Abstract
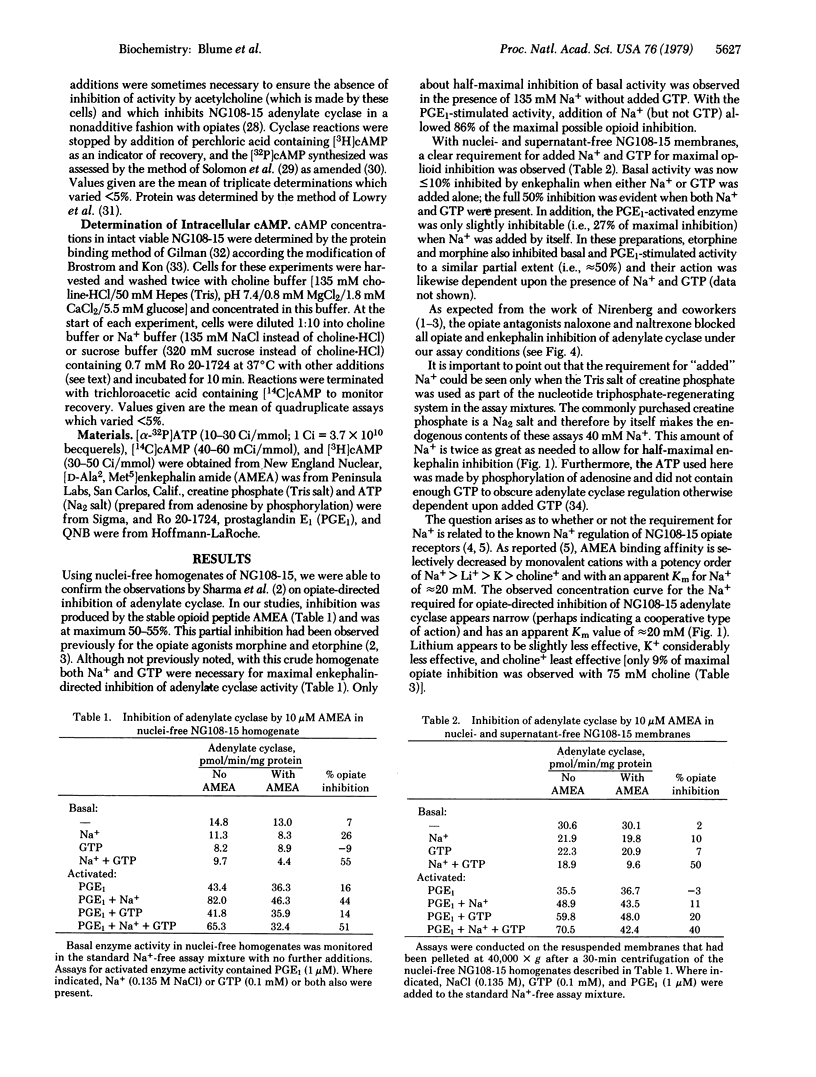
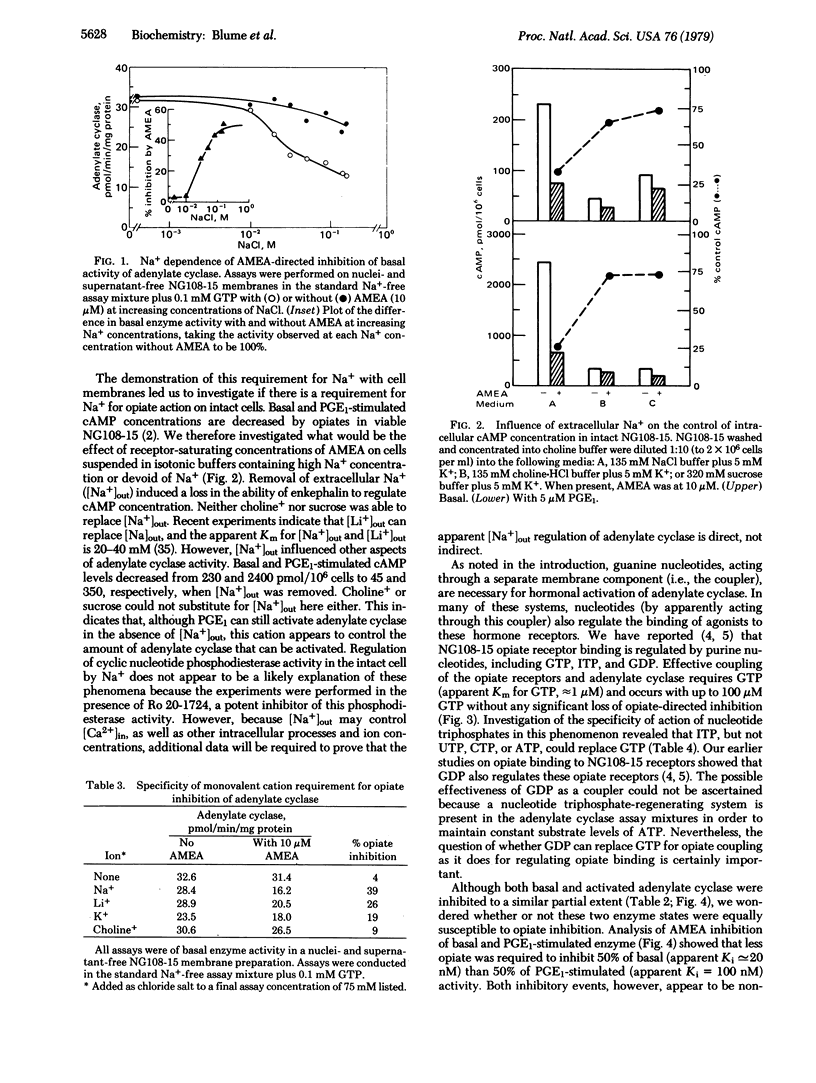
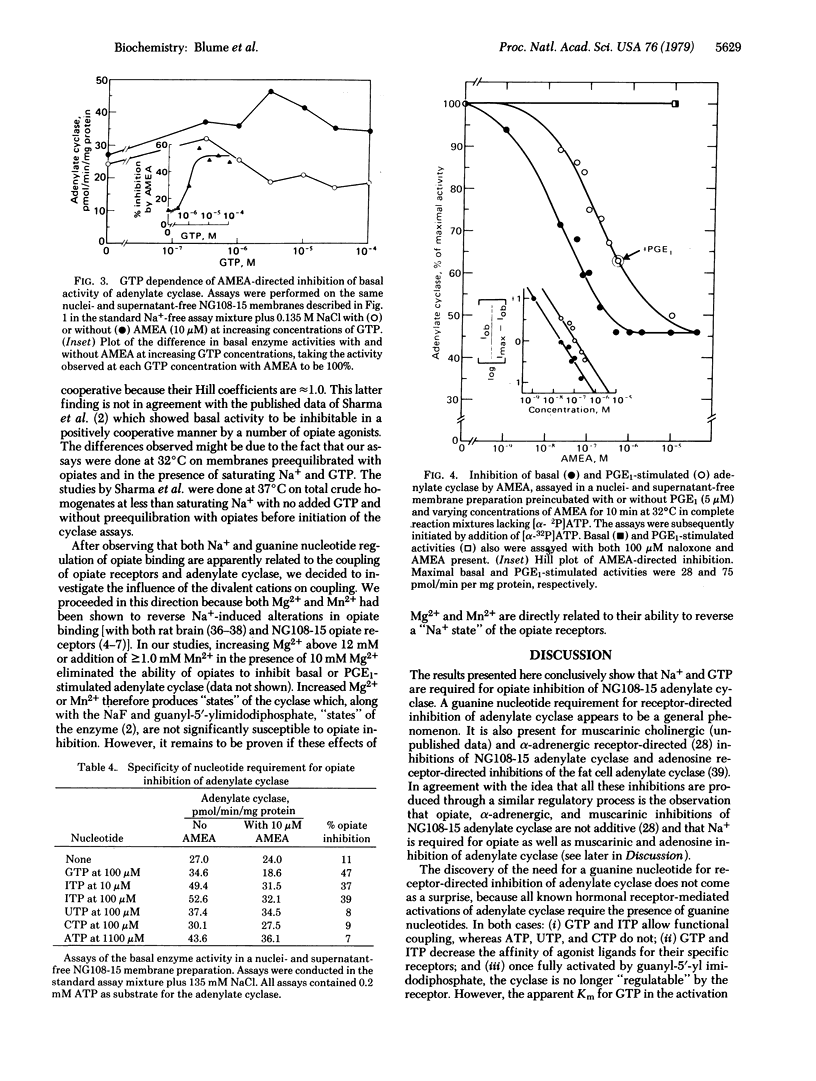
Inhibition of the adenylate cyclase activity in homogenates of mouse neuroblastoma-glioma hybrid cells (NG108-15) by the opioid peptide [D-Ala2,Met5]enkephalin amide (AMEA) requires the presence of Na+ and GTP. In this process, the selectivity for monovalent cations is Na+ greater than or equal Li+ greater than K+ greater than choline+; ITP will replace GTP but ATP, UTP, or CTP will not. The apparent Km for Na+ is 20 mM and for GTP it is 1 microM. Under saturating Na+ and GTP conditions, the apparent Ki for AMEA-directed inhibition is 20 nM for basal and 100 nM for prostaglandin E1-activated adenylate cyclase activity. For both cyclase activities, maximal inhibition is only partial (i.e., approximately 55% of control in each case). In intact viable NG108-15 cells, the decrease in basal and prostaglandin E1-stimulated intracellular cyclic AMP concentrations by AMEA is also dependent upon extracellular Na+. The enkephalin-directed reductions in cyclic AMP concentrations are at least 75%. The specificity of the monovalent cation requirement for enkephalin action on intact cells is the same as for enkephalin regulation of homogenate adenylate cyclase activity. Based on these data, a model is presented in which the transfer of information from opiate receptors to adenylate cyclase requires active separate membrane components, which correspond to the sites of action of Na+ and GTP in this process.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blume A. J. Interaction of ligands with the opiate receptors of brain membranes: regulation by ions and nucleotides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Apr;75(4):1713–1717. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.4.1713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blume A. J. Opiate binding to membrane preparations of neuroblastoma x glioma hybrid cells NG108-15: effects of ions and nucleotides. Life Sci. 1978 May 22;22(20):1843–1852. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(78)90602-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brostrom C. O., Kon C. An improved protein binding assay for cyclic AMP. Anal Biochem. 1974 Apr;58(2):459–468. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90214-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang K. J., Miller R. J., Cuatrecasas P. Interaction of enkephalin with opiate receptors in intact cultured cells. Mol Pharmacol. 1978 Nov;14(6):961–970. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Childers S. R., Snyder S. H. Guanine nucleotides differentiate agonist and antagonist interactions with opiate receptors. Life Sci. 1978 Aug 21;23(7):759–761. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(78)90077-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman A. G. A protein binding assay for adenosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Sep;67(1):305–312. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.1.305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haga T., Ross E. M., Anderson H. J., Gilman A. G. Adenylate cyclase permanently uncoupled from hormone receptors in a novel variant of S49 mouse lymphoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 May;74(5):2016–2020. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.5.2016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Insel P. A., Maguire M. E., Gilman A. G., Bourne H. R., Coffino P., Melmon K. L. Beta adrenergic receptors and adenylate cyclase: products of separate genes? Mol Pharmacol. 1976 Nov;12(6):1062–1069. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura N., Nakane K., Nagata N. Activation by GTP of liver adenylate cyclase in the presence of high concentrations of ATP. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Jun 21;70(4):1250–1256. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)91036-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klee W. A., Nirenberg M. A neuroblastoma times glioma hybrid cell line with morphine receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Sep;71(9):3474–3477. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.9.3474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lad P. M., Welton A. F., Rodbell M. Evidence for distinct guanine nucleotide sites in the regulation of the glucagon receptor and of adenylate cyclase activity. J Biol Chem. 1977 Sep 10;252(17):5942–5946. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lefkowitz R. J., Mullikin D., Wood C. L., Gore T. B., Mukherjee C. Regulation of prostaglandin receptors by prostaglandins and guanine nucleotides in frog erythrocytes. J Biol Chem. 1977 Aug 10;252(15):5295–5303. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levinson S. L., Blume A. J. Altered guanine nucleotide hydrolysis as basis for increased adenylate cyclase activity after cholera toxin treatment. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jun 10;252(11):3766–3774. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichtshtein D., Boone G., Blume A. J. A physiological requirement of Na+ for the regulation of cAMP levels in intact NG108-15 cells. Life Sci. 1979 Sep 11;25(11):985–991. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(79)90504-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Limbird L. E., Lefkowitz R. J. Resolution of beta-adrenergic receptor binding and adenylate cyclase activity by gel exclusion chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jan 25;252(2):799–802. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Londos C., Cooper D. M., Schlegel W., Rodbell M. Adenosine analogs inhibit adipocyte adenylate cyclase by a GTP-dependent process: basis for actions of adenosine and methylxanthines on cyclic AMP production and lipolysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Nov;75(11):5362–5366. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.11.5362. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maguire M. E., Van Arsdale P. M., Gilman A. G. An agonist-specific effect of guanine nucleotides on binding to the beta adrenergic receptor. Mol Pharmacol. 1976 Mar;12(2):335–339. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. J., Chang K. J., Leighton J., Cuatrecasas P. Interaction of iodinated enkephalin analogues with opiate receptors. Life Sci. 1978 Feb;22(5):379–388. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(78)90284-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orly J., Schramm M. Coupling of catecholamine receptor from one cell with adenylate cyclase from another cell by cell fusion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Dec;73(12):4410–4414. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.12.4410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasternak G. W., Snowman A. M., Snyder S. H. Selective enhancement of [3H]opiate agonist binding by divalent cations. Mol Pharmacol. 1975 Nov;11(6):735–744. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pert C. B., Pasternak G., Snyder S. H. Opiate agonists and antagonists discriminated by receptor binding in brain. Science. 1973 Dec 28;182(4119):1359–1361. doi: 10.1126/science.182.4119.1359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pert C. B., Snyder S. H. Properties of opiate-receptor binding in rat brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Aug;70(8):2243–2247. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.8.2243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeuffer T. GTP-binding proteins in membranes and the control of adenylate cyclase activity. J Biol Chem. 1977 Oct 25;252(20):7224–7234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeuffer T., Helmreich E. J. Activation of pigeon erythrocyte membrane adenylate cyclase by guanylnucleotide analogues and separation of a nucleotide binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1975 Feb 10;250(3):867–876. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodbell M., Krans H. M., Pohl S. L., Birnbaumer L. The glucagon-sensitive adenyl cyclase system in plasma membranes of rat liver. IV. Effects of guanylnucleotides on binding of 125I-glucagon. J Biol Chem. 1971 Mar 25;246(6):1872–1876. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodbell M., Lin M. C., Salomon Y., Londos C., Harwood J. P., Martin B. R., Rendell M., Berman M. Role of adenine and guanine nucleotides in the activity and response of adenylate cyclase systems to hormones: evidence for multisite transition states. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1975;5:3–29. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross E. M., Gilman A. G. Reconstitution of catecholamine-sensitive adenylate cyclase activity: interactions of solubilized components with receptor-replete membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Sep;74(9):3715–3719. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.9.3715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross E. M., Gilman A. G. Resolution of some components of adenylate cyclase necessary for catalytic activity. J Biol Chem. 1977 Oct 25;252(20):6966–6969. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross E. M., Howlett A. C., Ferguson K. M., Gilman A. G. Reconstitution of hormone-sensitive adenylate cyclase activity with resolved components of the enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1978 Sep 25;253(18):6401–6412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross E. M., Maguire M. E., Sturgill T. W., Biltonen R. L., Gilman A. G. Relationship between the beta-adrenergic receptor and adenylate cyclase. J Biol Chem. 1977 Aug 25;252(16):5761–5775. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabol S. L., Nirenberg M. Regulation of adenylate cyclase of neuroblastoma x glioma hybrid cells by alpha-adrenergic receptors. I. Inhibition of adenylate cyclase mediated by alpha receptors. J Biol Chem. 1979 Mar 25;254(6):1913–1920. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salomon Y., Londos C., Rodbell M. A highly sensitive adenylate cyclase assay. Anal Biochem. 1974 Apr;58(2):541–548. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90222-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarzmeier J. D., Gilman A. G. Reconstitution of catecholamine-sensitive adenylate cyclase activity: interaction of components following cell-cell and membrane-cell fusion. J Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1977 Aug;3(4):227–238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharma S. K., Klee W. A., Nirenberg M. Opiate-dependent modulation of adenylate cyclase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Aug;74(8):3365–3369. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.8.3365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharma S. K., Nirenberg M., Klee W. A. Morphine receptors as regulators of adenylate cyclase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Feb;72(2):590–594. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.2.590. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simantov R., Snowman A. M., Snyder S. H. Temperature and ionic influences on opiate receptor binding. Mol Pharmacol. 1976 Nov;12(6):977–986. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simantov R., Snyder S. H. Morphine-like peptides, leucine enkephalin and methionine enkephalin: interactions with the opiate receptor. Mol Pharmacol. 1976 Nov;12(6):987–998. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon E. J., Groth J. Kinetics of opiate receptor inactivation by sulfhydryl reagents: evidence for conformational change in presence of sodium ions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jun;72(6):2404–2407. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.6.2404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon E. J., Hiller J. M., Edelman I., Groth J., Stahl K. D. Opiate receptors and their interactions with agnoists and antagonists. Life Sci. 1975 Jun 15;16(12):1795–1800. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(75)90277-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon E. J., Hiller J. M., Edelman I. Stereospecific binding of the potent narcotic analgesic (3H) Etorphine to rat-brain homogenate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jul;70(7):1947–1949. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.7.1947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon E. J., Hiller J. M., Groth J., Edelman I. Further properties of stereospecific opiate binding sites in rat brain: on the nature of the sodium effect. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1975 Mar;192(3):531–537. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



