proteins in membranes and the control of adenylate cyclase activity. J Biol Chem. 1977 Oct 25;252(20):7224–7234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeuffer T., Helmreich E. J. Activation of pigeon erythrocyte membrane adenylate cyclase by guanylnucleotide analogues and separation of a nucleotide binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1975 Feb 10;250(3):867–876. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross E. M., Gilman A. G. Reconstitution of catecholamine-sensitive adenylate cyclase activity: interactions of solubilized components with receptor-replete membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Sep;74(9):3715–3719. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.9.3715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross E. M., Howlett A. C., Ferguson K. M., Gilman A. G. Reconstitution of hormone-sensitive adenylate cyclase activity with resolved components of the enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1978 Sep 25;253(18):6401–6412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sahyoun N., Schmitges C. J., Le Vine H., 3rd, Cuatrecasas P. Molecular resolution and reconstitution of the GPP (NH) P and NAF sensitive adenylate cyclase system. Life Sci. 1977 Dec 15;21(12):1857–1863. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(77)90169-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salomon Y., Londos C., Rodbell M. A highly sensitive adenylate cyclase assay. Anal Biochem. 1974 Apr;58(2):541–548. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90222-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternweis P. C., Gilman A. G. Reconstitution of catecholamine-sensitive adenylate cyclase. Reconstitution of the uncoupled variant of the S40 lymphoma cell. J Biol Chem. 1979 May 10;254(9):3333–3340. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Symons R. H. Preparation of [alpha-32P]nucleoside and deoxynucleoside 5'-triphosphates from 32Pi and protected and unprotected nucleosides. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Oct 22;190(2):548–550. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(69)90105-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watterson D. M., Harrelson W. G., Jr, Keller P. M., Sharief F., Vanaman T. C. Structural similarities between the Ca2+-dependent regulatory proteins of 3':5'-cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase and actomyosin ATPase. J Biol Chem. 1976 Aug 10;251(15):4501–4513. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westcott K. R., La Porte D. C., Storm D. R. Resolution of adenylate cyclase sensitive and insensitive to Ca2+ and calcium-dependent regulatory protein (CDR) by CDR-sepharose affinity chromatography. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):204–208. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamura H., Lad P. M., Rodbell M. GTP stimulates and inhibits adenylate cyclase in fat cell membranes through distinct regulatory processes. J Biol Chem. 1977 Nov 25;252(22):7964–7966. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamura H., Lad P. M., Rodbell M. GTP stimulates and inhibits adenylate cyclase in fat cell membranes through distinct regulatory processes. J Biol Chem. 1977 Nov 25;252(22):7964–7966. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



