Abstract
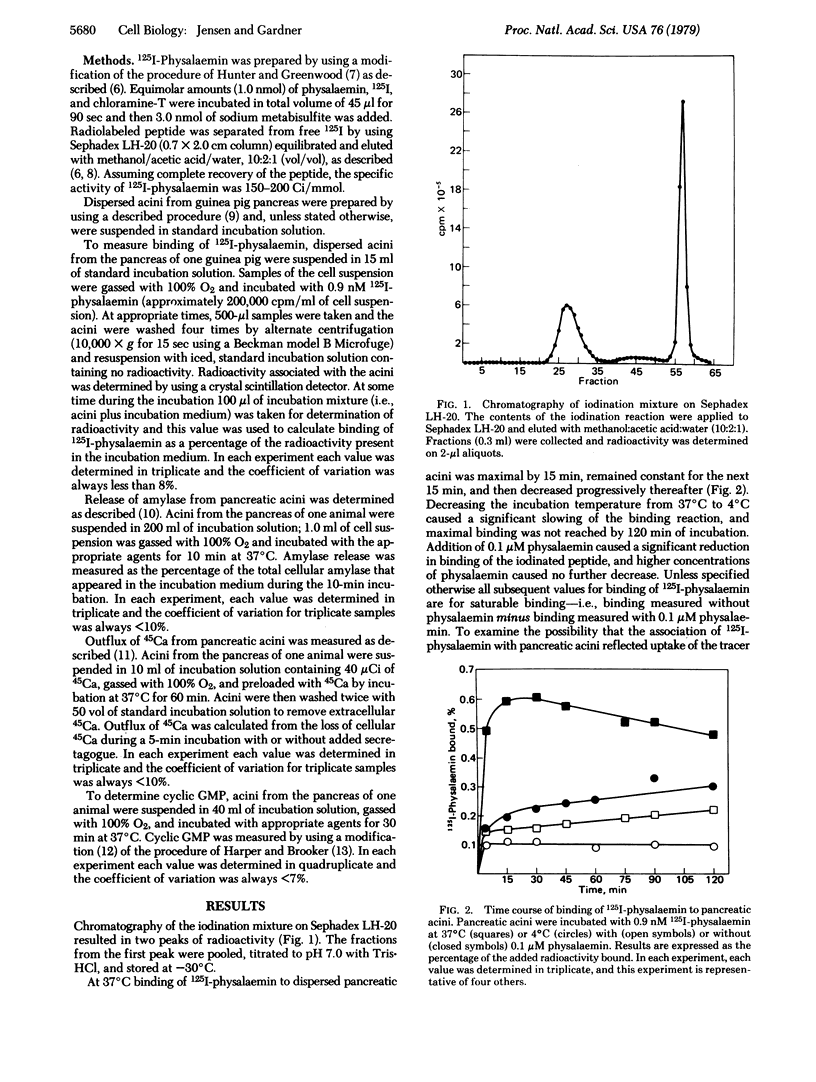
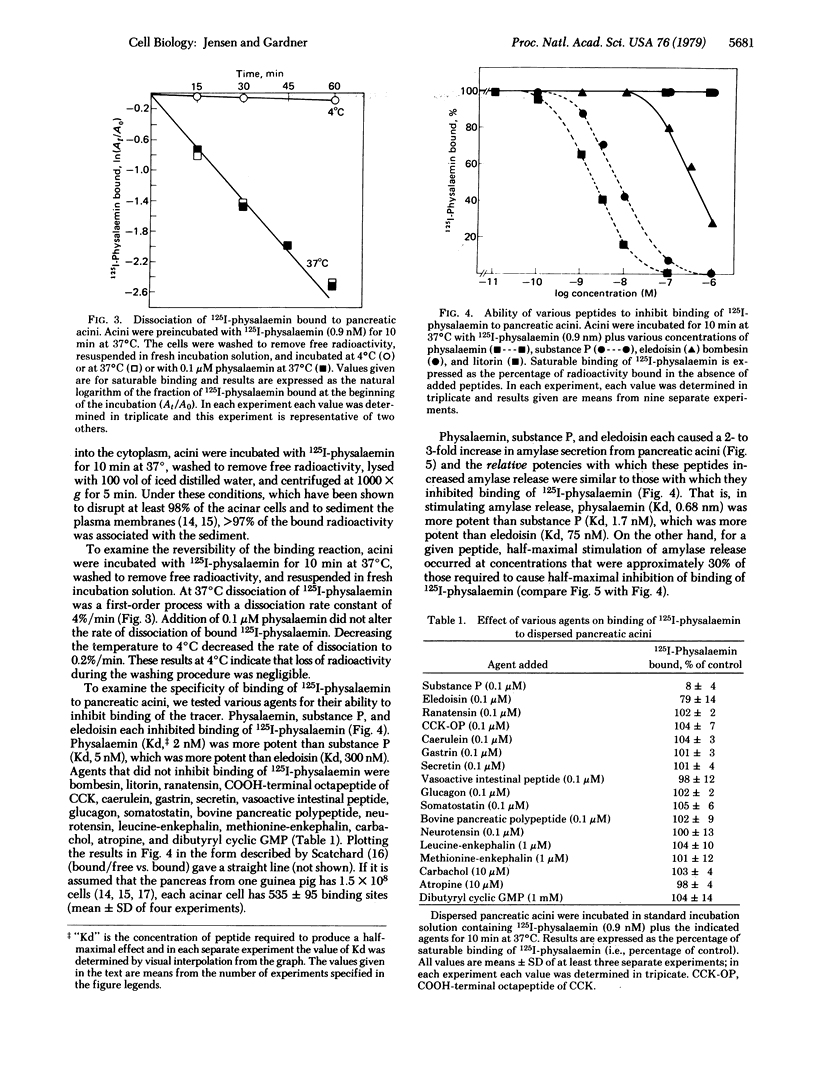
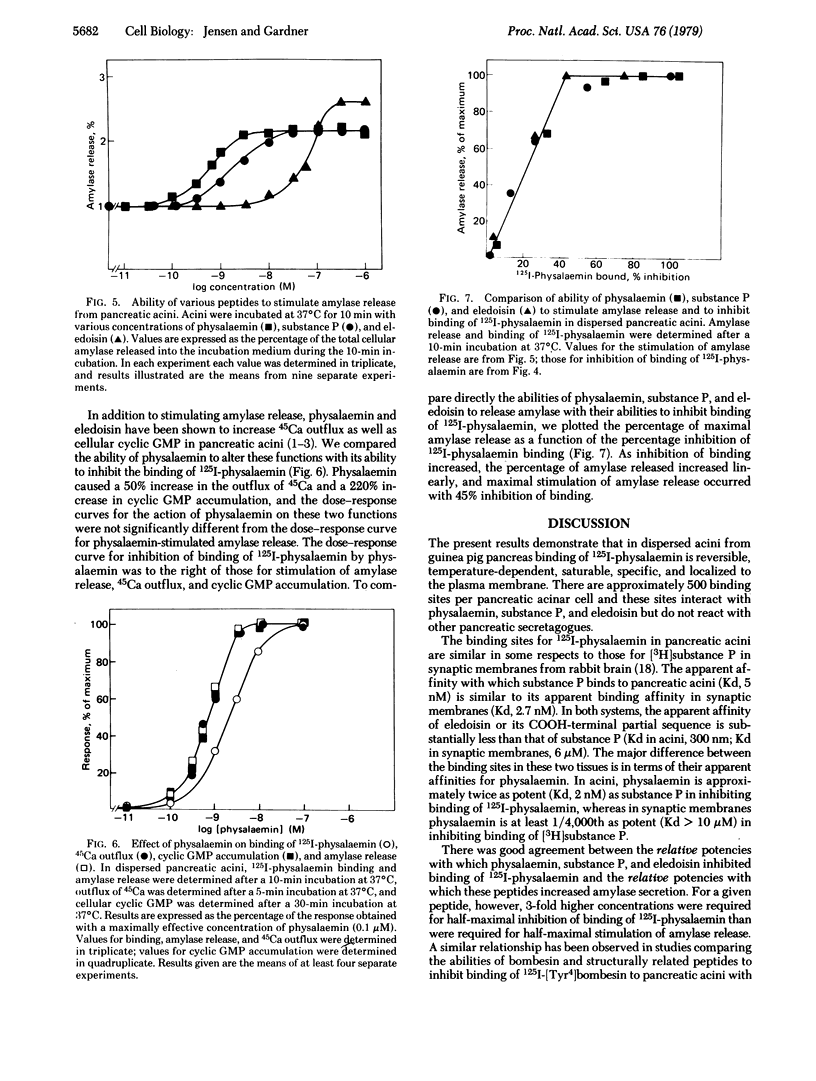
We have prepared 125I-labeled physalaemin and have examined the kinetics, stoichiometry, and chemical specificity with which the labeled peptide binds to dispersed acini from guinea pig pancreas. Binding of 125I-labeled physalaemin was saturable, temperature-dependent, and reversible and reflected interaction of the labeled peptide with a single class of binding sites on the plasma membrane of pancreatic acinar cells. Each acinar cell possessed approximately 500 binding sites, and binding of the tracer to these sites could be inhibited by physalaemin [concentration for half-maximal effect (Kd), 2 nM], substance P (Kd, 5 nM), or eledoisin (Kd, 300 nM) but not by cholecystokinin, caerulein, bombesin, litorin, gastrin, secretin, vasoactive intestinal peptide, glucagon, somatostatin, neurotensin, bovine pancreatic polypeptide, leucine-enkephalin, methionine-enkephalin, atropine, or carbamylcholine. With physalaemin, substance P, and eledoisin, there was a close correlation between the relative potency for inhibition of binding of labeled physalaemin and that for stimulation of amylase secretion. For a given peptide, however, a 3-fold higher concentration was required for half-maximal inhibition of binding than for half-maximal stimulation of amylase secretion, calcium outflux, or cyclic GMP accumulation. These results indicate that dispersed acini from guinea pig pancreas possess a single class of receptors that interact with physalaemin, substance P, and eledoisin and that occupation of 45% of these receptors will cause a maximal biological response.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chan-Palay V., Palay S. L. Immunocytochemical identification of substance P cells and their processes in rat sensory ganglia and their terminals in the spinal cord: light microscopic studies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Aug;74(8):3597–3601. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.8.3597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christophe J. P., Conlon T. P., Gardner J. D. Interaction of porcine vasoactive intestinal peptide with dispersed pancreatic acinar cells from the guinea pig. Binding of radioiodinated peptide. J Biol Chem. 1976 Aug 10;251(15):4629–4634. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deschodt-Lanckman M., Robberecht P., De Neef P., Lammens M., Christophe J. In vitro action of bombesin and bombesin-like peptides on amylase secretion, calcium efflux, and adenylate cyclase activity in the rat pancreas: a comparison with other secretagogues. J Clin Invest. 1976 Oct;58(4):891–898. doi: 10.1172/JCI108542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dufau M. L., Tsuruhara T., Horner K. A., Podesta E., Catt K. J. Intermediate role of adenosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate and protein kinase during gonadotropin-induced steroidogenesis in testicular interstitial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Aug;74(8):3419–3423. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.8.3419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner J. D., Conlon T. P., Kleveman H. L., Adams T. D., Ondetti M. A. Action of cholecystokinin and cholinergic agents on calcium transport in isolated pancreatic acinar cells. J Clin Invest. 1975 Aug;56(2):366–375. doi: 10.1172/JCI108101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner J. D., Hahne W. F. Calcium transport in dispersed acinar cells from rat pancreas. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Dec 15;471(3):466–476. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(77)90050-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner J. D., Jackson M. J. Regulation of amylase release from dispersed pancreatic acinar cells. J Physiol. 1977 Sep;270(2):439–454. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner J. D., Klaeveman H. L., Bilezikian J. P., Aurbach G. D. Effect of beta-adrenergic catecholamines on sodium transport in turkey erythrocytes. J Biol Chem. 1973 Aug 25;248(16):5590–5597. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNTER W. M., GREENWOOD F. C. Preparation of iodine-131 labelled human growth hormone of high specific activity. Nature. 1962 May 5;194:495–496. doi: 10.1038/194495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper J. F., Brooker G. Femtomole sensitive radioimmunoassay for cyclic AMP and cyclic GMP after 2'0 acetylation by acetic anhydride in aqueous solution. J Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1975;1(4):207–218. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heitz P., Polak J. M., Timson D. M., Pearse A. G. Enterochromaffin cells as the endocrine source of gastrointestinal substance P. Histochemistry. 1976 Nov 12;49(4):343–347. doi: 10.1007/BF00496138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwatsuki N., Petersen O. H. In vitro action of bombesin on amylase secretion, membrane potential, and membrane resistance in rat and mouse pancreatic acinar cells. A comparison with other secretagogues. J Clin Invest. 1978 Jan;61(1):41–46. doi: 10.1172/JCI108923. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen R. T., Moody T., Pert C., Rivier J. E., Gardner J. D. Interaction of bombesin and litorin with specific membrane receptors on pancreatic acinar cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Dec;75(12):6139–6143. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.12.6139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazarus L. H., Perrin M. H., Brown M. R. Mast cell binding of neurotensin. I. Iodination of neurotensin and characterization of the interaction of neurotensin with mast cell receptor sites. J Biol Chem. 1977 Oct 25;252(20):7174–7179. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopatin R. N., Gardner J. D. Effects of calcium and chelating agents on the ability of various agonists to increase cyclic GMP in pancreatic acinar cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Nov 1;543(4):465–475. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(78)90301-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- May R. J., Conlon T. P., Erspamer V., Gardner J. D. Actions of peptides isolated from amphibian skin on pancreatic acinar cells. Am J Physiol. 1978 Aug;235(2):E112–E118. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1978.235.2.E112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakata Y., Kusaka Y., Segawa T., Yajima H., Kitagawa K. Substance P: regional distribution and specific binding to synaptic membranes in rabbit central nervous system. Life Sci. 1978 Jan;22(3):259–267. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(78)90527-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson G., Larsson L. I., Håkanson R., Brodin E., Pernow B., Sundler F. Localization of substance P-like immunoreactivity in mouse gut. Histochemistry. 1975;43(1):97–99. doi: 10.1007/BF00490158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson G., Pernow B., Fischer G. H., Folkers K. Presence of substance P-like immunoreactivity in plasma from man and dog. Acta Physiol Scand. 1975 Aug;94(4):542–544. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1975.tb05915.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearse A. G., Polak J. M. Immunocytochemical localization of substance P in mammalian intestine. Histochemistry. 1975;41(4):373–375. doi: 10.1007/BF00490081. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peikin S. R., Costenbader C. L., Gardner J. D. Actions of derivatives of cyclic nucleotides on dispersed acini from guinea pig pancreas. Discovery of a competitive antagonist of the action of cholecystokinin. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jun 25;254(12):5321–5327. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peikin S. R., Rottman A. J., Batzri S., Gardner J. D. Kinetics of amylase release by dispersed acini prepared from guinea pig pancreas. Am J Physiol. 1978 Dec;235(6):E743–E749. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1978.235.6.E743. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shelby H. T., Gross L. P., Lichty P., Gardner J. D. Action of cholecystokinin and cholinergic agents on membrane-bound calcium in dispersed pancreatic acinar cells. J Clin Invest. 1976 Dec;58(6):1482–1493. doi: 10.1172/JCI108605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi T., Konishi S., Powell D., Leeman S. E., Otsuka M. Identification of the motoneuron-depolarizing peptide in bovine dorsal root as hypothalamic substance P. Brain Res. 1974 Jun 14;73(1):59–69. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(74)91007-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhlemann E. R., Rottman A. J., Gardner J. D. Actions of peptides isolated from amphibian skin on amylase release from dispersed pancreatic acini. Am J Physiol. 1979 May;236(5):E571–E576. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1979.236.5.E571. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- V Euler U. S., Gaddum J. H. An unidentified depressor substance in certain tissue extracts. J Physiol. 1931 Jun 6;72(1):74–87. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1931.sp002763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanaihara C., Sato H., Hirohashi M., Sakagami M., Yamamoto K. Substance P radioimmunoassay using Nalpha-tyrosyl-substance P and demonstration of the presence of substance P-like immunoreactivities in human blood and porcine tissue extracts. Endocrinol Jpn. 1976 Dec;23(6):457–463. doi: 10.1507/endocrj1954.23.457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



