Abstract
Cytoplasmic tubulin and the microtubule organizing centers (MTOCs) for the cytoskeletal microtubule system of the flagellate Polytomella have been isolated. The isolated MTOCs serve as sites for the in vitro assembly of the purified tubulin protein. The major proteins (four polypeptides of molecular weights 190,000-210,000) functioning in this assembly have been extracted from the MTOCs and purified. Kinetic studies and experiments with in vivo 35S-labeled MTOC proteins (or 35S-labeled tubulin) demonstrate that these proteins function specifically in microtubule initiation and do not contribute to microtubule elongation. The results indicate that microtubule assembly in vivo is controlled by microtubule initiating proteins associated with the organelles termed MTOCs.
Full text
PDF

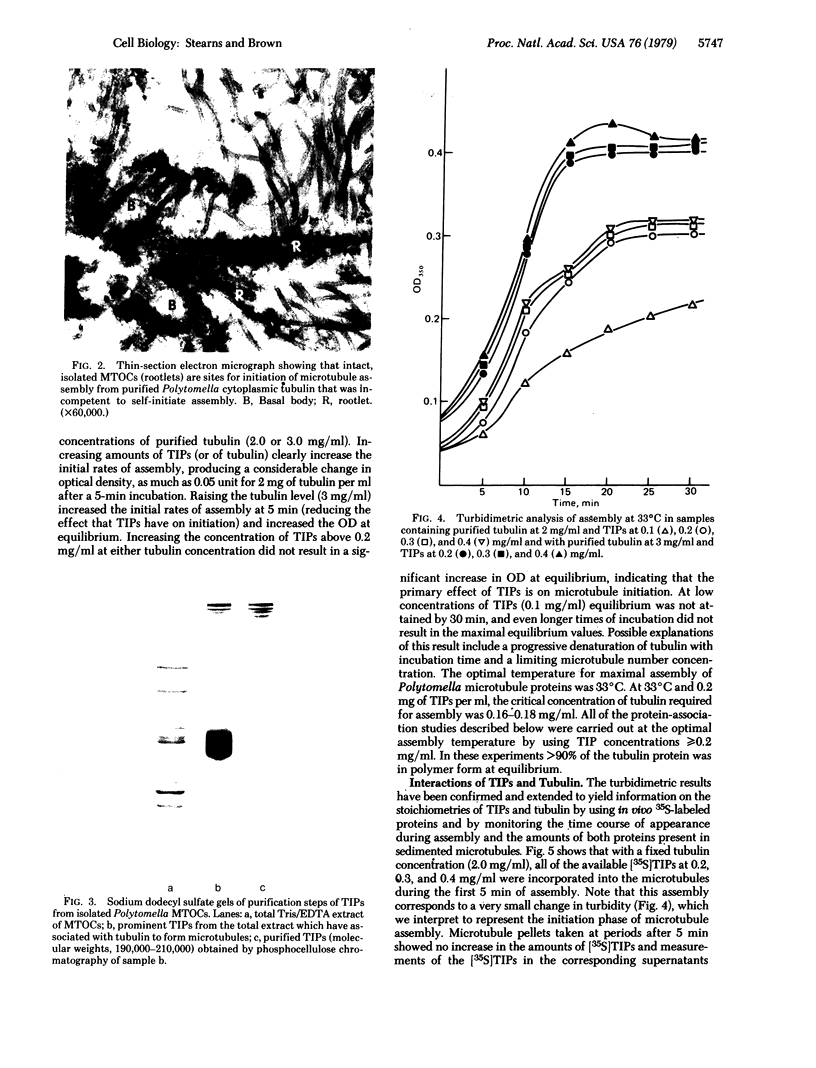
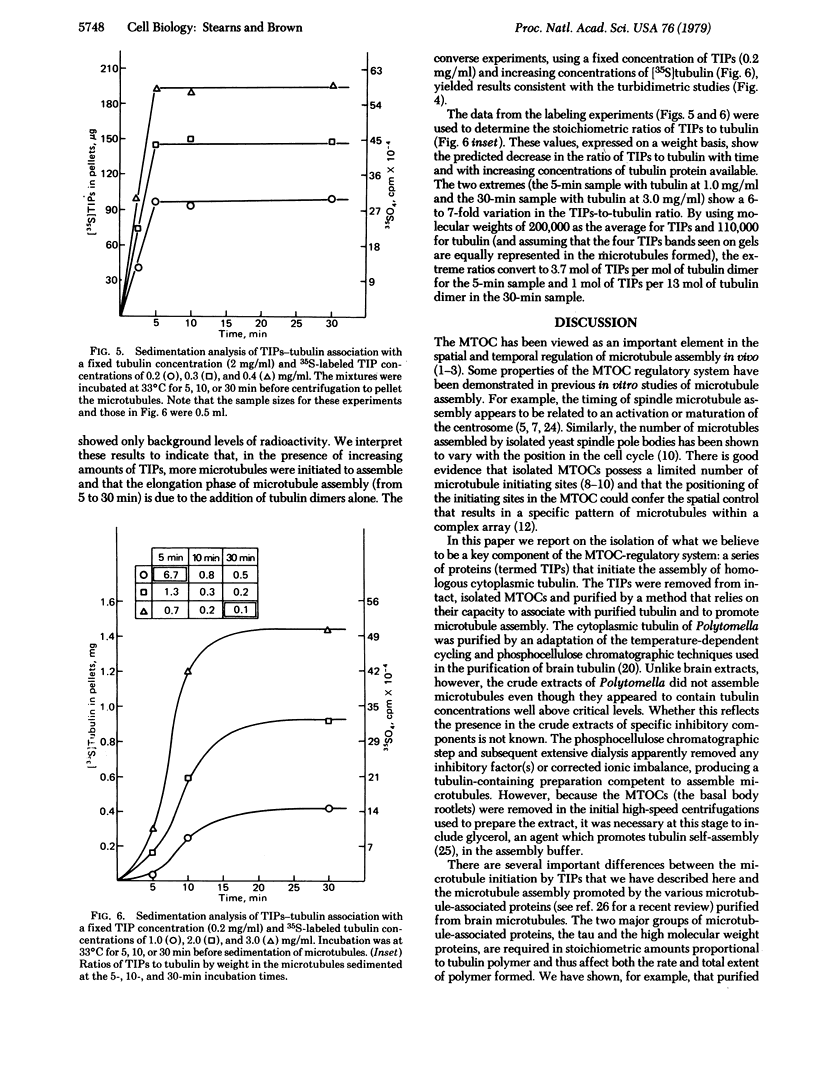

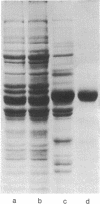
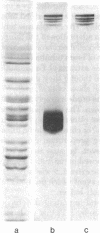
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Behnke O., Forer A. Evidence for four classes of microtubules in individual cells. J Cell Sci. 1967 Jun;2(2):169–192. doi: 10.1242/jcs.2.2.169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. L., Massalski A., Patenaude R. Organization of the flagellar apparatus and associate cytoplasmic microtubules in the quadriflagellate alga Polytomella agilis. J Cell Biol. 1976 Apr;69(1):106–125. doi: 10.1083/jcb.69.1.106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. L., Rogers K. A. Hydrostatic pressure-induced internalization of flagellar axonemes, disassembly, and reutilization during flagellar regeneration in Polytomella. Exp Cell Res. 1978 Dec;117(2):313–324. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(78)90145-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byers B., Shriver K., Goetsch L. The role of spindle pole bodies and modified microtubule ends in the initiation of microtubule assembly in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Cell Sci. 1978 Apr;30:331–352. doi: 10.1242/jcs.30.1.331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould R. R., Borisy G. G. Quantitative initiation of microtubule assembly by chromosomes from Chinese hamster ovary cells. Exp Cell Res. 1978 May;113(2):369–374. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(78)90377-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould R. R., Borisy G. G. The pericentriolar material in Chinese hamster ovary cells nucleates microtubule formation. J Cell Biol. 1977 Jun;73(3):601–615. doi: 10.1083/jcb.73.3.601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartree E. F. Determination of protein: a modification of the Lowry method that gives a linear photometric response. Anal Biochem. 1972 Aug;48(2):422–427. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(72)90094-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyams J. S., Borisy G. G. Nucleation of microtubules in vitro by isolated spindle pole bodies of the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Cell Biol. 1978 Aug;78(2):401–414. doi: 10.1083/jcb.78.2.401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirschner M. W. Microtubule assembly and nucleation. Int Rev Cytol. 1978;54:1–71. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)60164-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langford G. M. In vitro assembly of dogfish brain tubulin and the induction of coiled ribbon polymers by calcium. Exp Cell Res. 1978 Jan;111(1):139–151. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(78)90244-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. C., Timasheff S. N. The reconstitution of microtubules from purified calf brain tubulin. Biochemistry. 1975 Nov 18;14(23):5183–5187. doi: 10.1021/bi00694a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGill M., Brinkley B. R. Human chromosomes and centrioles as nucleating sites for the in vitro assembly of microtubules from bovine brain tubulin. J Cell Biol. 1975 Oct;67(1):189–199. doi: 10.1083/jcb.67.1.189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagle B. W., Doenges K. H., Bryan J. Assembly of tubulin from cultured cells and comparison with the neurotubulin model. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):573–586. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90258-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder J. A., McIntosh J. R. Initiation and growth of microtubules from mitotic centers in lysed mammalian cells. J Cell Biol. 1975 Dec;67(3):744–760. doi: 10.1083/jcb.67.3.744. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stearns M. E., Brown D. L. Purification of a microtubule-associated protein based on its preferential association with tubulin during microtubule initiation. FEBS Lett. 1979 May 1;101(1):15–20. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stearns M. E., Connolly J. A., Brown D. L. Cytoplasmic microtubule organizing centers isolated from Polytomella agilis. Science. 1976 Jan 16;191(4223):188–191. doi: 10.1126/science.1246607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Telzer B. R., Moses M. J., Rosenbaum J. L. Assembly of microtubules onto kinetochores of isolated mitotic chromosomes of HeLa cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Oct;72(10):4023–4027. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.10.4023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilney L. G., Gibbins J. R. Differential effects of antimitotic agents on the stability and behavior of cytoplasmic and ciliary microtubules. Protoplasma. 1968;65(1):167–179. doi: 10.1007/BF01666377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weatherbee J. A., Luftig R. B., Weihing R. R. In vitro polymerization of microtubules from HeLa cells. J Cell Biol. 1978 Jul;78(1):47–57. doi: 10.1083/jcb.78.1.47. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weingarten M. D., Lockwood A. H., Hwo S. Y., Kirschner M. W. A protein factor essential for microtubule assembly. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 May;72(5):1858–1862. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.5.1858. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisenberg R. C., Rosenfeld A. C. In vitro polymerization of microtubules into asters and spindles in homogenates of surf clam eggs. J Cell Biol. 1975 Jan;64(1):146–158. doi: 10.1083/jcb.64.1.146. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]