Abstract
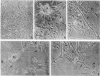
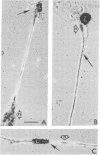
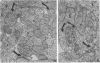
In vitro conditions were defined under which Schwann cells, from a population of dissociated embryonic chicken spinal cord cells, migrate along the growing neuronal fibers and wrap bundles as well as individual axons, in a pattern similar to that found in a developing peripheral nervous system in vivo. The migration of Schwann cells and their wrapping of nerve fibers was found to be a function of plasmin activity in the growth medium. It was determined that at least one cell type among the spinal cord cells is producing plasminogen activator, the enzyme that activates the plasminogen that is a constituent of any serum. It is concluded that, to achieve wrapping of neurons by Schwann cells in culture, it is essential to have an active plasmin-generating system in the medium. It is hypothesized that the Schwann cell produces plasminogen activator. The possible role of both the Schwann cell and the plasminogen possible role of both the Schwann cell and the plasminogen activator in the formation of the neuromuscular junction is discussed.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atsumi S. Development of neuromuscular junctions of fast and slow muscles in the chick embryo: a light and electron microscopic study. J Neurocytol. 1977 Dec;6(6):691–709. doi: 10.1007/BF01176380. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beers W. H. Follicular plasminogen and plasminogen activator and the effect of plasmin on ovarian follicle wall. Cell. 1975 Nov;6(3):379–386. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90187-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird M., James D. W. Myelin formation in cultures of previously dissociated mouse spinal cord. Cell Tissue Res. 1975 Sep 16;162(1):93–105. doi: 10.1007/BF00223265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blinzinger K., Kreutzberg G. Displacement of synaptic terminals from regenerating motoneurons by microglial cells. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1968;85(2):145–157. doi: 10.1007/BF00325030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bunge M. B., Bunge R. P., Peterson E. R., Murray M. R. A light and electron microscope study of long-term organized cultures of rat dorsal root ganglia. J Cell Biol. 1967 Feb;32(2):439–466. doi: 10.1083/jcb.32.2.439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bunge R. P., Wood P. Studies on the transplantation of spinal cord tissue in the rat. I. The development of a culture system for hemisections of embryonic spinal cord. Brain Res. 1973 Jul 27;57(2):261–276. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(73)90135-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu-Wang I. W., Oppenheim R. W. Cell death of motoneurons in the chick embryo spinal cord. II. A quantitative and qualitative analysis of degeneration in the ventral root, including evidence for axon outgrowth and limb innervation prior to cell death. J Comp Neurol. 1978 Jan 1;177(1):59–85. doi: 10.1002/cne.901770106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edgington T. S., Plow E. F. Effector mechanisms and products of the physiological fibrinolytic systems. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1976;5:85–120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischbach G. D., Berg D. K., Cohen S. A., Frank E. Enrichment of nerve--muscle synapses in spinal cord--muscle cultures and identification of relative peaks of ACh sensitivity at sites of transmitter release. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1976;40:347–357. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1976.040.01.034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischbach G. D., Dichter M. A. Electrophysiologic and morphologic properties of neurons in dissociated chick spinal cord cell cultures. Dev Biol. 1974 Mar;37(1):100–116. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(74)90172-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischbach G. D. Synapse formation between dissociated nerve and muscle cells in low density cell cultures. Dev Biol. 1972 Jun;28(2):407–429. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(72)90023-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glazer E. J., Baker T., Riker W. F., Jr The neuropathology of DFP at cat soleus neuromuscular junction. J Neurocytol. 1978 Dec;7(6):741–758. doi: 10.1007/BF01205148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirano H. Ultrastructural study on the morphogenesis of the neuromuscular junction in the skeletal muscle of the chick. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1967;79(2):198–208. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James D. W., Tresman R. L. An electron-microscopic study of the de novo formation of neuromuscular junctions in tissue culture. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1969;100(1):126–140. doi: 10.1007/BF00343826. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalderon N., Epstein M. L., Gilula N. B. Cell-to-cell communication and myogenesis. J Cell Biol. 1977 Dec;75(3):788–806. doi: 10.1083/jcb.75.3.788. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly A. M., Zacks S. I. The fine structure of motor endplate morphogenesis. J Cell Biol. 1969 Jul;42(1):154–169. doi: 10.1083/jcb.42.1.154. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kidokoro Y., Heinemann S., Schubert D., Brandt B. L., Klier F. G. Synapse formation and neurotrophic effects on muscle cell lines. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1976;40:373–388. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1976.040.01.036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim S. U. Formation of synapses and myelin sheaths in cultures of dissociated chick embryonic spinal cord. Exp Cell Res. 1972 Aug;73(2):528–530. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(72)90087-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lodin Z., Faltin J., Booher J., Hartman J., Sensenbrenner M. Fiber formation and myelinization of cultivated dissociated neurons from chicken dorsal root ganglia: an electron microscopic and scanning electron microscopic study. Neurobiology. 1973;3(2):66–87. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien R. A., Ostberg A. J., Vrbová G. Observations on the elimination of polyneuronal innervation in developing mammalian skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1978 Sep;282:571–582. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012482. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orenstein N. S., Dvorak H. F., Blanchard M. H., Young M. Nerve growth factor: a protease that can activate plasminogen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Nov;75(11):5497–5500. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.11.5497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ossowski L., Biegel D., Reich E. Mammary plasminogen activator: correlation with involution, hormonal modulation and comparison between normal and neoplastic tissue. Cell. 1979 Apr;16(4):929–940. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90108-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PETERS A., MUIR A. R. The relationship between axons and Schwann cells during development of peripheral nerves in the rat. Q J Exp Physiol Cogn Med Sci. 1959 Jan;44(1):117–130. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1959.sp001366. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pappas G. D., Peterson E. R., Masurovsky E. B., Crain S. M. Electron microscopy of the in vitro development of mammalian motor end plates. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1971 Sep 15;183:33–45. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1971.tb30740.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peper K., Dreyer F., Sandri C., Akert K., Moor H. Structure and ultrastructure of the frog motor endplate. A freeze-etching study. Cell Tissue Res. 1974 Jun 24;149(4):437–455. doi: 10.1007/BF00223024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ronnevi L-O Spontaneous phagocytosis of boutons on spinal motoneurons during early postnatal development. An electron microscopical study in the cat. J Neurocytol. 1977 Oct;6(5):487–504. doi: 10.1007/BF01205215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shahar A., Grunfeld Y., Spiegelstein M. Y., Monzain R. Myelinization in long-term cultures of dissociated mammalian neurons. Brain Res. 1975 Apr 25;88(1):44–51. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(75)90945-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strickland S., Beers W. H. Studies on the role of plasminogen activator in ovulation. In vitro response of granulosa cells to gonadotropins, cyclic nucleotides, and prostaglandins. J Biol Chem. 1976 Sep 25;251(18):5694–5702. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strickland S., Reich E., Sherman M. I. Plasminogen activator in early embryogenesis: enzyme production by trophoblast and parietal endoderm. Cell. 1976 Oct;9(2):231–240. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90114-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unkeless J., Dano K., Kellerman G. M., Reich E. Fibrinolysis associated with oncogenic transformation. Partial purification and characterization of the cell factor, a plasminogen activator. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jul 10;249(13):4295–4305. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varon S. S., Bunge R. P. Trophic mechanisms in the peripheral nervous system. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1978;1:327–361. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.01.030178.001551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WESTON J. A. A radioautographic analysis of the migration and localization of trunk neural crest cells in the chick. Dev Biol. 1963 Jun;6:279–310. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(63)90016-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]