Abstract
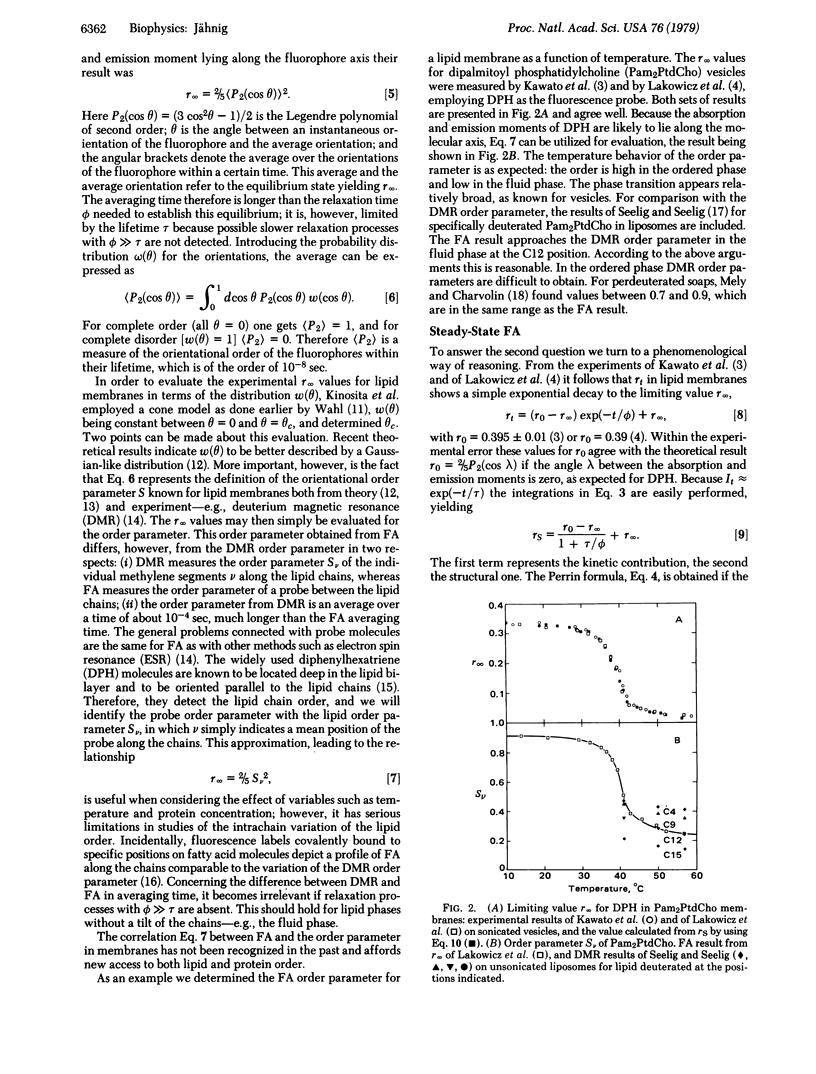
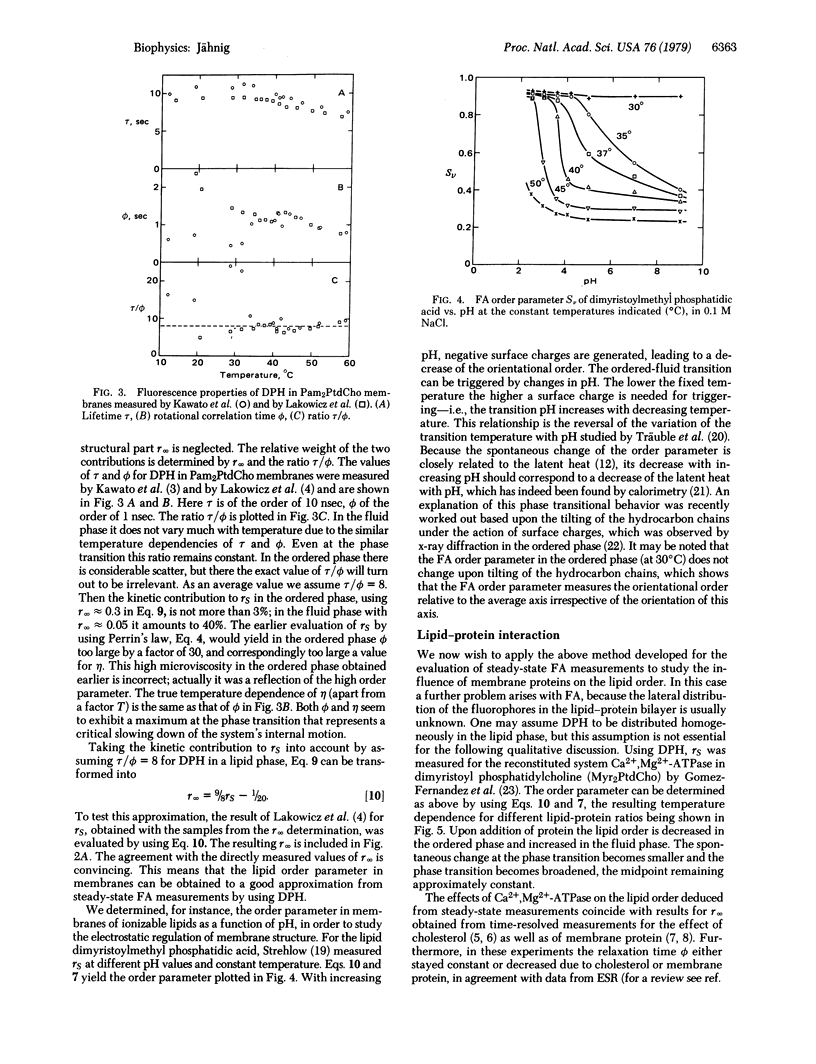
The limiting long-time value of fluorescence anisotropy in membranes is correlated with the orientational order parameter, which characterizes the structural anisotropy of membranes. Existing experimental results for diphenylhexatriene in lipid bilayers are evaluated for the order parameter of lipid order. Steady-state measurements of fluorescence anisotropy can provide the order parameter in good approximation. Proteins in a fluid lipid phase increase the lipid order parameter so determined. Upon comparison with the order parameter from deuterium magnetic resonance, it is concluded that proteins increase the order of the surrounding lipids in off-normal directions. Order parameters of protein order obtained from the limiting value of protein fluorescence anisotropy are discussed with respect to the influence of lipid order on protein order.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrich M. P., Vanderkooi J. M. Temperature dependence of 1,6-diphenyl-1,3,5-hexatriene fluorescence in phophoslipid artificial membranes. Biochemistry. 1976 Mar 23;15(6):1257–1261. doi: 10.1021/bi00651a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman D., Cornell B. A., Ellasz A. W., Perry A. Interactions of helical polypepetide segments which span the hydrocarbon region of lipid bilayers. Studies of the gramicidin A lipid-water system. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jul 5;113(3):517–538. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90236-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen L. A., Dale R. E., Roth S., Brand L. Nanosecond time-dependent fluorescence depolarization of diphenylhexatriene in dimyristoyllecithin vesicles and the determination of "microviscosity". J Biol Chem. 1977 Apr 10;252(7):2163–2169. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curatolo W., Verma S. P., Sakura J. D., Small D. M., Shipley G. G., Wallach D. F. Structural effects of myelin proteolipid apoprotein on phospholipids: a Raman spectroscopic study. Biochemistry. 1978 May 2;17(9):1802–1807. doi: 10.1021/bi00602a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glatz P. Limited rotational diffusion of DPH in human erythrocyte membranes. Anal Biochem. 1978 Jun 15;87(1):187–194. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90584-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gómez-Fernández J. C., Goñi F. M., Bach D., Restall C., Chapman D. Protein--lipid interactions. A study of (Ca2+-Mg2+)ATPase reconstituted with synthetic phospholipids. FEBS Lett. 1979 Feb 15;98(2):224–228. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80187-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyn M. P., Cherry R. J., Müller U. Transient and linear dichroism studies on bacteriorhodopsin: determination of the orientation of the 568 nm all-trans retinal chromophore. J Mol Biol. 1977 Dec 15;117(3):607–620. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90060-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hildenbrand K., Nicolau C. Nanosecond fluorescence anisotropy decays of 1,6-diphenyl-1,3,5-hexatriene in membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Jun 2;553(3):365–377. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(79)90292-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jähnig F., Harlos K., Vogel H., Eibl H. Electrostatic interactions at charged lipid membranes. Electrostatically induced tilt. Biochemistry. 1979 Apr 17;18(8):1459–1468. doi: 10.1021/bi00575a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawato S., Kinosita K., Jr, Ikegami A. Dynamic structure of lipid bilayers studied by nanosecond fluorescence techniques. Biochemistry. 1977 May 31;16(11):2319–2324. doi: 10.1021/bi00630a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawato S., Kinosita K., Jr, Ikegami A. Effect of cholesterol on the molecular motion in the hydrocarbon region of lecithin bilayers studied by nanosecond fluorescence techniques. Biochemistry. 1978 Nov 14;17(23):5026–5031. doi: 10.1021/bi00616a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinosita K., Jr, Kawato S., Ikegami A. A theory of fluorescence polarization decay in membranes. Biophys J. 1977 Dec;20(3):289–305. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(77)85550-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lakowicz J. R., Prendergast F. G., Hogen D. Differential polarized phase fluorometric investigations of diphenylhexatriene in lipid bilayers. Quantitation of hindered depolarizing rotations. Biochemistry. 1979 Feb 6;18(3):508–519. doi: 10.1021/bi00570a021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Longmuir K. J., Capaldi R. A., Dahlquist F. W. Nuclear magnetic resonance studies of lipid-protein interactions. A model of the dynamics and energetics of phosphatidylcholine bilayers that contain cytochrome c oxidase. Biochemistry. 1977 Dec 27;16(26):5746–5755. doi: 10.1021/bi00645a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcelja S. Chain ordering in liquid crystals. II. Structure of bilayer membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Oct 29;367(2):165–176. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(74)90040-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcelja S. Lipid-mediated protein interaction in membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Nov 11;455(1):1–7. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90149-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh D., Watts A., Maschke W., Knowles P. F. Protein--immobilized lipid in dimyristoylphosphatidylcholine-substituted cytochrome oxidase: evidence for both boundary and trapped-bilayer lipid. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Mar 30;81(2):397–402. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91546-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldfield E., Gilmore R., Glaser M., Gutowsky H. S., Hshung J. C., Kang S. Y., King T. E., Meadows M., Rice D. Deuterium nuclear magnetic resonance investigation of the effects of proteins and polypeptides on hydrocarbon chain order in model membrane systems. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):4657–4660. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.4657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigler R., Ehrenberg M. Fluorescence relaxation spectroscopy in the analysis of macromolecular structure and motion. Q Rev Biophys. 1976 Feb;9(1):1–19. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500002122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothschild K. J., Clark N. A. Polarized infrared spectroscopy of oriented purple membrane. Biophys J. 1979 Mar;25(3):473–487. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(79)85317-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seelig A., Seelig J. Lipid-protein interaction in reconstituted cytochrome c oxidase/phospholipid membranes. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1978 Dec;359(12):1747–1756. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1978.359.2.1747. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seelig A., Seelig J. The dynamic structure of fatty acyl chains in a phospholipid bilayer measured by deuterium magnetic resonance. Biochemistry. 1974 Nov 5;13(23):4839–4845. doi: 10.1021/bi00720a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seelig J. Deuterium magnetic resonance: theory and application to lipid membranes. Q Rev Biophys. 1977 Aug;10(3):353–418. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500002948. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinitzky M., Barenholz Y. Fluidity parameters of lipid regions determined by fluorescence polarization. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Dec 15;515(4):367–394. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(78)90010-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Susi H., Sampugna J., Hampson J. W., Ard J. S. Laser-Raman investigation of phospholipid-polypeptide interactions in model membranes. Biochemistry. 1979 Jan 23;18(2):297–301. doi: 10.1021/bi00569a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thulborn K. R., Treloar F. E., Sawyer W. H. A microviscosity barrier in the lipid bilayer due to the presence of phospholipids containing unsaturated acyl chains. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Mar 15;81(1):42–49. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91628-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyäuble H., Teubner M., Woolley P., Eibl H. Electrostatic interactions at charged lipid membranes. I. Effects of pH and univalent cations on membrane structure. Biophys Chem. 1976 Jul;4(4):319–342. doi: 10.1016/0301-4622(76)80013-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaz W. L., Austin R. H., Vogel H. The rotational diffusion of cytochrome b5 in lipid bilayer membranes. Influence of the lipid physical state. Biophys J. 1979 Jun;26(3):415–426. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(79)85262-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veatch W. R., Stryer L. Effect of cholesterol on the rotational mobility of diphenylhexatriene in liposomes: a nanosecond fluorescence anisotrophy study. J Mol Biol. 1977 Dec 25;117(4):1109–1113. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80017-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl P., Kasai M., Changeux P. A study on the motion of proteins in excitable membrane fragments by nanosecond fluorescence polarization spectroscopy. Eur J Biochem. 1971 Feb 1;18(3):332–341. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb01248.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weidekamm E., Bamberg E., Brdiczka D., Wildermuth G., Macco F., Lehmann W., Weber R. Raman spectroscopic investigation of the interaction of gramicidin A with dipalmitoyl phosphatidylcholine liposomes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Jan 21;464(2):442–447. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(77)90017-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


