Abstract
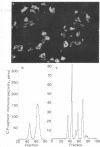
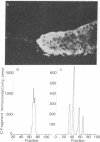
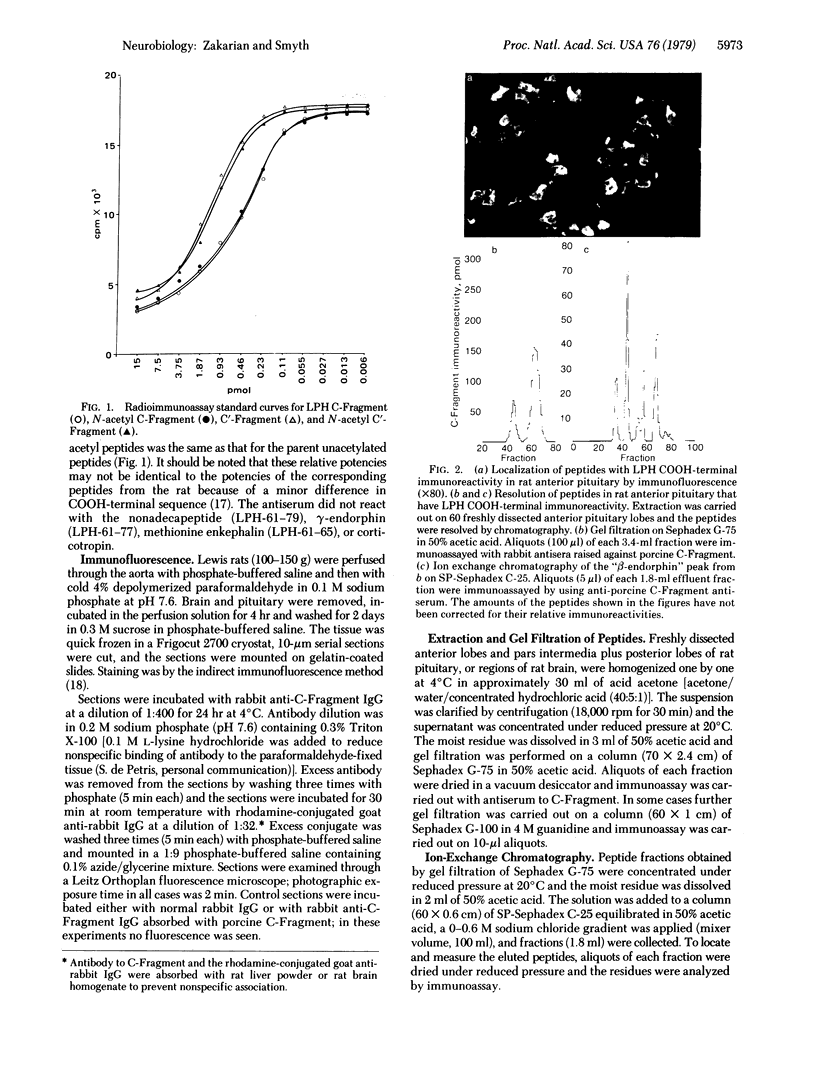
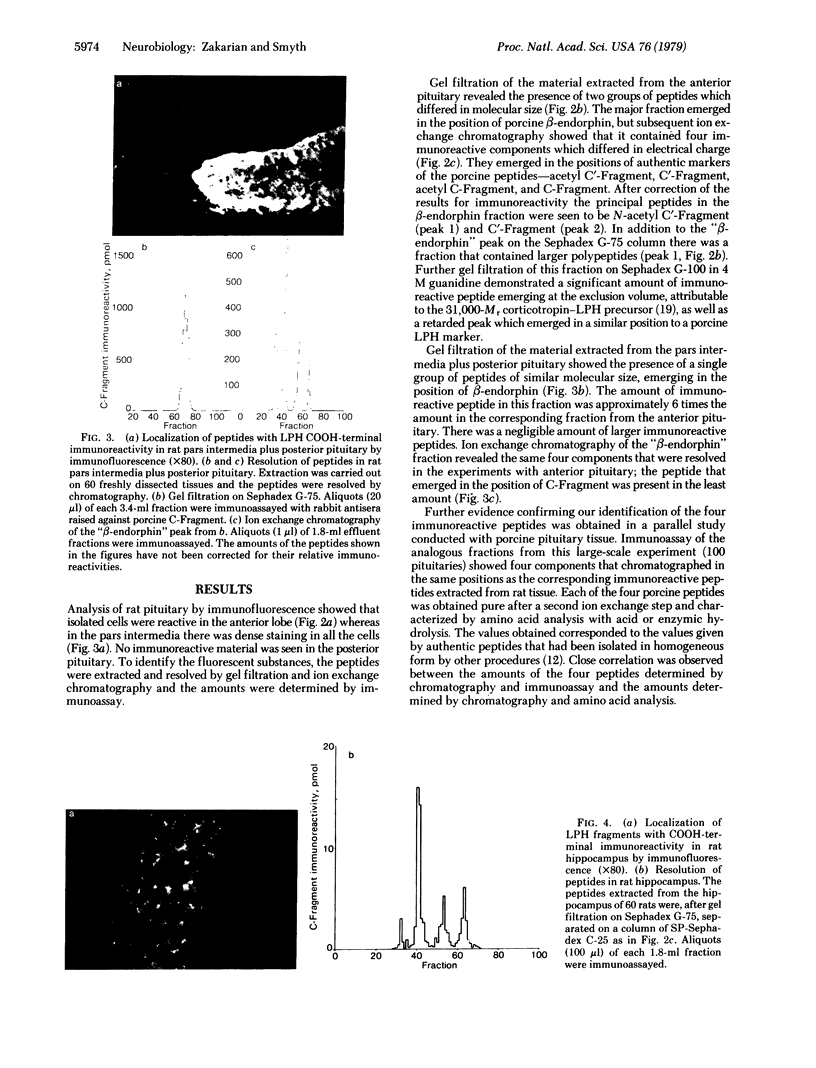
The recent isolation and identification of alpha-N-acetyl forms of the C-Fragment of lipotropin (beta-endorphin, residues 61-91) and the C'-Fragment (residues 61-87) [Smyth, D.G., Massey, D.E., Zakarian, S. & Finnie, M. (1979) Nature (London) 279, 252-254] has led to a study of their distribution in the pituitary and brain of the rat. Regions were mapped by the method of immunofluorescent staining and the reactive peptides were determined by immunoassay after extraction, gel filtration, and ion exchange chromatography. The major immunoreactive peptides in both lobes of the pituitary were found to be C'-Fragment and N-acetyl C'-Fragment, which are weakly active or inactive as opiates; the C-Fragment and its N-acetyl derivative represented minor components. This indicates that in the rat the circulating "endorphins" released from pituitary would have little morphinomimetic activity. The same four immunoreactive peptides were observed in rat brain. In the hippocampus the C'-Fragment was the principal component in the midbrain there was more C-Fragment but C'-Fragment predominated; in the hypothalamus the C-Fragment was the major peptide, almost to the exclusion of the other peptides. The results demonstrate that the processing of lipotropin is under differential control in anatomically distinct regions of the central nervous system. The processing of lipotropin in the hypothalamus is directed specifically to the production of lipotropin C-Fragment.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bloom F., Battenberg E., Rossier J., Ling N., Guillemin R. Neurons containing beta-endorphin in rat brain exist separately from those containing enkephalin: immunocytochemical studies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Mar;75(3):1591–1595. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.3.1591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradbury A. F., Smyth D. G., Snell C. R. Lipotropin: precursor to two biologically active peptides. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Apr 19;69(4):950–956. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90465-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung A. L., Goldstein A. Failure of hypophysectomy to alter brain content of opioid peptides (endorphins). Life Sci. 1976 Oct 1;19(7):1005–1008. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(76)90291-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doneen B. A., Chung D., Yamashiro D., Law P. Y., Loh H. H., Li C. H. beta-Endorphin: structure-activity relationships in the guinea pig ileum and opiate receptor binding assays. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Jan 24;74(2):656–662. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)90353-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eberle A., Leukart O., Schiller P., Fauchère J. L., Schwyzer R. Hormone--receptor interactions: [4-carboranylalanine, 5-leucine]-enkephalin as a structural probe for the opiate receptor. FEBS Lett. 1977 Oct 15;82(2):325–328. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80612-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldberg W., Smyth D. G. C-fragment of lipotropin--an endogenous potent analgesic peptide. Br J Pharmacol. 1977 Jul;60(3):445–453. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1977.tb07521.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geisow M. J., Deakin J. F., Dostrovsky J. O., Smyth D. G. Analgesic activity of lipotropin C fragment depends on carboxyl terminal tetrapeptide. Nature. 1977 Sep 8;269(5624):167–168. doi: 10.1038/269167a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graf L., Szekely J. I., Ronai A. Z., Dunai-Kovacs Z., Bajusz S. Comparative study on analgesic effect of Met5-enkephalin and related lipotropin fragments. Nature. 1976 Sep 16;263(5574):240–242. doi: 10.1038/263240a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guillemin R., Ling N., Vargo T. Radioimmunoassays for alpha-endorphin and beta-endorphin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Jul 11;77(1):361–366. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(77)80205-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbert V., Lau K. S., Gottlieb C. W., Bleicher S. J. Coated charcoal immunoassay of insulin. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1965 Oct;25(10):1375–1384. doi: 10.1210/jcem-25-10-1375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Höllt V., Przewlocki R., Herz A. Radioimmunoassay of beta-endorphin basal and stimulated levels in extracted rat plasma. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1978 Jun;303(2):171–174. doi: 10.1007/BF00508064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krieger D. T., Liotta A., Suda T., Palkovits M., Brownstein M. J. Presence of immunoassayable beta-lipotropin in bovine brain and spinal cord: lack of concordance with ACTH concentrations. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Jun 6;76(3):930–936. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)91591-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liotta A. S., Suda T., Krieger D. T. beta-Lipotropin is the major opioid-like peptide of human pituitary and rat pars distalis: lack of significant beta-endorphin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2950–2954. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lissitsky J. C., Morin O., Dupont A., Labrie F., Seidah N. G., Chrétien M., Lis M., Coy D. H. Content of beta-LPH and its fragments (including endorphins) in anterior and intermediate lobes of the bovine pituitary gland. Life Sci. 1978 May 15;22(19):1715–1722. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(78)90623-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loh H. H., Tseng L. F., Wei E., Li C. H. beta-endorphin is a potent analgesic agent. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Aug;73(8):2895–2898. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.8.2895. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowry P. J., Scott A. P. The evolution of vertebrate corticotrophin and melanocyte stimulating hormone. Gen Comp Endocrinol. 1975 May;26(1):16–23. doi: 10.1016/0016-6480(75)90211-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mains R. E., Eipper B. A. Coordinate synthesis of corticotropins and endorphins by mouse pituitary tumor cells. J Biol Chem. 1978 Feb 10;253(3):651–655. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mains R. E., Eipper B. A., Ling N. Common precursor to corticotropins and endorphins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jul;74(7):3014–3018. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.7.3014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Przewłocki R., Höllt V., Herz A. Release of beta-endorphin from rat pituitary in vitro. Eur J Pharmacol. 1978 Sep 15;51(2):179–183. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(78)90342-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts J. L., Phillips M., Rosa P. A., Herbert E. Steps involved in the processing of common precursor forms of adrenocorticotropin and endorphin in cultures of mouse pituitary cells. Biochemistry. 1978 Aug 22;17(17):3609–3618. doi: 10.1021/bi00610a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossier J., Vargo T. M., Minick S., Ling N., Bloom F. E., Guillemin R. Regional dissociation of beta-endorphin and enkephalin contents in rat brain and pituitary. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):5162–5165. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.5162. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubinstein M., Stein S., Gerber L. D., Udenfriend S. Isolation and characterization of the opioid peptides from rat pituitary: beta-lipotropin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jul;74(7):3052–3055. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.7.3052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubinstein M., Stein S., Udenfriend S. Isolation and characterization of the opioid peptides from rat pituitary: beta-endorphin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):4969–4972. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.4969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidah N. G., Gianoulakis C., Crine P., Lis M., Benjannet S., Routhier R., Chrétien M. In vitro biosynthesis and chemical characterization of beta-lipotropin, gamma-lipotropin, and beta-endorphin in rat pars intermedia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jul;75(7):3153–3157. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.7.3153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smyth D. G., Massey D. E., Zakarian S., Finnie M. D. Endorphins are stored in biologically active and inactive forms: isolation of alpha-N-acetyl peptides. Nature. 1979 May 17;279(5710):252–254. doi: 10.1038/279252a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smyth D. G., Snell C. R., Massey D. E. Isolation of the C-fragment and C'-fragment of lipotropin from pig pituitary and C-fragment from brain. Biochem J. 1978 Oct 1;175(1):261–270. doi: 10.1042/bj1750261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson S. J., Barchas J. D., Li C. H. beta-Lipotropin: localization of cells and axons in rat brain by immunocytochemistry. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):5155–5158. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.5155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimi H., Matsukura S., Sueoka S., Fukase M., Yokota M., Hirata Y., Imura H. Radioimmunoassay for beta-endorphin: presence of immunoreactive "big-big" beta-endorphin ("big" beta-lipotropin) in human and rat pituitaries. Life Sci. 1978 Jun 26;22(24):2189–2195. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(78)90570-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]