Abstract
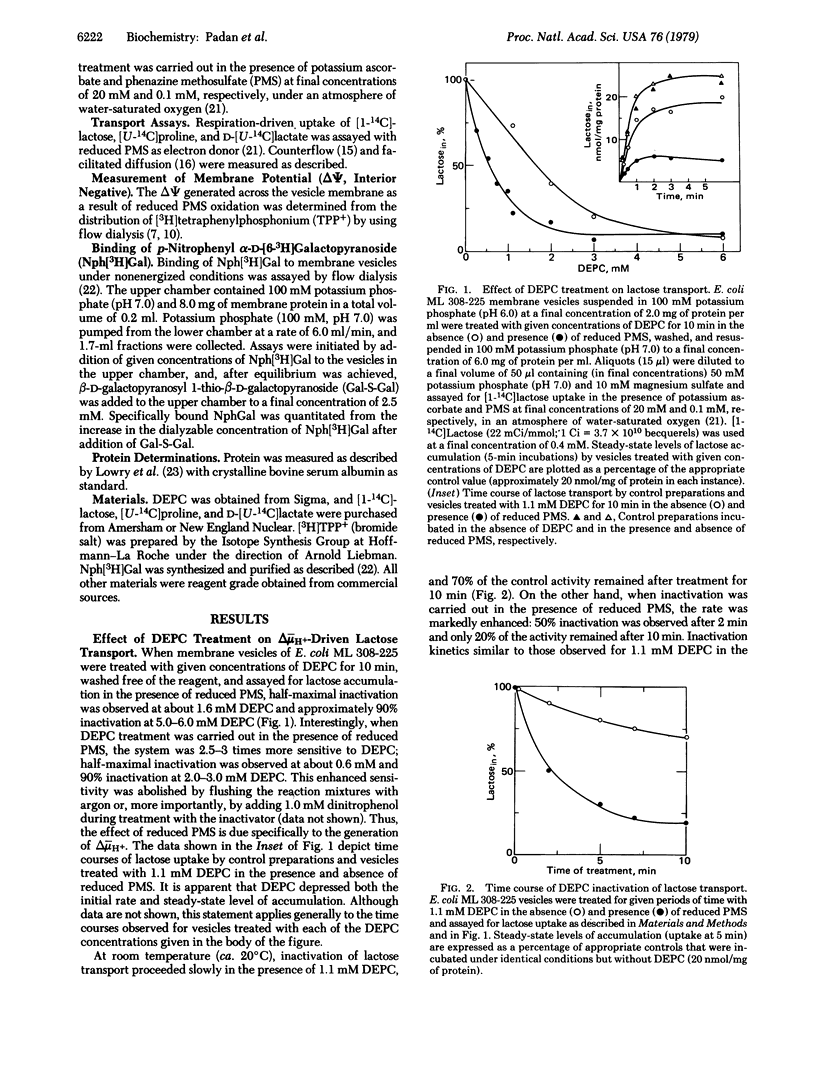
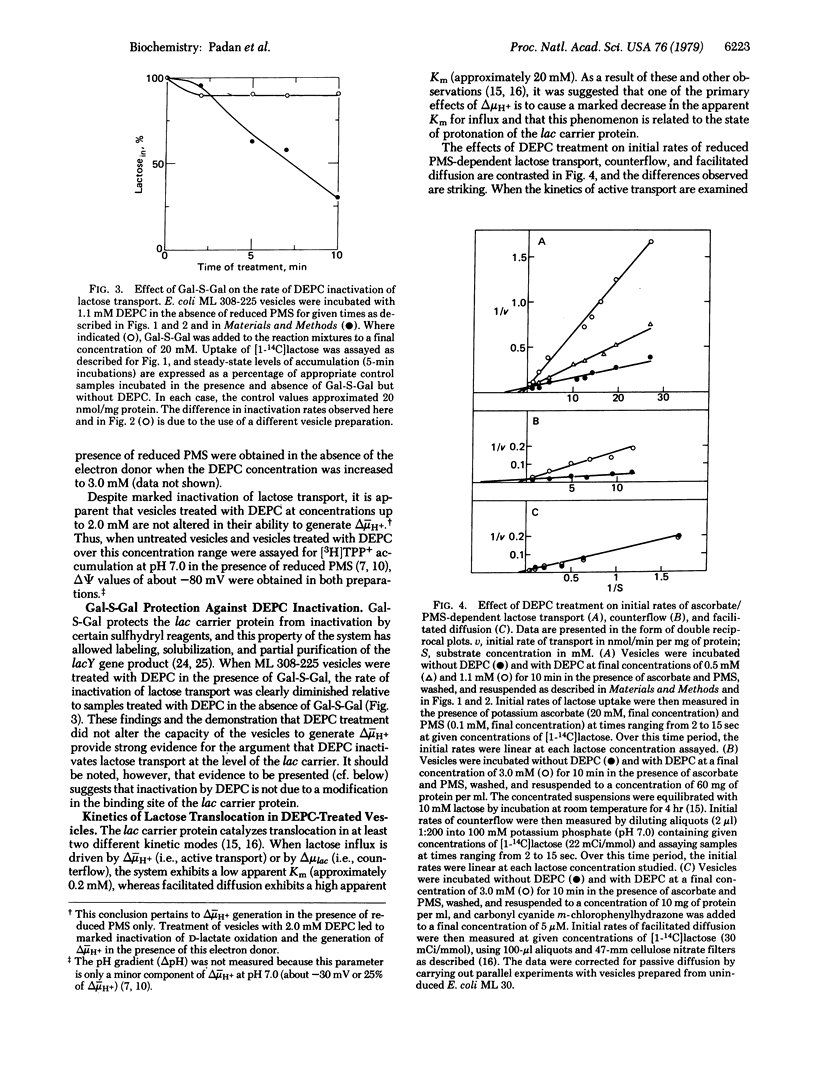
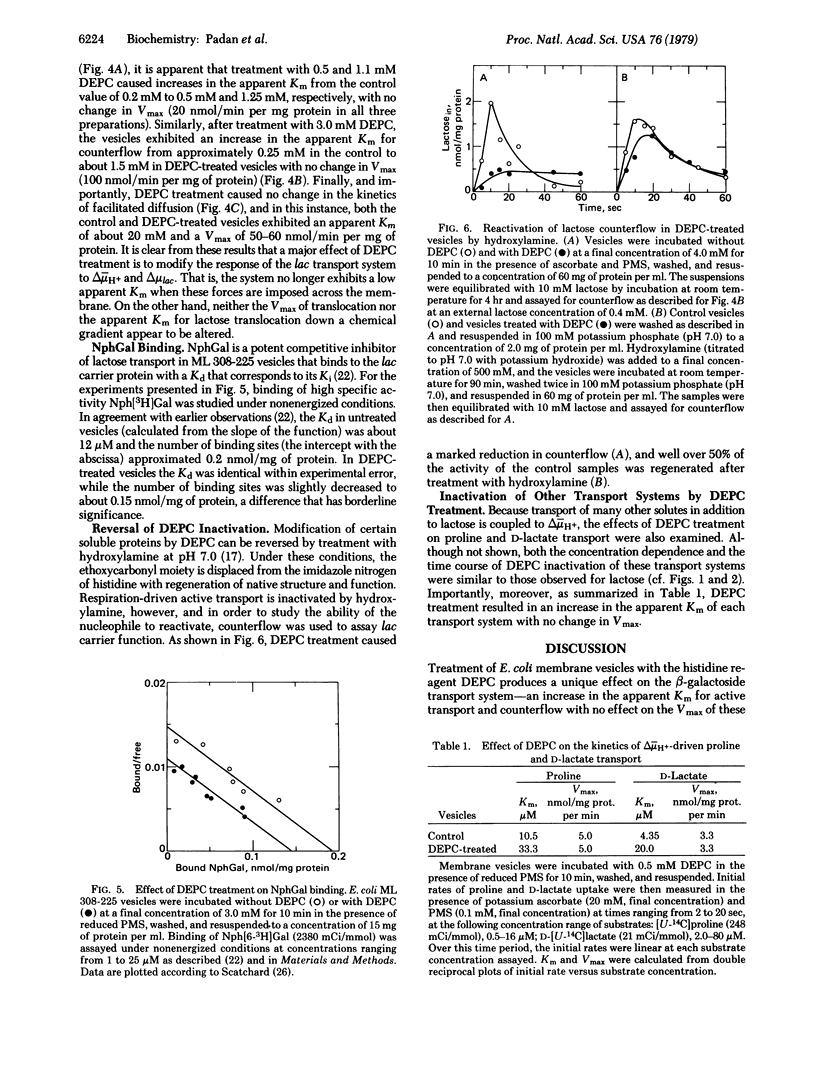
Exposure of Escherichia coli ML 308-225 membrane vesicles to the histidine-specific reagent diethylpyrocarbonate (DEPC) led to concentration- and time-dependent inactivation of active lactose transport, and the sensitivity of the system to inactivation was enhanced when an electrochemical proton gradient (delta- muH+, interior negative and alkaline) was generated across the vesicle membrane. Although beta-D-galactopyranosyl 1-thio-beta-D-galactopyranoside blocked DEPC inactivation, binding of p-nitrophenyl alpha-D-galactopyranoside was not significantly altered, indicating that DEPC does not react at the binding sites of the lac carrier protein. Strikingly, vesicles treated with DEPC exhibited an increased apparent Km for delta- muH+-driven lactose transport and counterflow but no change in the Vmax of these reactions and no change in the apparent Km or Vmax of facilitated diffusion. Moreover, DEPC treatment increased the apparent Km observed for delta- muH+-driven proline and D-lactate transport with no change in Vmax. Finally, the lactose counterflow activity of DEPC-treated vesicles was regenerated by subsequent exposure to hydroxylamine. It is suggested that a histidyl residue(s) in the lac carrier or another protein in the translocation complex is involved either in the binding and translocation of protons or in a conformational change that may occur upon protonation of the lac carrier protein.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boonstra J., Konings W. N. Generation of an electrochemical proton gradient by nitrate respiration in membrane vesicles from anaerobically grown Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Sep;78(2):361–368. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11748.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox C. F., Kennedy E. P. Specific labeling and partial purification of the M protein, a component of the beta-galactoside transport system of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Sep;54(3):891–899. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.3.891. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffee P., Lai C. Y., Pugh E. L., Horecker B. L. The function of histidine residues in rabbit muscle aldolase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Jan;57(1):107–113. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.1.107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hong J. S. An ecf mutation in Escherichia coli pleiotropically affecting energy coupling in active transport but not generation or maintenance of membrane potential. J Biol Chem. 1977 Dec 10;252(23):8582–8588. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaback H. R., Patel L. The role of functional sulfhydryl groups in active transport in Escherichia coli membrane vesicles. Biochemistry. 1978 May 2;17(9):1640–1646. doi: 10.1021/bi00602a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaback H. R. Transport in isolated bacterial membrane vesicles. Methods Enzymol. 1974;31:698–709. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)31075-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaback H. R. Transport studies in bacterial membrane vesicles. Science. 1974 Dec 6;186(4167):882–892. doi: 10.1126/science.186.4167.882. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaczorowski G. J., Kaback H. R. Mechanism of lactose translocation in membrane vesicles from Escherichia coli. 1. Effect of pH on efflux, exchange, and counterflow. Biochemistry. 1979 Aug 21;18(17):3691–3697. doi: 10.1021/bi00584a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaczorowski G. J., Robertson D. E., Kaback H. R. Mechanism of lactose translocation in membrane vesicles from Escherichia coli. 2. Effect of imposed delata psi, delta pH, and Delta mu H+. Biochemistry. 1979 Aug 21;18(17):3697–3704. doi: 10.1021/bi00584a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. A commentary on alternative hypotheses of protonic coupling in the membrane systems catalysing oxidative and photosynthetic phosphorylation. FEBS Lett. 1977;78(1):1–20. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80263-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. The Ninth Sir Hans Krebs Lecture. Compartmentation and communication in living systems. Ligand conduction: a general catalytic principle in chemical, osmotic and chemiosmotic reaction systems. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Mar 15;95(1):1–20. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb12934.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen P., Kaback H. R. Antigenic architecture of membrane vesicles from Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1979 Apr 17;18(8):1422–1426. doi: 10.1021/bi00575a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen P., Kaback H. R. Immunochemical analysis of membrane vesicles from Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1979 Apr 17;18(8):1413–1422. doi: 10.1021/bi00575a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen P., Kaback H. R. Molecular structure of membrane vesicles from Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jul;75(7):3148–3152. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.7.3148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramos S., Kaback H. R. The electrochemical proton gradient in Escherichia coli membrane vesicles. Biochemistry. 1977 Mar 8;16(5):848–854. doi: 10.1021/bi00624a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramos S., Kaback H. R. The relationship between the electrochemical proton gradient and active transport in Escherichia coli membrane vesicles. Biochemistry. 1977 Mar 8;16(5):854–859. doi: 10.1021/bi00624a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramos S., Kaback H. R. pH-dependent changes in proton:substrate stoichiometries during active transport in Escherichia coli membrane vesicles. Biochemistry. 1977 Sep 20;16(19):4270–4275. doi: 10.1021/bi00638a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramos S., Schuldiner S., Kaback H. R. The electrochemical gradient of protons and its relationship to active transport in Escherichia coli membrane vesicles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jun;73(6):1892–1896. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.6.1892. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riddle B., Jencks W. P. Acetyl-coenzyme A: arylamine N-acetyltransferase. Role of the acetyl-enzyme intermediate and the effects of substituents on the rate. J Biol Chem. 1971 May 25;246(10):3250–3258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudnick G., Schildiner S., Kaback H. R. Equilibrium between two forms of the lac carrier protein in energized and nonenergized membrane vesicles from Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1976 Nov 16;15(23):5126–5131. doi: 10.1021/bi00668a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Short S. A., Kaback H. R., Kohn L. D. Localization of D-lactate dehydrogenase in native and reconstituted Escherichia coli membrane vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jun 10;250(11):4291–4296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokuda H., Kaback H. R. Sodium-dependent methyl 1-thio-beta-D-galactopyranoside transport in membrane vesicles isolated from Salmonella typhimurium. Biochemistry. 1977 May 17;16(10):2130–2136. doi: 10.1021/bi00629a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West I. C., Wilson T. H. Galactoside transport dissociated from proton movement in mutants of Escherichia coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Jan 23;50(2):551–558. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)90875-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson T. H., Kusch M. A mutant of Escherichia coli K 12 energy-uncoupled for lactose transport. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Mar 17;255(3):786–797. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(72)90391-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson T. H., Kusch M., Kashket E. R. A mutant in Escherichia coli energy-uncoupled for lactose transporta defect in the lactose-operon. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Sep 30;40(6):1409–1414. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90024-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong P. T., Kashket E. R., Wilson T. H. Energy coupling in the lactose transport system of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Jan;65(1):63–69. doi: 10.1073/pnas.65.1.63. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


