Abstract
Emerging bacterial resistance to multiple drugs is an increasing problem in burn wound management. New non-pharmacologic interventions are needed for burn wound disinfection. Here we report on a novel physical method for disinfection: antiseptic pulsed electric field (PEF) applied externally to the infected burns. In a mice model, we show that PEF can reduce the load of multidrug resistant Acinetobacter baumannii present in a full thickness burn wound by more than four orders of magnitude, as detected by bioluminescence imaging. Furthermore, using a finite element numerical model, we demonstrate that PEF provides non-thermal, homogeneous, full thickness treatment for the burn wound, thus, overcoming the limitation of treatment depth for many topical antimicrobials. These modeling tools and our in vivo results will be extremely useful for further translation of the PEF technology to the clinical setting, as they provide the essential elements for planning of electrode design and treatment protocol.
INTRODUCTION
The global cost of wound care products is projected to reach US$20.3 billion by 20151. Wound infection management still remains challenging, and choosing an appropriate treatment is a difficult task2. Although more than 6000 types of wound dressings exist3, the problem of wound infections has yet to be solved. In the case of burn wounds, approximately 500,000 people seek medical treatment for every year in the United States; infection remains a major cause of morbidity and mortality in these patients4.
In addition to the extent and nature of the thermal injury affecting the susceptibility to infection, the type and amount of the microbial burden colonizing the wound appear to influence the risk of morbidity and mortality. Pathogens that infect burn wounds are primarily Acinetobacter baumannii, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, Pseudomonas, and Klebsiella5. These pathogens are increasingly resistant to various antimicrobial agents5.
Biofilm formation in the burn wound is problematic as the bacteria are protected by a difficult to dissolve layers of extracellular matrix; early, prophylactic treatment of the burn wound prevents the biofilm formation. Factors that lead to improved clinical outcomes include early surgical debridement and skin grafting, topical and prophylactic antibiotics, as well as other general methods of infection control6. However, current methods for treating burn wound infections are not always effective and sometimes harmful. For instance, a recent 2013 study that reviewed thirty six studies involving 2117 participants concluded that silver sulfadiazine applied directly to the burn actually increased the rates of infection by between 8% and 80%7.
Novel non-pharmacologic means of disinfecting wounds are clearly needed5. Here we report on a novel physical method for disinfection using antimicrobial pulsed electric field (PEF). High voltage, short PEF induce non-thermal permanent damage to cell membranes, presumably by membrane irreversible electroporation8,9. PEF has already been shown to be effective for non-thermal ablation of solid tumors10. Although proposed more than four decades ago for bacterial decontamination in the food industry11, PEF technology has yet to be evaluated for disinfection in medical applications. Previously, we developed procedures for long term control of bacteria in pharmaceuticals and food by applying PEF intermittently12-14. We also studied the impact of surface charge on bacterial resistance to PEF, and developed procedures for rapid PEF parameter optimization15,16. The current work was predicated on the notion that the set of tools previously developed for food and pharmaceutical applications would be ideal for difficult cases of wound management.
In the present report, we demonstrate the effectiveness of PEF in vivo by disinfecting third degree burn wound infections in mice, contaminated with antibiotic resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. A. baumannii is a gram-negative pathogenic bacterium, 1.0–1.5 by 1.5–2.5 micrometer size, which has a remarkable capability for multidrug resistance17,18, and has been reported to have caused intractable infections in traumatic wounds and burns suffered by military personnel injured in the Middle Eastern conflicts19,20. In this study, we demonstrate that direct application of PEF onto the infected burn wound shortly after infection reduces the bacterial load at the treated site by more than 4 orders of magnitude. In addition to in vivo experiments, we also developed a numerical model for antiseptic PEF distribution in burned and infected skin. This model is a key step toward translation of the PEF technology to clinical application, as it provides the essential elements for electrode and treatment protocol planning.
RESULTS
Pulsed electric field delivers homogeneous full thickness treatment
To study the electric field distribution within the infected skin as well as the possible thermal effects of PEF on the wound, we constructed a 2D numerical model using the Finite Element Methods (FEM). We modeled the geometry of burned murine skin located between two plate electrodes — the configuration used in our PEF treatment system. The schematic discription of the model, which includes the skin, composed of various layers, and electrodes, appears in Fig. 1a. The electrical and thermal properties of the skin layers used for modeling appear in Table 121-26. The electrical conductivity of the burned and infected tissue was calculated using Pouillet’s law as follows:
| (1) |
where σ is the electrical conductivity (S m−1), l(m) is the distance between electrodes, I (Amp) is the measured current, V (Volt) is the applied voltage, and A (m2) is the surface area of the electrodes.
Figure 1.
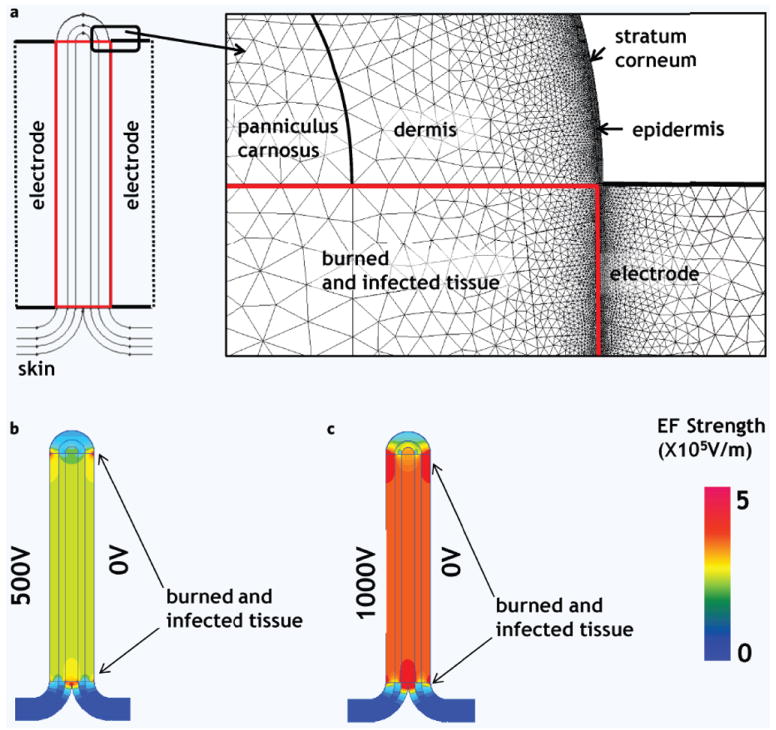
Electric field distribution in the infected burned murine skin and adjusted normal skin, numerical model. (a) Schematic illustration of the PEF treated skin. Skin model is composed of multiple layers with individual electrical properties (Table 1). Insert shows the details of the analyzed geometry and mesh used for FEM solution in QuickField. Burn injury destroys cell membranes; therefore we modeled the burned site as tissue with homogenous electrical properties. (b) Electric field distribution in the treated skin when 1000 Volts were delivered through the left electrode. (c) Electric field distribution in the treated skin when 500 Volts were delivered through the left electrode. The color map on the right bottom shows the strengths of calculated electric fields (EF).
Table 1.
Parameters used for electro-thermal model of pulsed electric field distribution in the burned skin. We used the average conductivity values from the in vivo experiments for the burned skin layers.
| Geometry | Electrical conductivity σ (S m−1) | Thermal conductivity λ (W K−1 m−1) | Heat capacitance cp (J kg−1 K−1) | Density ρ(kg m3) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Normal skin | |||||
| Stratum corneum | Thickness 5 μm | 0.23 | 3300 | 1100 | |
| Epidermis | Thickness 5 μm | 0.2 | 0.23 | 3300 | 1100 |
| Dermis | Thickness 400 μm | 0.2 | 0.45 | 3300 | 1100 |
| Panniculus carnosus | Thickness 300 μm | 0.4 | 0.5 | 3300 | 1100 |
| Subcutaneous tissue | Thickness 300 μm | 0.02 | 0.19 | 3300 | 1100 |
| Burned and infected skin | |||||
| Stratum corneum | Thickness 5 μm | 0.23 | 3300 | 1100 | |
| Epidermis | Thickness 5 μm | 0.13 | 0.23 | 3300 | 1100 |
| Dermis | Thickness 400 μm | 0.13 | 0.45 | 3300 | 1100 |
| Panniculus carnosus | Thickness 300 μm | 0.13 | 0.5 | 3300 | 1100 |
| Subcutaneous tissue | Thickness 300 μm | 0.13 | 0.19 | 3300 | 1100 |
| Electrodes | 1 cm2 surface area, 2 mm apart | 1.45 × 106 | 16 | 466 | 8000 |
The following assumptions are made in our model: (1) healthy skin tissue has both electrical resistance and capacitance properties; the charging time of the capacitor component of the healthy skin is very small in comparison to the pulse length8,27; (2) the skin cell membranes, vasculature and 3D ECM structure are destroyed during the burn; thus, capacitance component in the model is eliminated and the burned area can treated as a block with homogeneous conductivity; (3) the thermal properties of burned tissue are the same as that of normal tissue. Assumptions (1) and (2) allow for the use of DC conductance models to calculate the distribution of the electric fields in the infected tissue. To calculate the electric field distribution, we used the Laplace equation:
| (2) |
With the following boundary conditions on the two electrodes:
| (3) |
where Vl1 is the potential applied on the left electrode in the first treated group of animals, Vl2 is the potential applied on the left electrode in the second treated group of animals, Vr is the grounded right electrode.
FEM allows for the study of the electric field distribution in the complex geometry of objects with different electric properties. Figure 1b,c show the 2D map of the electric field distribution in skin containing a burned/infected area. The maps show the relatively homogeneous distribution of electric fields within the burned areas. Figure 1b describes the spatial distribution of electric fields in the treated area when 500 Volts were applied on the right electrode. The model analysis shows that the field strength was homogeneous in the treated region and was ~247 Vmm−1. Figure 1c describes the spatial distribution of electric fields when 1000 Volts was applied on the left electrode. The model shows that the field strength was homogeneous in the burned area and was ~490 Vmm−1.
The effect of pulsed electric field on bacteria is non-thermal
Using FEM we modeled the time depended temperature distribution in the infected area treated by PEF. To calculate the temperature increase resulting from the PEF application, we solved the transient heat transfer problem using the following equation:
| (4) |
where T is the temperature (K), λ (W K−1 m−1) is the thermal conductivity, cp (J K−1 kg−1) is the specific heat capacitance, t (s) is time, q (W m−3) is the volume power of heat sources. In our problem q is the average volume power supplied to the tissue by pulsed electric field. The following equation described the calculation of power supplied by square pulsed electric field:
| (5) |
where Qavg (W) is the total average power delivered by square pulsed electric field, R (ohm) is the resistance, VRMS is the root mean square voltage, V (Volt) is the applied voltage, tp (s) is the duration of the pulse, and f (Hz) is the frequency of pulse wave. The boundary conditions used to solve Equation (4) are:
| (6) |
where Tin is the initial temperature of the burned treated skin and also a constant temperature of the body. Tair is the constant temperature of the air. We assume that heat is transferred by convection between the surfaces of the body and electrodes, and the air. The also assume that the convection coefficient between skin surface, electrode surface and the air is 5 W K−1 m−2.28
Figure 2a shows the model solution results for 1000 Volts applied at 1 Hz for 80 pulses. The largest heating is observed in the deep layer of the burned and infected dermis and subcutaneous tissue. Figure 2b shows the spatial distribution of the temperature in the treated skin after 80 seconds of continuous application of pulsed electric field. Figure 2c shows the time-dependent temperature change in the center of the tissue (marked as a black dot in Fig. 2a). Remarkably, the temperature increases during first 20 pulses (20 seconds) and then stabilizes at a new steady-state with the surrounding environment. The maximum temperature, which is located in the center of the treated skin, does not increase above 41°C. This temperature increase is insufficient to cause any thermal damage to bacteria. Thermal damage generally requires significantly higher temperatures, of at least 55°C, as well as longer than in our work exposure times, of greater than 15 minutes29. Therefore, our model results suggest that any effect of PEF on bacterial load reduction by non-thermal means.
Figure 2.
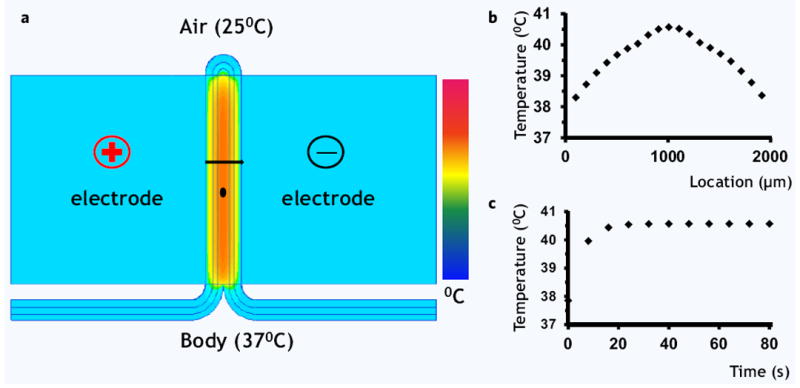
Thermal effects of pulsed electric field on the skin, numerical model. (a) Color map of temperature distribution after 80 seconds of continuous treatment with PEF at 1000 Volts. Most of the temperature increase was observed in the deeper layers of the wound. The black line shows the contour, through which spatial temperature distribution was modeled (b). The black dot shows the location where the time-dependent temperature increase was modeled (b).
Pulsed electric field reduces the Acinetobacter baumannii load in third degree burn wounds by more than 4 orders of magnitude
The experiment is described in Fig. 3. Briefly, animals were subjected to third degree burns at T0, infected with bioluminescent A. baumannii 5 minutes after the burn, and then treated twice with PEF; bioluminescent imaging was used throughout the experiment for infection monitoring (Fig. 3a). The third degree burn created a clear demarcation in the skin (Fig. 3b). A representative bioluminescent signal captured from the A. baumannii infected area is shown in Fig. 3b.
Figure 3.
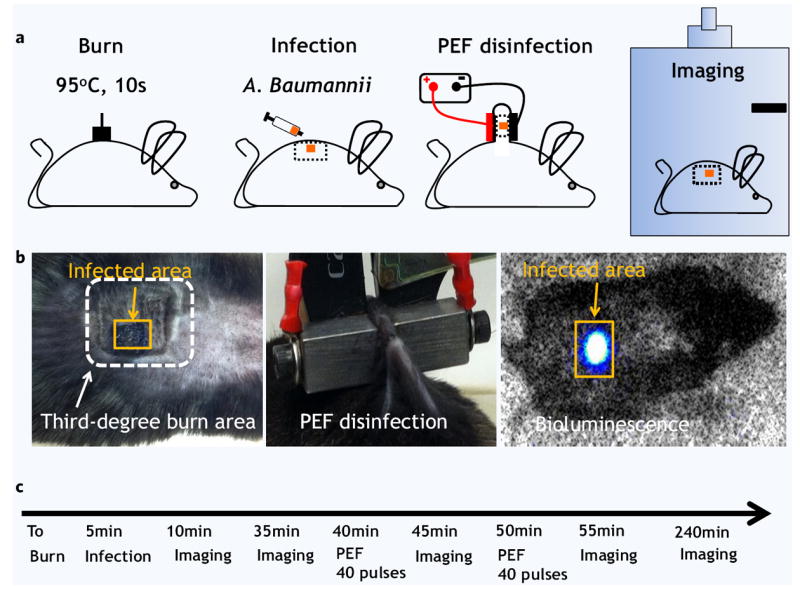
Pulsed electric field disinfection in vivo: C57BL/6 black mice model. (a) Schematic illustration for procedures we used in this study. The 1 cm2 burn injury was followed by dispersion of A. baumannii on part of the wound. Next, pulsed electric field was applied using two plate electrodes. A. baumannii infection load was quantified using bioluminescent imaging. (b) Left panel shows digital photography of the burned (white frame) and infected (orange frame) areas of the skin. Central panel shows digital photography of the applied electrodes. Right panel shows the images of the mice as observed inside the dark imaging box. Orange frame shows the infected area as detected by a strong bioluminescent signal emitted from bacteria. (c) The experiment timeline.
The electrode positioning for PEF delivery is shown in Fig. 3b. Two plate electrodes were positioned on either side of the infected area for pulse delivery. The maximum current delivered with 1000 Volts was 6.4 ± 0.7 Amp, and the maximum current delivered with 500 Volts was 3.1 ± 0.4 Amp. The measured values were used for the modeling of thermal effects of PEF as described in the previous sections. The in vivo experimental design sequence appears in Fig. 3c.
Figure 4 describes the effect of electric field strength and number of pulses on bacteria survival immediately after treatment. The bacterial load reduction, R, was calculated using the following equation:
| (7) |
where R is the log 10 reduction of bacterial load, SF is the survival fraction of bacteria calculated as
| (8) |
where RLUbt is the RLU (for RLU definition see Materials and Methods section, Bioluminescent Imaging of Bacterial Load), measurement of the infected skin before treatment with PEF, and RLUat is the RLU measurement of the infected skin at various time points after PEF treatments.
Figure 4.
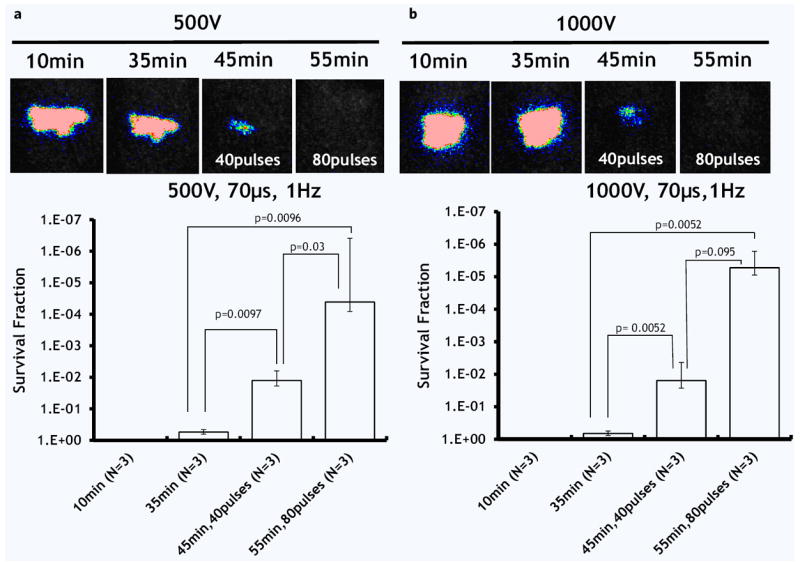
The effect of pulse number and electric field strength on A. baumannii infection load reduction. (a) Applied voltage 500 V. (b) Applied voltage 1000 V. Top panel shows the post-burn time when the images were taken. The bottom panel shows the survival fraction of microorganisms as detected by the top panel images (logarithmic, inversed scale). N shows the number of animals per group. Error bar ± standard deviation of the mean.
First two panels on the left in Fig. 4a,b show that the population of bacteria on the skin surface during the first 35 minutes after the burn did not change; therefore, the infection model was stable. In the first experimental group (Fig. 4a), the application of 40 pulses at 500 Volts reduced the bioluminescent signal, which represents a reduction in the bacterial load, by 1.49 ± 0.07 log 10. The application of 80 pulses at 500 Volts reduced the bioluminescent signal by 5.30 ± 0.85 log 10. In the second experimental group (Fig. 4b), we increased the applied voltage from 500 to 1000 Volts. The application of 40 pulses at 1000 Volts reduced the bioluminescent signal by 2.04 ± 0.29 log 10. The application of 80 pulses at 1000 Volts reduced the bioluminescent signal by 5.53 ± 0.30 log 10 immediately after treatment.
Figure 5 describes the effect of electric field strength on bacteria survival 3 hours after the PEF treatment. In the control (Fig. 4a), PEF untreated, burned and infected skin, the 1 log 10 reduction is most likely due to the penetration of bacteria into the deep tissue and natural death of a portion of the bacterial population. In the first experimental group (Fig. 5b), the application of 80 pulses at 500 Volts led to 5.30 ± 0.85 log 10 immediately after PEF treatment; however, 3 hours after this treatment, the total reduction was only 2.66 ± 0.30 log 10, because of regrowth of the bacteria in the tissue. In the second experimental group (Fig. 5c), the application of 80 pulses at 1000 Volts led to 5.53 ± 0.30 log 10 immediately after PEF treatment; 3 hours after this treatment, the total reduction was still 4.91 ± 0.71 log 10 in comparison with initial bacterial load. Figure 6 summarizes the log reduction rates observed 3 hours after PEF treatment for both experimental groups.
Figure 5.
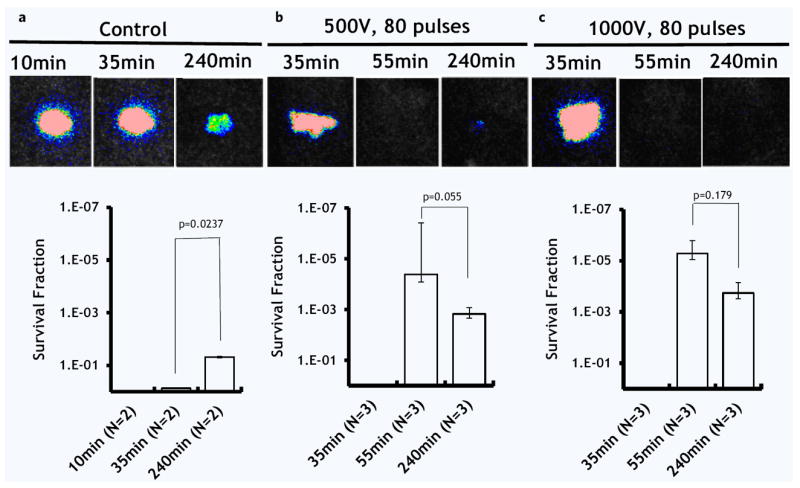
The effect of pulse electric field strength on the recovery of A. baumannii 3 hours after treatment. (a) Control: Not treated, burned and infected skin. (b) Applied voltage 500 V. (c) Applied voltage 1000 V. Top panel shows the post-burn time when the images were taken. The bottom panel shows the survival fraction of microorganisms as detected by the top panel images (logarithmic, inversed scale). N shows the number of animals per group. Error bar ± standard deviation of the mean.
Figure 6.
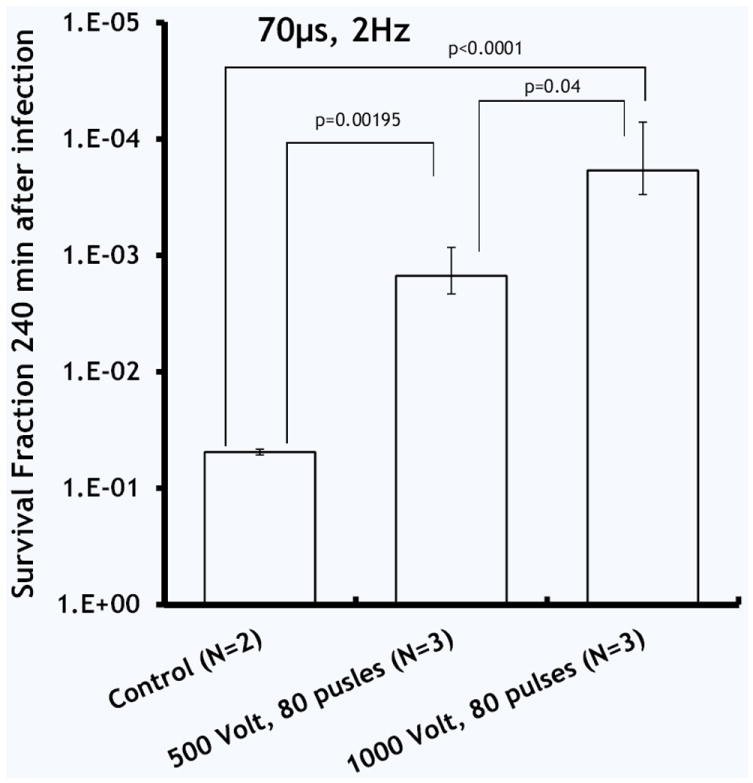
Summary of A. baumannii survival 3 hours after PEF, the effect of electric field intensity. N shows the number of animals per group. Error bar ± standard deviation of the mean.
DISCUSSION
PEF to inactivate bacteria has been under scrutiny for the last 50 years. During this time multiple PEF parameters were reported for a wide range of bacteria11. Most of the reports, however, focused on the bacteria which are common food pathogens; parameters of PEF were optimized for large scale food processing facilities11. According to the FDA the typical electric field used for food disinfection applications is 200–800 Vmm−1 with pulse duration of several microseconds and pulse number of up to 3030. Here we report on the treatment of bacterial wound infections with non-thermal PEF. PEF efficiently disinfected contaminated burned murine skin. Using 80 pulses of 500 Vmm−1, we achieved stable disinfection with 4.91 ± 0.71 log 10 reduction of Acinetobacter baumannii, 3 hours after treatment (Figs. 5c, 6). Numerical modeling suggested that PEF penetrated homogeneously throughout the entire segment of infected tissue (Fig. 1). Our modeling also suggested that the effects of PEF on bacterial load reduction are non-thermal (Fig. 2).
Bacterial re-growth due to recontamination or incomplete disinfection is commonly observed after all types of disinfection technologies. It was shown in multiple previous studies that bacterial disinfection by PEF follows Weibull or Fermi distributions as a function of electric field strength and pulse number11. Therefore, complete 100% disinfection using electric fields alone is hardly possible. In this work, we observed bacterial regrowth when using low doses of PEF (Fig. 5). To address the regrowth problem, we have previously introduced the Intermittently Delivered Pulsed Electric Field Process (IDPEF)12,13. In IDPEF, electric fields are applied intermittently on the targeted area for an indefinite period of time to prevent recontamination. The application frequency is defined by the bacterial regrowth rate. Future translation of antimicrobial PEF technology will require the adaptation of IDPEF methodology and devices for the clinical setting.
Cells with a large diameter are usually more vulnerable to PEF compared to smaller cells. Therefore, PEF which destroys bacteria most likely will affect the host cells which survived the burn injury. This non-selectivity of the PEF method may be a concern when treating infection in healthy uninjured tissue. To address the effects of PEF on the non-target tissue, we have previously investigated the healing process of normal healthy skin ablated by PEF31. Our results show that PEF is selective to the cell membrane; however, it preserved the extracellular matrix (ECM) and the vasculature of the treated area31. More importantly, we showed that PEF-ablated skin regenerated rapidly without scars31.
The magnitude of disinfection was correlated with both the electric field strength and the number of delivered pulses. Interesting, the increase in pulse number led to a larger reduction in bacterial load and bioluminescent signal immediately after treatment, as compared to the increase in the field strength. Increasing the pulse number from 40 to 80, led to a 255% increase in the reduction of bacterial load in the wound, from 1.49 ± 0.07 log 10 to 5.30 ± 0.85 log 10 (Fig. 4). Increasing the applied voltage, however, from 500 to 1000 V, while keeping the number of pulses at 40, led to only a ~37% increase in the log reduction of bacterial load in the wound, from 1.49 ± 0.07 log 10 to 2.04 ± 0.29 log 10 (Fig. 4).
Surprisingly, the increase of PEF-disinfection capability does not correlate with the increase of energy delivered. To calculate the delivered energy, we used the following equation:
| (9) |
where E (Joule) is the total delivered energy in Joules, IRMS (Amp) is the root mean square of the current, and T (s) is the total application time of all pulses.
For delivery of 80 pulses with 250 Vmm−1 at 1 Hz, ~9 Joules are needed. For delivery of 40 pulses with 500 Vmm−1 at 1 Hz, ~18 Joules are needed. These energy consumption findings are interesting: they show that increasing the number of pulses from 40 to 80, leads to a significantly larger bacterial load reduction than increasing the electric field strength from 250 to 500 Vmm−1, therefore bacterial killing does not necessarily depend on delivered energy. These findings are strikingly different from heat/radiation-based disinfection where the bacterial load reduction directly correlates with consumed energy. Our findings are consistent with the current aqueous pore electroporation theory27. According to the current theory, increasing the field strength increases the total electroporated surface of the cell membrane; increasing number of pulses, after the electroporation threshold potential is reached, increases the number and size of the aqueous pores of the membranes at the electroporated32-34 site. The novel aspect of our findings, however, is in demonstrating for the first time in vivo that decreasing the bacterial load can be achieved by consuming less energy through the application of multiple pulses.
PEF has recently emerged in the field of medicine as a procedure known as irreversible electroporation, which is currently under investigation for solid tumor ablation. Previous clinical trials in patients showed that the procedure is generally safe for tumor ablation35-39. However, PEF used for tumor ablation requires lower electric field strengths than those we used in this study for disinfection. Therefore, the safety of the voltages used in this study should be tested before clinical application can be considered.
An additional limitation of this study is the usage of a single strain of bioluminescent bacteria. Burns or other wounds can be contaminated by multiple types of microorganisms, and resistance to antibacterial therapies may increase in heterogeneous communities. Future studies should evaluate the effects of PEF on heterogeneous bacterial populations in wounds. The limitation of the animal model used in this study is the application of PEF on bacteria shortly after infection. This model demonstrates the use of PEF to eradicate the infection prophylactically, i.e. before the infection has time to take hold and bacteria form robust biofilms. Additional studies are needed to address the problems of deep infections and resistant biofilms. Finally, for rapid translation to the clinic, we believe additional studies should address the potential combination of PEF technology with existing systemic antibiotic regimens. PEF will not only increase drug penetration into bacterial cells, but it will also induce increased drug diffusion into biofilms40,41. We believe that PEF application in combination with currently used drugs will bring the largest benefit to burn patients.
Finally, the mechanism or combination of mechanisms by which PEF effects on bacteria and cells is not completely understood. Necrosis due to cell leakage, apoptosis due to calcium influx, cell membrane irreversible electroproation, oxidative damage to the membrane, local pH changes, ROS changes and others, all have been proposed in the last four decades and currently are under scrutiny9,42-46.
To summarize, in this work we introduced a new non-thermal method of wound disinfection using high voltage, short pulsed electric field. We believe that PEF, in combination with systemic antibiotics, will synergistically eradicate multidrug-resistant burn wound infections, prevent biofilm formation and restore natural skin microbiome. PEF provides a new platform for infection combat in patients, therefore it has a potential to significantly decreasing morbidity and mortality.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Animal research
The protocol was approved by the Massachusetts General Hospital Subcommittee on Research Animal Care. The study was carried out in strict accordance with the recommendations in the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals of the National Institutes of Health. C57BL/6 4-month-old, female mice (~30 g) were purchased from Charles River Laboratories (Wilmington, MA). The animals were housed in cages, 5 animals per cage, with access to food and water ad libitum, and were maintained on a 12-hour light/dark cycle in a temperature-controlled room. All surgery was performed under ketamine (100 mg/kg) and xylazine (10 mg/kg) anesthesia, and all efforts were made to minimize suffering.
Bacterial culture
The bioluminescent pathogenic Acinetobacter baumannii ATCC BAA 747 (ATCC, Manassas, VA) gram (-) bacterial strain was used. The bioluminescence genes (luxCDABE operon), originally cloned from P. luminescens47, contained the luxAB genes that encode the luciferase enzyme, which catalyzes the light-emitting reaction and the luxCDE genes that encode an enzyme complex that synthesizes the luciferase substrate. The luxCDABE operon contained in plasmid pMF 385, a stable genetic reporter in the gram (-) organisms48, was introduced into the clinical A. baumannii strain by following standard molecular cloning protocols49. Bacterial cells were grown overnight in brain heart infusion (BHI) at 37°C with 100 rpm orbital shaking. The optical density at 600 nm was measured by a spectrophotometer (Thermo Scientific, Waltham, MA), OD600 = 0.8, corresponding to 108 colony forming units CFU ml−1. The cells were washed and resuspended in PBS (Dulbecco) and used at a density of 108 CFU mL−1 for the in vivo experiments.
Burn injury
Before the creation of third-degree burns, the animals were anesthetized with ketamine/xylazine and their fur was clipped along the dorsal surface. Burns were produced by dorsal skin surface contact with brass blocks (surface area 1 cm2) preheated to 100°C for 10 seconds, resulting in a non-lethal 1 cm2, full-thickness burn50. One burn was created per animal. Immediately after the creation of the burns, the mice were resuscitated with Intraperitoneal (IP) injections of 0.5 ml sterile saline (Phoenix Scientific Inc., St. Joseph, MO) to prevent dehydration.
Burn infection model
Bacterial infection was as described by Ha and Jin51. The burns were allowed to cool for 5 minutes. Subsequently, a 40 μl suspension of A. baumannii, ATCC BAA 747 including the luxCDABE operon developed by Dai et al.52 in sterile PBS containing 108 cells, was inoculated onto the surface of each burn with a pipette tip. The drop was then spread onto the burn surface with an inoculating loop. The mice were imaged with the luminescence camera, as described in the following section, immediately after application of the bacteria, and 30 minutes after the infection to ensure that the bacterial inoculum applied to each burn remained consistent.
Pulsed electric field disinfection
A designated area was subjected to treatment with pulsed electric field (PEF) using contact electrodes with a surface area of 1 cm2. Pulses were delivered using a BTX 830 pulse generator (Harvard Apparatus Inc, Holliston MA, USA). Currents were measured in vivo using a PicoScope 4224 Oscilloscope with a Pico Current Clamp (60A AC/DC) and analyzed with Pico Scope 6 software (Pico technologies Inc., UK). The following PEF settings were used: 2 mm gap between electrodes; applied voltage of 1000 Volts in group 1 and 500 Volts in group 2; 70 μs pulse duration; 1 Hz pulse frequency. The pulses were delivered in two groups of 40 pulses with a 5-minute interval between groups to allow bioluminescence imaging for each dose of 40 pulses.
Bioluminescent imaging of bacterial load
The bioluminescent imaging system (Hamamatsu Photonics KK, Bridgewater, NJ) has been described in detail by Hamblin et al.53 Briefly, it consists of an intensified charge-coupled-device camera mounted in a light-tight specimen chamber fitted with a light-emitting diode — a setup that allowed a background grayscale image of the entire mouse to be captured. In the photon-counting mode, an image of the light emitted from the bacteria was captured by using an integration time of 2 minutes at a maximum setting on the image-intensifier control module. Through the use of ARGUS software (Hamamatsu), the luminescent image was presented as a false-color image superimposed on the grayscale reference image. The image-processing component of the software calculated the total pixel values (in Relative Light Units [RLU]) from the luminescent images of the infected wound area. Previously, we have correlated the luminescence readout of A. baumannii contaminated burns with colony forming units (CFU) isolated from homogenized tissue extracts54. In another study, carried out previously, the CFU and RLU correlation was also reported for methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) from homogenized tissue extracts55. Imaging was performed immediately after the injury, 30 minutes after the infection, after 40 pulses, after 80 pulses, and 3 hours after PEF treatment.
Numerical model
Numerical solutions for electric field distribution in skin and the thermal effects of electric fields were performed in QuickField (Terra Analysis, Denmark). The software files with the model appear as Supplementary Information.a A free (student) version of QuickField is available on http://quickfield.com/free_soft.htm// (Accessed November 2013).
Statistical analysis
Statistical analysis was performed with toolbox in MATLAB, R2009b (MathWorks, Natick, MA, USA). We performed Student-t analysis to compare groups. The error bars show the standard deviation of the mean.
Supplementary Material
INNOVATION.
Wound infection is the major cause of mortality and morbidity in civilian and military personnel with severe burns. Current methods for treating burn wound colonization and infections are predominantly based on a wide variety of antiseptic and antimicrobial dressings. The dressings are usually based on the release of poisonous to bacteria metal ions and chemicals. These antiseptic and antimicrobial materials have a host of undesirable characteristics including incomplete coverage, particularly of resistant bacterial species. In this work, we introduce a new technology for burn wound disinfection: non-thermal high voltage pulsed electric field (PEF). We show that PEF applied directly to the infected burn wound decreased the bacterial load of multidrug Acinetobacter baumannii by more than four orders of magnitude. We believe that PEF technology can serve as powerful intervention platform for many infection-fighting biomedical applications.
Acknowledgments
AG and MY acknowledge Shriners Grant #85120-BOS. Research in the Hamblin laboratory was supported by US grant NIH R01AI050875.
Footnotes
Supplementary Information of this paper can be downloaded from http://www.worldscientific.com/doi/suppl/10.1142/S2339547814500101
AUTHORS’ CONTRIBUTIONS
AG designed the study, performed the experiments, analyzed data and wrote the manuscript, GFB performed the experiments and analyzed data, DV analyzed data and draft ed the manuscript, SK performed the experiments and draft ed the manuscript, MRH, WJA, RLS and MLY reviewed the manuscript, ensured data integrity, and supervised the project.
COMPETING FINANCIAL INTERESTS
The authors declare no financial interest in the results of this work.
References
- 1.Thomas J, Corum LM, Mantlagh H. Advance Healthcare Network, Executive Insight. 2012. http://healthcare-executive-insight.advanceweb.com/Features/Articles/Chronic-Wounds-Infectious-Diseases-That-Wont-Go-Away-2.aspx .
- 2.Gottrup F. Controversies in wound healing. Int J Low Extrem Wounds. 2010;9:9. doi: 10.1177/1534734610362738. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Metzger S. Clinical and financial advantages of moist wound management. Home Healthc Nurse. 2004;22:586–590. doi: 10.1097/00004045-200409000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Church D, Elsayed S, Reid O, et al. Burn wound infections. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2006;19:403–434. doi: 10.1128/CMR.19.2.403-434.2006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Keen EF, 3rd, Robinson BJ, Hospenthal DR, et al. Prevalence of multidrug-resistant organisms recovered at a military burn center. Burns. 2009;36:819–825. doi: 10.1016/j.burns.2009.10.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Bowler PG, Duerden BI, Armstrong DG. Wound microbiology and associated approaches to wound management. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2001;14:244–269. doi: 10.1128/CMR.14.2.244-269.2001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Barajas-Nava LA, Lopez-Alcalde J, Roque i Figuls M, et al. Antibiotic prophylaxis for preventing burn wound infection. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013;6 doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008738.pub2. CD008738. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Weaver JC. Electroporation of cells and tissues. IEEE Trans Plasma Sci. 2000;28:24–33. [Google Scholar]
- 9.Golberg A, Yarmush ML. Nonthermal irreversible electroporation: Fundamentals, applications, and challenges. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 2013;60:707–714. doi: 10.1109/TBME.2013.2238672. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Neal RE, 2nd, Rossmeisl JH, Jr, Garcia PA, et al. Successful treatment of a large soft tissue sarcoma with irreversible electroporation. J Clin Oncol. 2011;29:e372–377. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2010.33.0902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Golberg A, Fischer Y, Rubinsky B. In: Irreversible Electroporation. Rubinsky B, editor. Springer; Berlin-Heidelberg: 2010. pp. 273–312. [Google Scholar]
- 12.Golberg A. Proceedings of Bio and Food Electro Technologies. Solerno; Italy: 2012. Microbial load control by intermittently delivered pulsed electric fields; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- 13.Golberg A, Kandel J, Belkin M, et al. Intermittently delivered pulsed electric fields for sterile storage of turbid media. IEEE Trans Plasma Sci. 2010;38:3211–3218. [Google Scholar]
- 14.Golberg A, Belkin M, Rubinsky B. Irreversible electroporation for microbial control of drugs in solution. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2009;10:881–886. doi: 10.1208/s12249-009-9277-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Golberg A, Rae CS, Rubinsky B. Listeria monocytogenes cell wall constituents exert a charge effect on electroporation threshold. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012;1818:689–694. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2011.11.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Fernand F, Rubinsky L, Golberg A, et al. Variable electric fields for high throughput electroporation protocol design in curvilinear coordinates. Biotechnol Bioeng. 2012;109:2168–2171. doi: 10.1002/bit.24479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Peleg AY. Optimizing therapy for Acinetobacter baumannii. Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 2007;28:662–671. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-996413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Perez F, Endimiani A, Bonomo RA. Why are we afraid of Acinetobacter baumannii? Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2008;6:269–271. doi: 10.1586/14787210.6.3.269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Scott P, Deye G, Srinivasan A, et al. An outbreak of multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii-calcoaceticus complex infection in the US military health care system associated with military operations in Iraq. Clin Infect Dis. 2007;44:1577–1584. doi: 10.1086/518170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.CDC. Acinetobacter baumannii infections among patients at military medical facilities treating injured U.S. service members, 2002–2004. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2004;53:1063–1066. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Pavselj N, Bregar Z, Cukjati D, et al. The course of tissue permeabilization studied on a mathematical model of a subcutaneous tumor in small animals. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 2005;52:1373–1381. doi: 10.1109/TBME.2005.851524. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Corovic S, Mir LM, Miklavcic D. In vivo muscle electroporation threshold determination: Realistic numerical models and in vivo experiments. J Membr Biol. 2012;245:509–520. doi: 10.1007/s00232-012-9432-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Pavselj N, Miklavcic D. A numerical model of permeabilized skin with local transport regions. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 2008;55:1927–1930. doi: 10.1109/TBME.2008.919730. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Weaver JC, Vaughan TE, Chizmadzhev Y. Theory of electrical creation of aqueous pathways across skin transport barriers. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 1999;35:21–39. doi: 10.1016/s0169-409x(98)00061-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Holmes K. Thermal properties. http://users.ece.utexas.edu/~valvano/research/Thermal.pdf .
- 26.Hasgall P, Neufeld E, Gosselin M, et al. IT’IS Database for thermal and electromagnetic parameters of biological tissues. Version 2.4. Jul 30, 2013. www.itis.ethz.ch/database .
- 27.Weaver JC. Electroporation of biological membranes from multicellular to nano scales. IEEE Trans Diel Electric Insul. 2003;10:754–768. [Google Scholar]
- 28.Kurazumi Y, Tsuchikawa T, Ishii J, et al. Radiative and convective heat transfer coefficients of the human body in natural convection. Build Environ. 2008;43:2142–2153. [Google Scholar]
- 29.Aranda J, Bardina C, Beceiro A, et al. Acinetobacter baumannii RecA protein in repair of DNA damage, antimicrobial resistance, general stress response, and virulence. J Bacteriol. 2011;193:3740–3747. doi: 10.1128/JB.00389-11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.FDA. Kinetics of microbial inactivation for alternative food processing technologies — Pulsed electric fields. http://www.fda.gov/Food/FoodScienceResearch/SafePracticesforFoodProcesses/ucm101662.htm .
- 31.Golberg A, Broelsch GF, Bohr S, et al. Non-thermal, pulsed electric field cell ablation: A novel tool for regenerative medicine and scarless skin regeneration. Technology. 2013;1:1–8. doi: 10.1142/S233954781320001X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Escoffre J-M, Portet T, Wasungu L, et al. What is (still not) known of the mechanism by which electroporation mediates gene transfer and expression in cells and tissues. Mol Biotechnol. 2009;41:286–295. doi: 10.1007/s12033-008-9121-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Gabriel B, Teissie J. Direct observation in the millisecond time range of fluorescent molecule asymmetrical interaction with the electropermeabilized cell membrane. Biophys J. 1997;73:2630–2637. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(97)78292-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Gabriel B, Teissie J. Time courses of mammalian cell electropermeabilization observed by millisecond imaging of membrane property changes during the pulse. Biophys J. 1999;76:2158–2165. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(99)77370-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Akinwande O, Samman M. Irreversible electroporation: Hype or hope? Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2013;36(6):1719–1720. doi: 10.1007/s00270-013-0664-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Bruix J, Izzo F, Crocetti L, et al. Irreversible electroporation for the treatment of early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma. A prospective multicenter phase 2 study assessing safety and efficacy. J Hepatol. 2012;56(Suppl 2):S554. [Google Scholar]
- 37.Martin RCG, McFarland K, Ellis S, et al. Irreversible electroporation therapy in the management of locally advanced pancreatic adenocarcinoma. J Am Coll Surg. 2012;215:361–369. doi: 10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2012.05.021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Onik G, Mikus P, Rubinsky B. Irreversible electroporation: Implications for prostate ablation. Tech Cancer Res Treat. 2007;6:295–300. doi: 10.1177/153303460700600405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Usman M, Moore W, Talati R, et al. Irreversible electroporation of lung neoplasm: A case series. Med Sci Monit. 2012;18:CS43–CS47. doi: 10.12659/MSM.882888. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Costerton JW, Ellis B, Lam K, et al. Mechanism of electrical enhancement of efficacy of antibiotics in killing biofilm bacteria. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1994;38:2803–2809. doi: 10.1128/aac.38.12.2803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Smith AW. Biofilms and antibiotic therapy: Is there a role for combating bacterial resistance by the use of novel drug delivery systems? Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2005;57:1539–1550. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2005.04.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Kotnik T, Kramar P, Pucihar G, et al. Cell membrane electroporation — Part 1: The Phenomenon. IEEE Electrc Insul Mag. 2012;28:14–23. [Google Scholar]
- 43.Maglietti F, Michinski S, Olaiz N, et al. The role of pH fronts in tissue electroporation based treatments. PLoS ONE. 2013;8:e80167. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0080167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Benov LC, Antonov PA, Ribarov SR. Oxidative damage of the membrane lipids after electroporation. Gen Physiol Biophys. 1994;13:85–97. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Pakhomova ON, Khorokhorina VA, Bowman AM, et al. Oxidative effects of nanosecond pulsed electric field exposure in cells and cell-free media. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2012;527:55–64. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2012.08.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Pinero J, Lopez-Baena M, Ortiz T, et al. Apoptotic and necrotic cell death are both induced by electroporation in HL60 human promyeloid leukaemia cells. Apoptosis. 1997;2:330–336. doi: 10.1023/a:1026497306006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Xi L, Cho K, Tu S. Cloning and nucleotide sequences of lux genes and characterization of luciferase of Xenorhabdus luminescens from a human wound. J Bacteriol. 1991;173:1339–1405. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.4.1399-1405.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Damidova T, Hamblin M. Photodynamic therapy target to pathogens. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2004;17:245–254. doi: 10.1177/039463200401700304. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Sambrook J, Russell D. Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual. 3. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory; Cold Spring Harbor, NY: 2001. [Google Scholar]
- 50.Dai T, Kharkwal GB, Tanaka M, et al. Animal models of external traumatic wound infections. Virulence. 2011;2:296–315. doi: 10.4161/viru.2.4.16840. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Ha U, Jin S. Expression of the soxR gene of Pseudomonas aeruginosa is inducible during infection of burn wounds in mice and is required to cause efficient bacteremia. Infect Immun. 1999;67:5324–5331. doi: 10.1128/iai.67.10.5324-5331.1999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Dai T, Tegos GP, Lu Z, et al. Photodynamic therapy for Acinetobacter baumannii burn infections in mice. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2009;53:3929–3934. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00027-09. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Hamblin MR, O’Donnell DA, Murthy N, et al. Rapid control of wound infections by targeted photodynamic therapy monitored by in vivo bioluminescence imaging. Photochem Photobiol. 2002;75:51–57. doi: 10.1562/0031-8655(2002)075<0051:rcowib>2.0.co;2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Ragas X, Dai T, Tegos GP, et al. Photodynamic inactivation of Acinetobacter baumannii using phenothiazinium dyes: In vitro and in vivo studies. Lasers Surg Med. 2010;42:384–390. doi: 10.1002/lsm.20922. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Vecchio D, Dai T, Huang L, et al. Antimicrobial photodynamic therapy with RLP068 kills methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and improves wound healing in a mouse model of infected skin abrasion PDT with RLP068/Cl in infected mouse skin abrasion. J Biophotonics. 2012;6:733–742. doi: 10.1002/jbio.201200121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.


