Abstract
Background
Amnesia is characterized by loss of memory that could result from abnormal neuro-chemical homeostasis, genetic predisposition or drug abuse. We earlier reported that B. monniera attenuates diazepam, scopolamine and L-NNA induced amnesia and wanted to test if SOD levels were affected by its administration.
Purpose
B. monniera is earlier reported to augment the defense system for oxidative stress by increasing the activities of superoxide dismutase, therefore, we investigated its levels after B. monniera administration in combination with different amnesic agents.
Methods
We treated mice with amnesic agents such as scopolamine, diazepam, L-NNA and MK 801 either with or without B. monniera.
Results
Diazepam (1.75 mg/kg ip) significantly reduced SOD activity while it was unaltered when Scopolamine (0.1 mg/kg ip), MK 801 (0.17 mg/kg ip) and L-NNA (30 mg/kg ip) were administered. B. monniera significantly attenuated diazepam induced suppression of SOD activity.
Conclusion
It is suggested that the mechanism of B. monniera’s antiamnesic effect may vary depending on the type of amnesic agent used. However, antioxidant mechanism may be central to evoking the memory enhancing effects of B. monniera against diazepam induced amnesia.
Keywords: Amnesia; Bacopa monniera; Diazepam; L-NNA, MK 801, Scopolamine; Superoxide dismutase
Introduction
Bacopa monniera (Brahmi) is a popular herbal drug used worldwide. Its medicinal efficacy, is reported in Indian traditional literature such as Athar-Ved, Charak Samhita, Susrutu Samhita,1 and is evidenced by various scientific studies in animals1-12 and humans.13-21 The major constituent of Bacopa was found to be bacoside-A and bacoside-B responsible for its cognition-facilitating effect. B. monniera in combination with Ginkgo biloba extract have shown improved anticholinesterase and antidementic activities in scopolamine induced amnestic mice.4 Bacopa monniera and Centella asiatica are major constituents of ‘Medhya rasayana’, a Indian Ayurvedic herbal medicine. Herbex-kid, a polyherbal preparation containing B. monniera possess antiallergic activity by 5-HT antagonism.22 In addition to the antiamnesic effects,6,7-9,12-23,24 it exerts antioxidant,25 antistress,26 anxiolytic,27,28 memory enhancing25 and antiulcerogenic activities.29 Recently it was reported that B. monniera also exerts anti-inflammatory30 and anti-arthritis activity.31 Centella asiatica is another herb reported to improve memory and promote the neuronal dendritic growth in hippocampus.32,33 It also attenuates the spatial memory deficit in rat model of Alzheimer’s disease.34 Hosamani and Muralidhara have reported the neuroprotective efficacy of Bacopa monnieri against rotenone induced oxidative stress and neurotoxicity in Drosophila melanogaster.35 Like animal studies, the clinical studies also provide equally robust evidence of B. monniera’s action on cognitive function. In a clinical study Sharma et al reported B. monniera’s effect on revitalizing the intellectual functions of children.36 Some studies have suggested that the choice of dose and duration of B. monniera’s treatment as being critical for bringing its optimal effects. For example, chronic administration of 300 mg oral B. monniera for about 5-12 weeks substantially improves the higher order of cognitive processes in healthy humans.21 Chronic administration of brahmi (Bacopa) decreases the rate of forgetting of newly acquired information in healthy humans.14
The pharmacological manipulation of LTP (long term potentiation) is useful in investigating the effect of various antiamnesic drugs and their mechanisms. Scopolamine, an acetylcholine receptor antagonist impairs LTP and exerts amnesic effect on spatial learning and memory37,38 when analysed by Morris water maze.39-41 Diazepam, benzodiazepine receptor agonist, causes amnesia42,43 and blocks long-term potentiation (LTP) in slices of hippocampus. When administered at chronic level (20 mg/kg/day, i.p.) for 21 days it induces anxiogenic reaction in mice.44 It is, therefore, also useful in evaluation of anti-amnesic drugs.45,46 MK 801 and L-NNA impair LTP by blocking NMDA receptor and inhibiting nitric oxide synthase enzyme respectively. MK 801 has been used as an amnesic agent for testing antiamnesic effect of cannabidiol-rich extracts,47 SB-399885 (a 5-HT6 receptor blocker),48 and thioperamide (a histamine-H3 receptor antagonist).49 Administration of 7-nitro-imidazole nitric oxide synthase (NOS) inhibitors have been reported to block hippocampal LTP and induce impairment of learning and memory in rats.50-52 Aminoguanidine and L-N-iminoethyl-lysine, inducible NOS inhibitors, are also found to exacerbate the deficit in cognitive performance, as assessed by Morris water maze.51 We earlier reported that B. monniera attenuates diazepam,7 scopolamine53,54 and L-NNA9 induced amnesia. The biochemical analysis of mouse brain revealed the role of calmodulin, protein kinase and pCREB in bringing about the antiamnesic effects of B. monniera. As Superoxide dysmutase (SOD) has earlier been reported to be responsible for detoxification for free radicals we wanted to test if B. monniera was able to augment an anti-oxidative defence system06-25-55-59 by increasing the activity of superoxide dismutase.56-58-61
Methods
Animal
Swiss albino mice (male, age matched, weight 25-35 g) were used in the study and housed four per cage with ad libitum access to food and water under controlled laboratory conditions. Experiments were conducted between 9.00 to 18.00 hrs in a semi-sound proof laboratory. All experiments were performed in accordance with the guidelines of Institute animal ethical committee and European Communities Council Directive (86/609/EEC). Adequate measures were taken to minimize pain or discomfort with animal experimental procedures.
Drugs and Chemicals
Bacopa monniera (brahmi) standardized extract, containing 55.34% of bacosides, was obtained from Lumen marketing company, Chennai. The standardized extract of B. monniera suspended in Tween 80 (5% % v/v in normal saline) and scopolamine, L-NNA and MK801 (Sigma Aldrich, USA) were dissolved in normal saline.
Drug Treatment Schedule
Mice in Group I were administered normal saline (10 ml kg-1) orally for 6 days. Group II mice were injected with 5% Tween 80 (10 ml kg-1) orally and normal saline (10 ml kg-1 ip) with a gap of 30 min. Group III to VI mice were treated with Tween-80 (10 ml kg-1, orally) and test amnesic agent. We used four amnesic agents separately: L-NNA (30 mg kg-1 i.p.), MK 801 (0.17 mg kg-1 i.p.), Scopolamine (0.1 mg kg-1 i.p.) and Diazepam (1.75 mg kg-1 i.p.). Group VII mice were administered standardized extract of B. monniera (80 mg kg-1 oral) and L-NNA (30 mg kg-1 i.p.) at 30 min of time interval. Group VIII-X mice were administered B. monniera (120 mg kg-1 oral) and MK 801 (0.17 mg kg-1 i.p.) / Scopolamine (0.1 mg kg-1 i.p.) / Diazepam (0.1 mg kg-1 i.p.) at similar time interval. We also studied per-se effect of B. monniera (120 mg kg-1).
Table 1: Drug Treatment Schedule.
| No. | Group | Treatment | Dose and Duration |
|---|---|---|---|
| I | Control | Normal Saline | 10 ml kg-1 orally, for 6 days |
| II | T80 | 5% Tween 80 and Normal Saline | T80: 10 ml kg-1 orally NS: 10 ml kg-1 i.p. with a gap of 30 min, for 6 days |
| III | L-NNA | 5% Tween 80 and L-NNA | T80: 10 ml kg-1 orally L-NNA: 30 mg kg-1 i.p. with a gap of 30 min, for 6 days |
| IV | MK | 5% Tween 80 and MK 801 | T80: 10 ml kg-1 orally MK: 0.17 mg kg-1 i.p. with a gap of 30 min, for 6 days |
| V | Sco | 5% Tween 80 and Scopolamine | T80: 10 ml kg-1 orally Sco: 0.1 mg kg-1 i.p. with a gap of 30 min, for 6 days |
| VI | DZ | 5% Tween 80 and Diazepam | T80: 10 ml kg-1 orally DZ: 1.75 mg kg-1 i.p. with a gap of 30 min, for 6 days |
| VII | BM + L-NNA | B. monniera and L-NNA | BM: 80 mg kg-1 orally L-NNA: 30 mg kg-1 i.p. with a gap of 30 min, for 6 days |
| VIII | BM + MK | B. monniera and MK 801 | BM: 120 mg kg-1 orally MK: 0.17 mg kg-1 i.p. with a gap of 30 min, for 6 days |
| IX | BM + Sco | B. monniera and Scopolamine | BM: 120 mg kg-1 orally Sco: 0.1 mg kg-1 i.p. with a gap of 30 min, for 6 days |
| X | BM + DZ | B. monniera and Diazepam | BM: 120 mg kg-1 orally DZ: 0.1 mg kg-1 i.p. with a gap of 30 min, for 6 days |
| XI | BM | B. monniera | 120 mg kg-1 orally, for 6 days |
Superoxide Dismutase
After six days the mice were sacrificed by cervical dislocation. Isolated brain was frozen for biochemical estimation. Brain homogenate and the supernatant were preserved for future analysis. SOD level was measured by superoxide dysmutase estimation kit (Sigma, USA). The standard protocol available with the kit was used for estimating SOD, which was further normalized by total protein. The total protein was estimated by Bradford method.
The biochemical results were analyzed by ANOVA followed by post hoc tests such as least significance difference (LSD). ‘a’ indicates significance at p < 0.05 of treated group versus control group. ‘b’ indicates significance at p < 0.05 of treated group versus amnesic (scopolamine/diazepam/L-NNA/MK 801) group.
Results
B. monniera exerts antioxidative effects by attenuating diazepam induced suppression of superoxide dismutase
SOD activity was reduced with diazepam treatment of mice as compared to control mice. B. monniera alleviated the suppressed SOD activity when B. monniera was administered with diazepam when compared to diazepam treated mice. It suggests that an antioxidant mechanism might play an important role in the reversal of diazepam induced amnesia. Tween 80, used as a vehicle to prepare the suspension of B. monniera did not alter the SOD activity as compared to control mice. Similarly B. monniera alone did not affect the SOD activity as compared to control mice (Fig 1A).
Fig. 1:
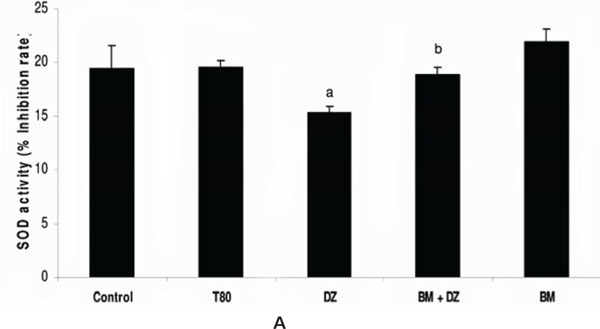
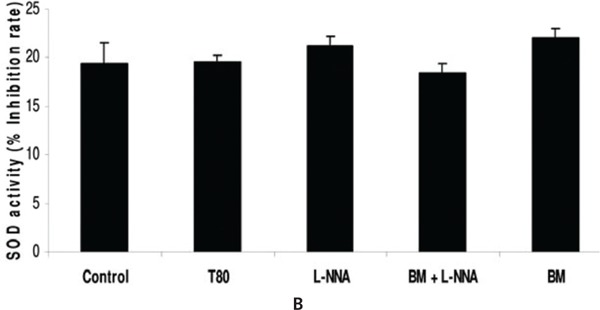
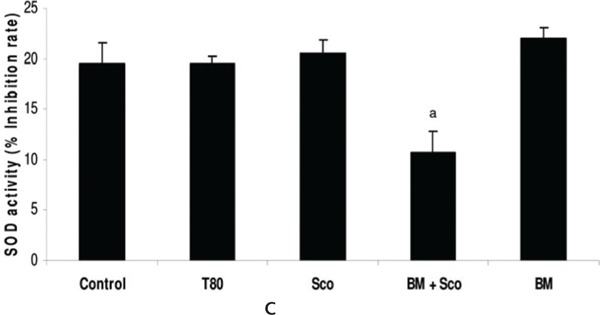
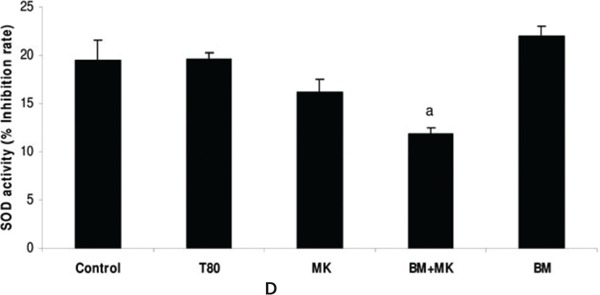
Bacopa monniera selectively attenuates suppression of Superoxide Dismutase activity. 5% Tween 80 and B. monniera (120 mg/kg oral) did not alter SOD activity. Diazepam 1.75 mg/kg ip (fig 1A) and MK 801(0.17 mg/kg ip (fig 1D) significantly reduced SOD activity, while Scopolamine 0.1 mg/kg ip (C) and L-NNA 30 mg/kg ip (fig 1B) could not change it. B. monniera significantly attenuated diazepam induced suppression of SOD activity (fig 1A). On the other hand B. monniera did not produce significant impact of L-NNA (fig 1B) and MK 801 (fig 1D) pretreated mice, while it further suppressed SOD activity in Scopolamine pretreated mice (fig 1C). These values were obtained after normalization with total protein. Data was analyzed by ANOVA followed by LSD test. ‘s ’ indicates significant difference for treated group vs control group at p< 0.05, ‘b ’ indicates significant difference for treated group vs amnesic agent (diazepam/ scopolamine/L-NNA//MK 801) group at p < 0.05.
Endogenous antioxidative defense mechanism is unaltered with B. monniera in L-NNA treated mice
SOD activity was not significantly affected by L-NNA treatment as compared to control mice. Similarly B. monniera did not affect SOD activity in L-NNA pretreated group (Fig 1B).
Scopolamine and MK 801 alone do not, but along with B. monniera reduce antioxidative effect in mice
B. monniera, when administered with scopolamine, partially reduced the SOD activity, but when scopolamine was administered alone, it did not alter the SOD activity significantly as compared to control mice (Fig 1C). Similarly, B. monniera and Tween 80 per se did not affect SOD activity.
SOD activity was not significantly reduced with MK 801 treatment in mice as compared to control mice. It was further suppressed by pre treatment of B. monniera with MK 801 (Fig 1D).
Discussion
This preliminary study demonstrates that B. monniera extract enhances the learning ability of rats.62 B. monniera is known to reduce the level of amyloid especially Abeta 1-40 and 1-42 in doubly transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer’s Disease.63 Subsequent studies have indicated that cognition-facilitating effect of standardized extract of B. monniera has been due to two prominent constituents, bacoside-A64,65 and bacoside-B.65,66 Another active constituent of B. monniera, Betulinic acid, attenuates interleukin-6 production and exerts anti-inflammatory effect.30 B. monniera promotes cell survival in response to oxidative stress by suppressing the formation of reactive oxygen species and any change in the activity of redox regulated proteins, i.e., NF-kappaB, Sirt1, ERK1/2, and p66Shc involved in the pathophysiology of Alzheimer’s Disease.67
When B. monniera was administered as adjunct it was shown to improve the beneficial effect of ginkgo biloba on cognition deficits2 besides reducing the side effects (i.e. cognition deficit) of Phenytoin.24 Combined with these studies, we additionally reported that B. monniera significantly reverses diazepam,7,11 scopolamine23-53 and L-NNA induced amnesia but not MK801 induced amnesia.9 In order to correlate the behavioural results for understanding the intracellular molecular pathway we investigated B. monniera’s effect on various downstream molecules and enzymes in amnesic mice brains. We have shown in our earlier studies that scopolamine downregulates protein kinase C and iNOS but it does not affect cAMP, protein kinase A, calmodulin, MAP kinase, nitrite, CREB and pCREB. B. monniera reverses the scopolamine induced amnesia by significantly improving calmodulin and partially attenuating protein kinase C and pCREB.23 Moreover, we also found that B. monniera increases calmodulin (CaM) and pCREB/CREB levels when L-NNA was used as amnesic agent. We did not find alteration in cAMP, PDE, nitrate, nitrite, iNOS and total CREB levels in L-NNA or MK 801 treated mice (data not shown). Diazepam upregulates MAP kinase, pCREB and iNOS, while it downregulates nitrite, nitrate, total nitrite, CREB expression, phosphodiesterase, cAMP without affecting calmodulin levels. Bacopa monniera also suppressed the diazepam induced upregulation of MAP kinase, pCREB and iNOS and attenuated the downregulation of nitrite. It, however, does not affect the cAMP, PDE, nitrate, total nitrite, total CREB level.12
Since B. monniera has a differential antiamensic effect which can not be explained by a universal pathway, we analysed SOD for antiamnesic effect of B. monniera. We found that the level of SOD was significantly reduced with diazepam and partially reduced with MK 801 treatment, but it was not affected by scopolamine and L-NNA treatment. B. monniera alleviated the SOD activity when B. monniera was administered with diazepam. It suggests that the antioxidant mechanism plays dominant role in reversing diazepam induced amnesia. To support our hypothesis, we report El-Sokkary’s findings that antioxidants like melatonin and vitamin C could restore the levels of superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity and glutathione (GSH) concentration in liver tissues of rats administered with diazepam.68
B. monniera did not attenuate the SOD activity in the L-NNA group. On the other hand B. monniera partially reduced the SOD activity in scopolamine pretreated mice and MK801 pretreated group (Fig 1A-D). We earlier found that total nitrite was not much affected by scopolamine alone while the combination of scopolamine and B. monniera suppresses the total nitrite. We assume that the superoxide dismutase enzyme was consumed for deactivation of the free radicals due to formation of nitric oxide metaboliltes. It suggests that the antioxidant mechanism participates indirectly in association with other mechanism for reversal of scopolamine induced amnesia. Alongwith the evidence from our previous studies11,12-23 we can conclude that the mechanism of B. monniera’s antiamnesic effect is different for diazepam than that for scopolamine. However, antioxidant mechanism may contribute towards antiamnesic effects of B. monniera against diazepam induced amnesia (Fig 2). B. monniera is shown to improve the cognitive deficit possibly by exhibiting free radical scavenging and anti-lipid peroxidative effects58 that protect the brain from oxidative damage, and by augmenting the anti-oxidative defence system of glutathione, vitamin C, vitamin E, and vitamin A alongwith the activities of superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase, glutathione peroxidase (GPX) and glutathione reductase (GR) while maintaining the levels of trace elements such as copper, iron, zinc and selenium.58
Fig. 2:
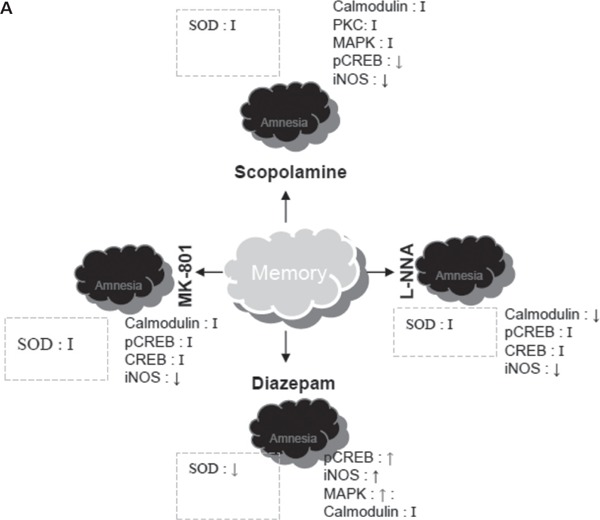
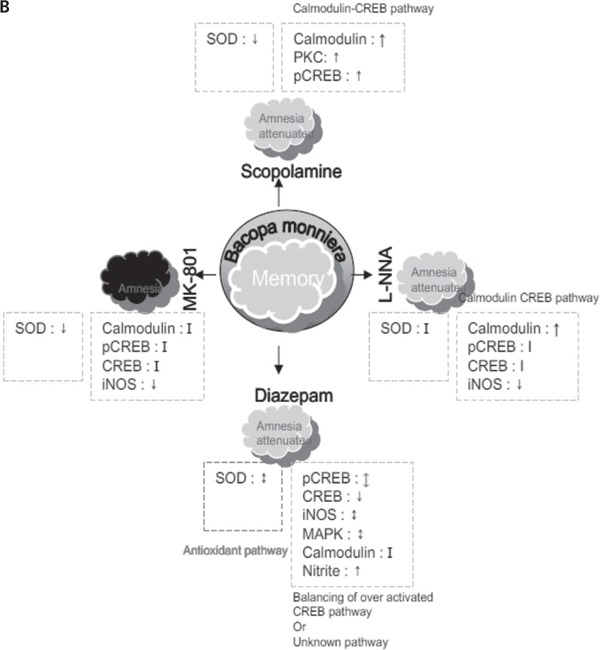
A hypothetical representation of mechanism of Bacopa monniera. (A) Scopolamine, Diazepam, L-NNA and MK 801 impair the memory and produce amnesia. Scopolamine, diazepam and L-NNA downregulate (or do not change) intracellular messenger molecules such as Calmodulin, pCREB, iNOS etc. On the other hand, Diazepam upregulates most of these molecules. (B) Bacopa monniera protects the brain from exposure of these drugs and attenuates the amnesia produced by scopolamine, diazepam and L-NNA. But it does not revert the amnesia induced by MK801. Bacopa monniera attenuates the SOD activity and balances the over activation of CaM - CREB pathway which indicates important role of antioxidant pathway over CaM-CREB pathway. However CaM - CREB pathway plays a substantial role for reversal of scopolamine and L-NNA induced amnesia by Bacopa monniera. MK801 treatment does not affect either Cal-CREB pathway or antioxidant pathway.
B. monniera and Tween 80 per se did not affect SOD activity (Fig 1A-D). In earlier behavioral studies with Morris water maze we were not able to find any significant effect of B. monniera per-se on normal acquisition and retrieval of memory.7-11-23-53
Conclusion
On the basis of our findings we conclude that B. monniera extract possesses antioxidant activities that are possibly mediated by SOD. However, additional studies with the use of antioxidants as controls managing the homeostasis of antioxidant profile in brain tissue can further make such studies more valuable.
Acknowledgement
The work was supported by Department of Biotechnology, New Delhi (India). We thank Mr. Sumit and Mr. Anil for technical and logistical help.
Footnotes
The article complies with International committee of Medical Journal Editor’s uniform requirements for the manuscripts.
Competing interests: None
Source of Funding: Department of Biotechnology, New Delhi (India)
References
- 1.Kishore K, Singh M. Effect of bacosides, alcoholic extract of Bacopa monniera Linn. (brahmi), on experimental amnesia in mice. Indian J Exp Biol. 2005;43:640–645. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Das A, Shanker G, Nath C et al. A comparative study in rodents of standardized extracts of Bacopa monniera and Ginkgo biloba: anticholinesterase and cognitive enhancing activities. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2002;73:893–900. doi: 10.1016/s0091-3057(02)00940-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Channa S, Dar A, Anjum S et al. Anti-inflammatory activity of Bacopa monniera in rodents. J Ethnopharmacol. 2006;104:286–289. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2005.10.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Saraf M. Memory – mechanisms, tools and aids. Annals of Neurosciences. 2009;16(3):119–122. [Google Scholar]
- 5.Sinha J, Raay B, Das N et al. Bacopasaponin C: critical evaluation of anti-leishmanial properties in various delivery modes. Drug Deliv. 2002;9:55–62. doi: 10.1080/107175402753413181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Dhanasekaran M, Tharakan B, Holcomb LA et al. Neuroprotective mechanisms of ayurvedic antidementia botanical Bacopa monniera. Phytother Res. 2007;21:965–969. doi: 10.1002/ptr.2195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Prabhakar S, Saraf MK, Pandhi P et al. Bacopa monniera exerts antiamnesic effect on diazepam-induced anterograde amnesia in mice. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 2008;200:27–37. doi: 10.1007/s00213-007-1049-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Vijayan V, Helen A. Protective activity of Bacopa monniera Linn. on nicotine-induced toxicity in mice. Phytother Res. 2007;21:378–381. doi: 10.1002/ptr.2073. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Saraf MK, Prabhakar S, Anand A. Bacopa monniera alleviates N(omega)-nitro-L-arginine arginine-induced but not MK-801-induced amnesia: a mouse Morris watermaze study. Neuroscience. 2009;160:149–155. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2009.02.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Zhou Y, Peng L, Zhang WD et al. Effect of triterpenoid saponins from Bacopa monniera on scopolamine-induced memory impairment in mice. Planta Med. 2009;75:568–574. doi: 10.1055/s-0029-1185339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Saraf MK, Prabhakar S, Pandhi P et al. Bacopa monniera ameliorates amnesic effects of diazepam qualifying behavioral-molecular partitioning. Neuroscience. 2008;155:476–484. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2008.05.043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Prabhakar S, Saraf MK, Pandhi P et al. Bacopa monniera exerts antiamnesic effect on diazepam-induced anterograde amnesia in mice. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 2008;200:27–37. doi: 10.1007/s00213-007-1049-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Nathan PJ, Clarke J, Lloyd J et al. The acute effects of an extract of Bacopa monniera (Brahmi) on cognitive function in healthy normal subjects. Hum Psychopharmacol. 2001;16:345–351. doi: 10.1002/hup.306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Roodenrys S, Booth D, Bulzomi S et al. Chronic effects of Brahmi (Bacopa monnieri) on human memory. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2002;27:279–281. doi: 10.1016/S0893-133X(01)00419-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Maher BF, Stough C, Shelmerdine A et al. The acute effects of combined administration of Ginkgo biloba and Bacopa monniera on cognitive function in humans. Hum Psychopharmacol. 2002;17:163–164. doi: 10.1002/hup.379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Ernst E. Herbal remedies for anxiety – a systematic review of controlled clinical trials. Phytomedicine. 2006;13:205–208. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2004.11.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Nathan PJ, Tanner S, Lloyd J et al. Effects of a combined extract of Ginkgo biloba and Bacopa monniera on cognitive function in healthy humans. Hum Psychopharmacol. 2004;19:91–96. doi: 10.1002/hup.544. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Kidd PM. A review of nutrients and botanicals in the integrative management of cognitive dysfunction. Altern Med Rev. 1999;4:144–161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Pravina K, Ravindra KR, Goudar KS et al. Safety evaluation of BacoMind in healthy volunteers: a phase I study. Phytomedicine. 2007;14:301–308. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2007.03.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Stough C, Downey LA, Lloyd J et al. Examining the nootropic effects of a special extract of Bacopa monniera on human cognitive functioning: 90 day double-blind placebo-controlled randomized trial. Phytother Res. 2008;22:1629–1634. doi: 10.1002/ptr.2537. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Stough C, Lloyd J, Clarke J et al. The chronic effects of an extract of Bacopa monniera (Brahmi) on cognitive function in healthy human subjects. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 2001;156:481–484. doi: 10.1007/s002130100815. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Kumar A, Prasad R, Jogge NM et al. Herbex-kid inhibits immediate hypersensitivity reactions in mice and rats. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2008;5:289–294. doi: 10.1093/ecam/nem034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Saraf MK, Prabhakar S, Khanduja KL Antiamnesic action of Bacopa monniera is mediated through protein kinase-CREB. pathway in amnesic mice induced by Scopolamine.; In Society for Neuroscience: 2007; San Diego, CA, USA.. 2007. p. 19. [Google Scholar]
- 24.Vohora D, Pal SN, Pillai KK. Protection from phenytoin-induced cognitive deficit by Bacopa monniera, a reputed Indian nootropic plant. J Ethnopharmacol. 2000;71:383–390. doi: 10.1016/s0378-8741(99)00213-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Tripathi YB, Chaurasia S, Tripathi E et al. Bacopa monniera Linn. as an antioxidant: mechanism of action. Indian J Exp Biol. 1996;34:523–526. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Chowdhuri DK, Parmar D, Kakkar P et al. Antistress effects of bacosides of Bacopa monnieri: modulation of Hsp70 expression, superoxide dismutase and cytochrome P450 activity in rat brain. Phytother Res. 2002;16:639–645. doi: 10.1002/ptr.1023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Singh RH, Singh RL. Studies on the antioxidant anxiety effect of the Medhay Rasayan drug Brahmi (Bacopa monniera Linn)- Part II (experimental studies). J Res Ind Med Yoga Homeo. 1980;14:1–6. [Google Scholar]
- 28.Shanker G, Singh HK. Anxiolytic profile of standardized Brahmi extract. Ind J Phamacol. 2000;32:152. [Google Scholar]
- 29.Goel RK, Sairam K, Babu MD et al. In vitro evaluation of Bacopa monniera on anti-Helicobacter pylori activity and accumulation of prostaglandins. Phytomedicine. 2003;10:523–527. doi: 10.1078/094471103322331494. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Viji V, Shobha B, Kavitha SK et al. Betulinic acid isolated from Bacopa monniera (L.) Wettst suppresses lipopolysaccharide stimulated interleukin-6 production through modulation of nuclear factor-kappaB in peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Int Immunopharmacol. 2010;10(8):843–849. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2010.04.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Viji V, Kavitha SK, Helen A. Bacopa monniera (L.) wettst inhibits type II collagen-induced arthritis in rats. Phytother Res. 2010;24(9):1377–1383. doi: 10.1002/ptr.3135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Mohandas Rao KG, Muddanna Rao S, Gurumadhva Rao S. Enhancement of amygdaloid neuronal dendritic arborization by fresh leaf juice of Centella asiatica (Linn) during growth spurt period in rats. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2009;6:203–210. doi: 10.1093/ecam/nem079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Mohandas Rao KG, Muddanna Rao S, Gurumadhva Rao S. Centella asiatica (L.) Leaf extract treatment during the growth spurt period enhances hippocampal CA3 neuronal dendritic arborization in rats. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2006;3:349–357. doi: 10.1093/ecam/nel024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Uabundit N, Wattanathorn J, Mucimapura S et al. Cognitive enhancement and neuroprotective effects of Bacopa monnieri in Alzheimer ’s disease model. J Ethnopharmacol. 2010;127(1):26–31. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2009.09.056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Hosamani R, Muralidhara Neuroprotective efficacy of Bacopa monnieri against rotenone induced oxidative stress and neurotoxicity in Drosophila melanogaster. Neurotoxicology. 2009;30(6):977–985. doi: 10.1016/j.neuro.2009.08.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Sharma R, Chaturvedi C, Tewari PV. Efficacy of Bacopa monniera in revitalizing intellectual functions in children. J Res Edu Ind Med. 1987;23:1–12. [Google Scholar]
- 37.Ennaceur A, Meliani K. Effects of physostigmine and scopolamine on rats ’ performances in object-recognition and radial-maze tests. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 1992;109:321–330. doi: 10.1007/BF02245880. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Rupniak NM, Field MJ, Samson NA et al. Direct comparison of cognitive facilitation by physostigmine and tetrahydroaminoacridine in two primate models. Neurobiol Aging. 1990;11:609–613. doi: 10.1016/0197-4580(90)90025-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Jalkanen AJ, Puttonen KA, Venalainen JI et al. Beneficial effect of prolyl oligopeptidase inhibition on spatial memory in young but not in old scopolamine-treated rats. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2007;100:132–138. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-7843.2006.00021.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Kim DH, Jeon SJ, Son KH et al. The ameliorating effect of oroxylin A on scopolamine-induced memory impairment in mice. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2007;87:536–546. doi: 10.1016/j.nlm.2006.11.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Yen A, Roberson MS, Varvayanis S et al. Retinoic acid induced mitogen-activated protein (MAP)/extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) kinase-dependent MAP kinase activation needed to elicit HL-60 cell differentiation and growth arrest. Cancer Res. 1998;58:3163–3172. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Saraf MK, Kishore K, Thomas KM et al. Role of platelet activating factor in triazolobenzodiazepines-induced retrograde amnesia. Behav Brain Res. 2003;142:31–40. doi: 10.1016/s0166-4328(02)00365-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Tomaz C, Dickinson-Anson H, McGaugh JL. Basolateral amygdala lesions block diazepam-induced anterograde amnesia in an inhibitory avoidance task. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1992;89:3615–3619. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.8.3615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Joshi D, Naidu PS, Kulkarni SK. Reversal of diazepam tolerance and withdrawal-induced hyper locomotor activity and anxiety by melatonin in mice. Annals of Neurosciences. 2006;13(2):31–35. [Google Scholar]
- 45.Parle M, Dhingra D. Ascorbic Acid: a promising memory-enhancer in mice. J Pharmacol Sci. 2003;93:129–135. doi: 10.1254/jphs.93.129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Parle M, Dhingra D, Kulkarni SK. Memory-strengthening activity of Glycyrrhiza glabra in exteroceptive and interoceptive behavioral models. J Med Food. 2004;7:462–466. doi: 10.1089/jmf.2004.7.462. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Fadda P, Robinson L, Fratta W et al. Scopolamine and MK801-induced working memory deficits in rats are not reversed by CBD-rich cannabis extracts. Behav Brain Res. 2006;168:307–311. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2005.11.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Perez-Garcia G, Meneses A. Oral administration of the 5-HT6 receptor antagonists SB-357134 and SB-399885 improves memory formation in an autoshaping learning task. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2005;81:673–782. doi: 10.1016/j.pbb.2005.05.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Bernaerts P, Lamberty Y, Tirelli E. Histamine H3 antagonist thioperamide dose-dependently enhances memory consolidation and reverses amnesia induced by dizocilpine or scopolamine in a one-trial inhibitory avoidance task in mice. Behav Brain Res. 2004;154:211–219. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2004.02.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Holscher C. Inhibitors of metabotropic glutamate receptors produce amnestic effects in chicks. Neuroreport. 1994;5:1037–1040. doi: 10.1097/00001756-199405000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Sinz EH, Kochanek PM, Dixon CE et al. Inducible nitric oxide synthase is an endogenous neuroprotectant after traumatic brain injury in rats and mice. J Clin Invest. 1999;104:647–656. doi: 10.1172/JCI6670. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Tong XK, Hamel E. Regional cholinergic denervation of cortical microvessels and nitric oxide synthase-containing neurons in Alzheimer’s disease. Neuroscience. 1999;92:163–75. doi: 10.1016/s0306-4522(98)00750-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Saraf MK, Prabhakar S, Anand A. A possible link between cholinergic and GABAergic system in induction of amnesia.; In 18th Meetings of the European Neurological Society; Journal of Neurology; Nice, France. Springer. 2008. 2008. [Google Scholar]
- 54.Saraf MK, Prabhakar S, Anand A. Bacopa monniera attenuates Scopolamine induced impairment of spatial memory in mice. doi:10.1093/ecam/neq038. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2011 doi: 10.1093/ecam/neq038. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Anbarasi K, Kathirvel G, Vani G et al. Cigarette smoking induces heat shock protein 70 kDa expression and apoptosis in rat brain: Modulation by bacoside A. Neuroscience. 2006;138:1127–1135. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2005.11.029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Rohini G, Sabitha KE, Devi CS. Bacopa monniera Linn. extract modulates antioxidant and marker enzyme status in fibrosarcoma bearing rats. Indian J Exp Biol. 2004;42:776–780. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Russo A, Izzo AA, Borrelli F et al. Free radical scavenging capacity and protective effect of Bacopa monniera L. on DNA damage. Phytother Res. 2003;17:870–875. doi: 10.1002/ptr.1061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Anbarasi K, Vani G, Balakrishna K et al. Effect of bacoside A on brain antioxidant status in cigarette smoke exposed rats. Life Sci. 2006;78:1378–1384. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2005.07.030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Bhattacharya SK, Bhattacharya A, Kumar A et al. Antioxidant activity of Bacopa monniera in rat frontal cortex, striatum and hippocampus. Phytother Res. 2000;14:174–179. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1099-1573(200005)14:3<174::aid-ptr624>3.0.co;2-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Jyoti A, Sethi P, Sharma D. Bacopa monniera prevents from aluminium neurotoxicity in the cerebral cortex of rat brain. J Ethnopharmacol. 2007;111:56–62. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2006.10.037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Sairam K, Rao CV, Babu MD et al. Prophylactic and curative effects of Bacopa monniera in gastric ulcer models. Phytomedicine. 2001;8:423–430. doi: 10.1078/S0944-7113(04)70060-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Singh HK, Dhawan BN. Effect of Bacopa monniera Linn. (brahmi) extract on avoidance responses in rat. J Ethnopharmacol. 1982;5:205–214. doi: 10.1016/0378-8741(82)90044-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Holcomb LA, Dhanasekaran M, Hitt AR et al. Bacopa monniera extract reduces amyloid levels in PSAPP mice. J Alzheimers Dis. 2006;9:243–251. doi: 10.3233/jad-2006-9303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Chatterji N, Rastogi RP, Dhar ML. Chemical examination of Bacopa monniera Wettst. Part II: The constitution of Bacoside A. Ind J Chem. 1965;3:24–29. [Google Scholar]
- 65.Singh HK, Rastogi RP, Srimal RC et al. Effects of Bacosides A and B on avoidance response in rats Phytotherap Res. 1988;2:70–75. [Google Scholar]
- 66.Basu N, Rastogi RP, Dhar ML. Chemical examination of Bacopa monniera Wettst Part III: The constitution of Bacoside-B. Indian J Chem. 1967;5:84. [Google Scholar]
- 67.Singh M, Murthy V, Ramasamy C. Modulation of hydrogen peroxide and acrolein-induced oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunctions and redox regulated pathways by the Bacopa monniera extract: potential implication in Alzheimer ’s disease. J Alzheimers Dis. 2010;21(1):229–247. doi: 10.3233/JAD-2010-091729. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.El-Sokkary GH. Melatonin and vitamin C administration ameliorate diazepam-induced oxidative stress and cell proliferation in the liver of rats. Cell Prolif. 2008;41(1):168–176. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2184.2007.00503.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


