Abstract
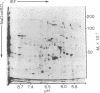
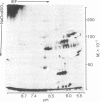
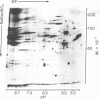
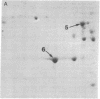
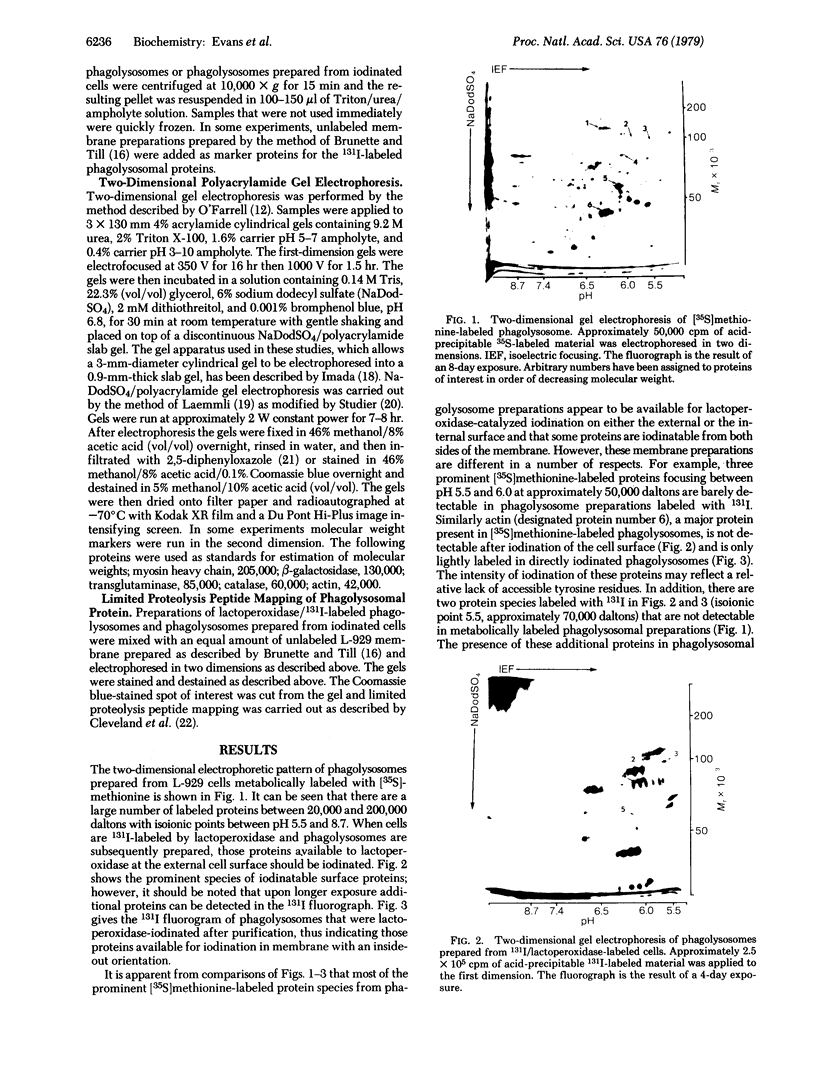
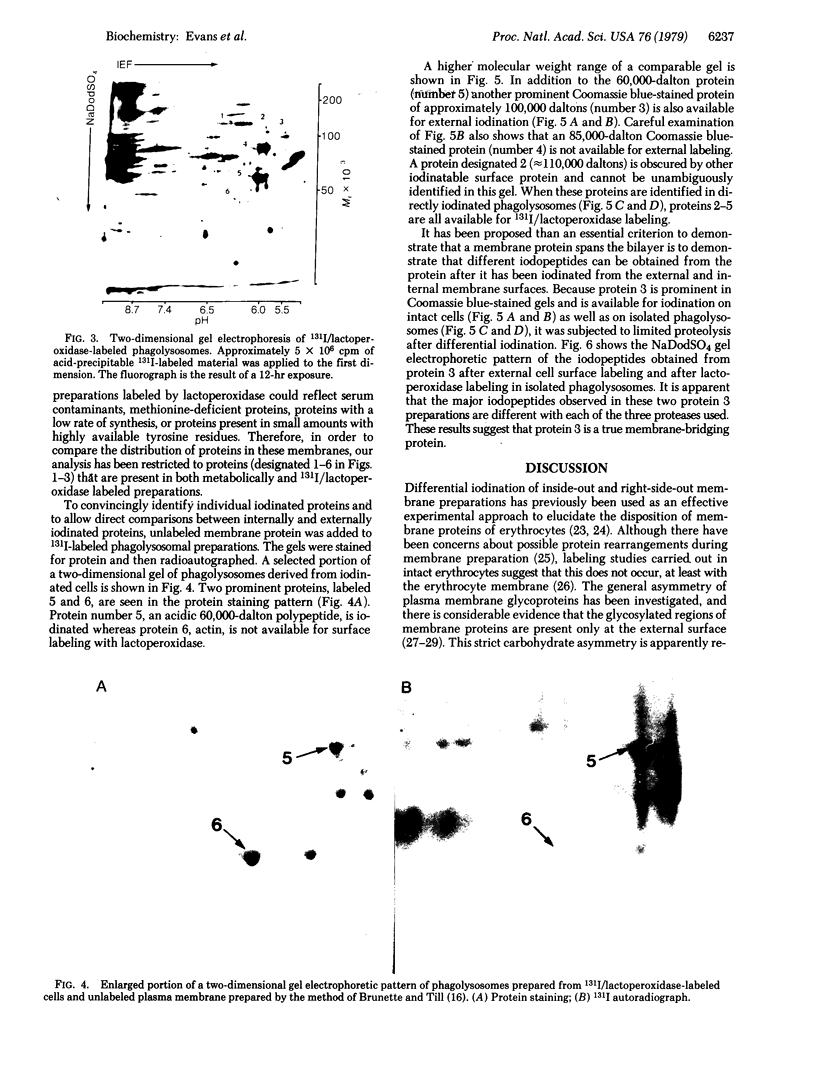
The distribution of plasma membrane-associated proteins was studied by using latex-filled phagolysosomes prepared from cultured mouse L-929 cells as a model of "inside-out" membrane. Proteins from 131I/lactoperoxidase-labeled phagolysosomes, phagolysosomes derived from 131I/lactoperoxidase-labeled cells, and phagolysosomes prepared from [35S]methionine metabolically labeled cells were analyzed by high-resolution two-dimensional gel electrophoresis. The gel patterns of iodinated proteins showed specific differences in the availability of membrane proteins to lactoperoxidase labeling between inside-out and right-side-out membranes. However, at least two prominent [35S]methionine-labeled proteins of approximately 60,000 and 100,000 daltons were available for iodination at both sides of the membrane. Partial proteolysis of the 100,000-dalton protein revealed that different peptides were iodinated when the iodination was performed on intact cells or on phagolysosomes, consisent with the idea that this protein spans the plasma membrane.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ash J. F., Louvard D., Singer S. J. Antibody-induced linkages of plasma membrane proteins to intracellular actomyosin-containing filaments in cultured fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5584–5588. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5584. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ash J. F., Singer S. J. Concanavalin-A-induced transmembrane linkage of concanavalin A surface receptors to intracellular myosin-containing filaments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Dec;73(12):4575–4579. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.12.4575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cann J. R., Stimpson D. I., Cox D. J. Isoelectric focusing of interacting systems III. Carrier ampholyte-induced macromolecular association or dissociation into subunits. Anal Biochem. 1978 May;86(1):34–49. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90316-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cann J. R., Stimpson D. I. Isoelectric focusing of interacting systems. I. Carrier ampholyte-induced macromolecular isomerization. Biophys Chem. 1977 Sep;7(2):103–114. doi: 10.1016/0301-4622(77)80003-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carraway K. L. Covalent labeling of membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Dec 29;415(4):379–410. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(75)90005-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Fischer S. G., Kirschner M. W., Laemmli U. K. Peptide mapping by limited proteolysis in sodium dodecyl sulfate and analysis by gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 10;252(3):1102–1106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. M., Fink L. M. Identification of transmembrane bridging proteins in the plasma membrane of cultured mouse L cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5341–5344. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flanagan J., Koch G. L. Cross-linked surface Ig attaches to actin. Nature. 1978 May 25;273(5660):278–281. doi: 10.1038/273278a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabbiani G., Chaponnier C., Zumbe A., Vassalli P. Actin and tubulin co-cap with surface immunoglobulins in mouse B lymphocytes. Nature. 1977 Oct 20;269(5630):697–698. doi: 10.1038/269697a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guidotti G. Membrane proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1972;41:731–752. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.41.070172.003503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbard A. L., Cohn Z. A. Externally disposed plasma membrane proteins. II. Metabolic fate of iodinated polypeptides of mouse L cells. J Cell Biol. 1975 Feb;64(2):461–479. doi: 10.1083/jcb.64.2.461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes R. O. Alteration of cell-surface proteins by viral transformation and by proteolysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Nov;70(11):3170–3174. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.11.3170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes R. O., Destree A. T. Relationships between fibronectin (LETS protein) and actin. Cell. 1978 Nov;15(3):875–886. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90272-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imada M. A new design of gel electrophoresis glass plates for two-dimensional analysis of proteins. Anal Biochem. 1978 Aug 15;89(1):292–296. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90753-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ivarie R. D., O'Farrell P. H. The glucocorticoid domain: steroid-mediated changes in the rate of synthesis of rat hepatoma proteins. Cell. 1978 Jan;13(1):41–55. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90136-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izant J. G., Lazarides E. Invariance and heterogeneity in the major structural and regulatory proteins of chick muscle cells revealed by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Apr;74(4):1450–1454. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.4.1450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones P. P. Analysis of H-2 and Ia molecules by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis. J Exp Med. 1977 Nov 1;146(5):1261–1279. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.5.1261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch G. L., Smith M. J. An association between actin and the major histocompatibility antigen H-2. Nature. 1978 May 25;273(5660):274–278. doi: 10.1038/273274a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskey R. A., Mills A. D. Quantitative film detection of 3H and 14C in polyacrylamide gels by fluorography. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Aug 15;56(2):335–341. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02238.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Litman G. W., Litman R. T., Merz D. C. Analysis of polypeptide disposition in human erythrocyte membranes employing membrane inversion. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Jul 3;394(3):348–360. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(75)90289-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu S. C., Fairbanks G., Palek J. Spontaneous, reversible protein cross-linking in the human erythrocyte membrane. Temperature and pH dependence. Biochemistry. 1977 Sep 6;16(18):4066–4074. doi: 10.1021/bi00637a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchesi V. T., Furthmayr H., Tomita M. The red cell membrane. Annu Rev Biochem. 1976;45:667–698. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.45.070176.003315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller T. J., Morrison M. The transmembrane proteins in the plasma membrane of normal human erythrocytes. J Biol Chem. 1974 Dec 10;249(23):7568–7573. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolson G. L., Singer S. J. The distribution and asymmetry of mammalian cell surface saccharides utilizing ferritin-conjugated plant agglutinins as specific saccharide stains. J Cell Biol. 1974 Jan;60(1):236–248. doi: 10.1083/jcb.60.1.236. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolson G. L. Transmembrane control of the receptors on normal and tumor cells. I. Cytoplasmic influence over surface components. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Apr 13;457(1):57–108. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(76)90014-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nigam V. N., Brailovsky C. A. Disposition of glycoproteins in plasma membrane of cultured rat embryonic fibroblasts. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Aug 1;468(3):472–485. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(77)90296-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pober J. S., Guild B. C., Strominger J. L. Phosphorylation in vivo and in vitro of human histocompatibility antigens (HLA-A and HLA-B) in the carboxy-terminal intracellular domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Dec;75(12):6002–6006. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.12.6002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roos E., Temmink J. H. Cytochemical comparison between wheat germ agglutinin and concanavalin A bound to mouse fibroblasts in vitro. Exp Cell Res. 1975 Aug;94(1):140–146. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(75)90540-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothman J. E., Lenard J. Membrane asymmetry. Science. 1977 Feb 25;195(4280):743–753. doi: 10.1126/science.402030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandra A., Pagano R. E. Phospholipid asymmetry in LM cell plasma membrane derivatives: polar head group and acyl chain distributions. Biochemistry. 1978 Jan 24;17(2):332–338. doi: 10.1021/bi00595a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlessinger J., Barak L. S., Hammes G. G., Yamada K. M., Pastan I., Webb W. W., Elson E. L. Mobility and distribution of a cell surface glycoprotein and its interaction with other membrane components. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jul;74(7):2909–2913. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.7.2909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt-Ullrich R., Mikkelsen R. B., Wallach D. F. Transmembrane disposition of the 55,000-dalton concanavalin A receptor protein of thymocyte plasma membranes. J Biol Chem. 1978 Oct 10;253(19):6973–6978. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staros J. V., Richards F. M. Photochemical labeling of the cytoplasmic surface of the membranes of intact human erythrocytes. J Biol Chem. 1975 Oct 25;250(20):8174–8178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stimpson D. I., Cann J. R. Isoelectric focusing of interacting systems. II. pH-dependent conformational transitions. Biophys Chem. 1977 Sep;7(2):115–119. doi: 10.1016/0301-4622(77)80004-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W. Bacteriophage T7. Science. 1972 Apr 28;176(4033):367–376. doi: 10.1126/science.176.4033.367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh F. S., Barber B. H., Crumpton M. J. Preparation of inside-out vesicles of pig lymphocyte plasma membrane. Biochemistry. 1976 Aug 10;15(16):3557–3563. doi: 10.1021/bi00661a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh F. S., Crumpton M. J. Orientation of cell-surface antigens in the lipid bilayer of lymphocyte plasma membrane. Nature. 1977 Sep 22;269(5626):307–311. doi: 10.1038/269307a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wetzel M. G., Korn E. D. Phagocytosis of latex beads by Acahamoeba castellanii (Neff). 3. Isolation of the phagocytic vesicles and their membranes. J Cell Biol. 1969 Oct;43(1):90–104. doi: 10.1083/jcb.43.1.90. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whalen R. G., Butler-Browne G. S., Gros F. Protein synthesis and actin heterogeneity in calf muscle cells in culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jun;73(6):2018–2022. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.6.2018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zachowski A., Lelievre L., Aubry J., Charlemagne D., Paraf A. Roles of proteins from inner face of plasma membranes in susceptibility of of (Na+ + K+)-stimulated Mg2+ adenosinetriphosphatase to ouabain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):633–637. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]